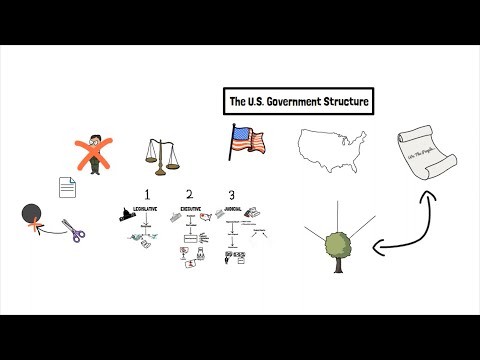
Understanding the Three Types of Local Government Structures: A Comprehensive Overview
Greetings! In this comprehensive overview, we will delve into the intricacies of the three types of local government structures commonly found in the United States. These structures play a vital role in shaping and governing our communities. From city councils to county governments, understanding how these systems operate is essential for both residents and individuals interested in public administration.
📋 Content in this article
1. Mayor-Council Structure:
The Mayor-Council structure is one of the most common forms of local government. In this system, an elected mayor serves as the chief executive officer of the city, overseeing various administrative functions. The mayor works alongside a council, which is typically made up of elected members who represent different districts within the city. The council’s primary responsibility is to legislate and establish policies for the local community.
2. Council-Manager Structure:
The Council-Manager structure is another widely adopted form of local government. Under this system, a council, similar to the one in the Mayor-Council structure, is responsible for making policy decisions and passing ordinances. However, instead of having a mayor as the chief executive officer, a professional city manager is appointed or hired to oversee day-to-day operations. The city manager acts as an administrator and implements the policies set by the council.
3. Commission Structure:
The Commission structure is less common but still employed by some local governments. In this setup, a board or commission serves as both the legislative and executive body. Commissioners are elected by residents and are responsible for making policy decisions and managing various administrative functions. Each commissioner typically heads a specific department or area of government, such as finance or public works.
It’s important to note that these structures can vary in terms of power distribution and decision-making processes. Some cities may have a strong mayor system, where the mayor has significant authority and veto power over council decisions. Others may have a weak mayor system, where the mayor’s role is largely ceremonial or limited in scope.
In summary, understanding the three types of local government structures – Mayor-Council, Council-Manager, and Commission – provides a solid foundation for comprehending how our community government functions. By knowing the roles and responsibilities of elected officials and administrators, citizens can actively participate in local governance and contribute to the betterment of their communities.
Understanding the Three Key Structures of Local Government
Understanding the Three Types of Local Government Structures: A Comprehensive Overview
When discussing local government in the United States, it is important to understand the three key structures that govern our communities. These structures, also known as forms of government, play a crucial role in shaping the decision-making processes and policies that affect our daily lives. In this comprehensive overview, we will explore the three types of local government structures commonly found across the nation.
The council-manager system is one of the most prevalent forms of local government in the United States. Under this structure, elected officials, commonly known as the city council or board of commissioners, are responsible for establishing policies and making decisions on behalf of the community. However, day-to-day administration and management of municipal affairs are delegated to a professional city manager or administrator. This system aims to provide professional expertise and ensure efficient governance by separating politics from administration.
The mayor-council system is another prominent form of local government. In this structure, a mayor is elected as the chief executive officer of the city or town, responsible for representing and leading the community. The mayor works alongside an elected council, which consists of members who represent different districts or wards. Together, they make policy decisions and establish regulations for the municipality. The mayor may have various powers depending on the jurisdiction, ranging from ceremonial duties to significant executive authority.
The commission form of government, although less common today, was historically influential in shaping local governance. Under this structure, a small group of elected commissioners, typically three to five individuals, collectively serves as both the legislative body and executive authority. Each commissioner is responsible for overseeing specific areas, such as finance, public safety, or public works. This type of government emphasizes direct accountability and decision-making by elected officials.
It is important to note that these three structures are not mutually exclusive, and variations exist within each type. Some local governments may adopt a combination of elements from different structures, creating a hybrid model that suits their unique needs.
Understanding the different types of local government structures is essential for citizens to actively participate in the democratic process and engage with their local officials effectively. By familiarizing ourselves with these structures, we can better comprehend the roles and responsibilities of our elected representatives, stay informed about the decision-making processes, and contribute to the development of our communities.
In conclusion, the council-manager system, mayor-council system, and commission form of government are the three primary types of local government structures in the United States. Each structure offers a unique approach to governance, emphasizing professional administration, mayoral leadership, or direct accountability. By understanding these structures, we can better comprehend the dynamics of our local governments and actively participate in shaping our communities’ future.
Understanding the Three Types of Local Government: A Comprehensive Explanation
Understanding the Three Types of Local Government Structures: A Comprehensive Overview
Local governments play a crucial role in governing communities and providing essential services to their residents. However, the structure and functions of local government can vary significantly from one jurisdiction to another. To help you navigate this complex landscape, this article provides a comprehensive overview of the three main types of local government structures in the United States.
1. Council-Manager System:
In this type of local government structure, power is divided between an elected council and a professional manager. The council, typically comprised of elected officials, sets policies and makes legislative decisions, while the manager is responsible for implementing these policies and overseeing day-to-day operations. The manager is generally appointed by the council and serves as the administrative head of the local government. The council-manager system is designed to promote professional management and ensure accountability.
Key features of the council-manager system include:
– Clear separation of powers: The council focuses on policy-making and legislative matters, while the manager handles administrative functions.
– Professional expertise: The manager is typically a professional with experience in public administration and management.
– Stability: The manager’s position is relatively insulated from political changes, which can provide continuity in governance.
– Accountability: The council holds the manager accountable for implementing policies effectively and efficiently.
2. Mayor-Council System:
In the mayor-council system, power is divided between an elected mayor and a legislative body, known as the council. The mayor serves as the chief executive, responsible for implementing policies, managing municipal services, and representing the local government. The council, elected by the community, holds legislative power and collaborates with the mayor to make important decisions.
Key features of the mayor-council system include:
– Strong executive leadership: The mayor has significant power and authority to govern and make executive decisions.
– Direct accountability: The mayor is directly accountable to the community for the administration of local government.
– Legislative oversight: The council provides checks and balances on the mayor’s power, ensuring that decisions are made collectively.
– Flexibility: The mayor-council system allows for customization and adaptation to suit the specific needs of a community.
3. Commission System:
The commission system is less common but still exists in some municipalities. Under this structure, the local government is led by a group of elected commissioners who collectively make decisions and oversee various departments. Each commissioner is responsible for a specific area, such as finance, public works, or public safety.
Key features of the commission system include:
– Shared decision-making: Commissioners collaborate to make policy decisions collectively.
– Departmental responsibilities: Each commissioner oversees a specific department and is accountable for its operations.
– Direct access to commissioners: Residents can directly engage with commissioners to address concerns or provide input.
– Limited executive authority: The commission typically appoints one of its members as a mayor or chairperson to preside over meetings and represent the local government.
It’s important to note that these three types of local government structures can further vary based on the size, population, and specific legal framework of a jurisdiction. Additionally, some communities may have hybrid systems that combine elements from multiple structures to best suit their needs.
Understanding the different types of local government structures can help you better engage with your local government, navigate the decision-making process, and participate in shaping your community’s future. Whether you live in a council-manager system, mayor-council system, or commission system jurisdiction, each structure offers unique opportunities for civic participation and influence.
In conclusion, local governments are diverse and complex entities. By understanding the three main types of local government structures – council-manager, mayor-council, and commission systems – you can better comprehend how decisions are made, who holds power, and how you can participate in shaping your community. Remember, active engagement with your local government is essential for building strong and vibrant communities.
Understanding the Three Models of Local Government: A Comprehensive Overview
Understanding the Three Types of Local Government Structures: A Comprehensive Overview
Local governments play a vital role in shaping the communities in which we live, work, and play. They provide essential services, make important policy decisions, and establish regulations that directly impact our daily lives. To truly understand how local governments operate, it is crucial to have a comprehensive understanding of the three types of local government structures: the council-manager model, the mayor-council model, and the commission model.
The Council-Manager Model:
In the council-manager model, the local government is headed by a professional manager who is appointed by the elected city or county council. This model is based on the principle that elected officials should focus on policy-making and leave the day-to-day administration to a trained professional. The manager is responsible for overseeing the implementation of policies, managing budgets, and supervising municipal employees. The council-manager model offers stability, expertise, and accountability in decision-making.
Key features of the council-manager model include:
The Mayor-Council Model:
The mayor-council model is characterized by a separately elected mayor who serves as the chief executive officer and a city or county council that holds legislative powers. This model emphasizes political leadership and allows for direct accountability to the electorate. Under this structure, the mayor is responsible for executing laws, managing administrative departments, and representing the local government.
Key features of the mayor-council model include:
The Commission Model:
The commission model, also known as the commission-manager model, is unique in that it combines both legislative and executive functions in a small group of elected officials known as commissioners. These commissioners collectively serve as both policymakers and administrators. Each commissioner oversees a specific area or department and works collaboratively to make decisions on behalf of the local government.
Key features of the commission model include:
Understanding the different types of local government structures is essential for citizens, businesses, and organizations to participate effectively in the democratic process. By grasping the nuances of each model, individuals can better comprehend how decisions are made, who holds authority, and how to engage with their local government. Whether your community operates under the council-manager, mayor-council, or commission model, having a clear understanding of the structure can empower you to make informed decisions and contribute to the betterment of your local community.
Understanding the Three Types of Local Government Structures: A Comprehensive Overview
As residents and citizens of the United States, it is important to stay informed and up-to-date on the various aspects of our government, including local government structures. These structures play a crucial role in shaping our communities and impacting our daily lives. By familiarizing ourselves with the three types of local government structures, we can better understand how decisions are made, resources are allocated, and services are provided in our own localities.
1. Mayor-Council Structure:
In this type of local government structure, power is divided between an elected mayor and a council or board. The mayor is the chief executive, responsible for implementing policies, managing the budget, and representing the locality. The council, on the other hand, is responsible for creating and passing laws, regulations, and ordinances. This structure allows for a clear separation of powers and provides a system of checks and balances.
2. Council-Manager Structure:
In a council-manager structure, the council is responsible for making policies and decisions, much like in the mayor-council structure. However, instead of an elected mayor, a professional manager is appointed to oversee the day-to-day operations of the local government. The manager is typically hired based on their expertise in public administration and is responsible for implementing policies, managing the budget, and coordinating the work of various departments. This structure aims to provide professional management while maintaining a strong elected body.
3. Commission Structure:
The commission structure is relatively less common but still exists in some localities. In this structure, elected commissioners serve as both executive administrators and legislative decision-makers. Each commissioner oversees a specific area or department and collectively makes decisions for the locality. While this structure may provide for more direct accountability to the electorate, it may also result in challenges in terms of coordination and efficiency.
It is important to note that these local government structures can vary from one locality to another. Although the basic principles remain the same, the specific powers, responsibilities, and organization may differ based on state laws, charters, and local ordinances. Therefore, it is crucial for readers to verify and contrast the content of this article with the local government structure in their particular locality.
Staying informed about local government structures is essential as it empowers us as citizens to actively participate in our communities. By understanding these structures, we can better engage with local officials, voice our concerns, and contribute to the decision-making process. Additionally, knowing the structure of our local government enables us to hold our elected officials accountable for their actions and encourages transparency and good governance.
In conclusion, understanding the three types of local government structures – mayor-council, council-manager, and commission – provides us with a comprehensive overview of how our localities are governed. It allows us to better comprehend the decision-making processes and ultimately empowers us to actively participate in shaping our communities. Remember to verify and contrast the content of this article with your specific locality to ensure accurate information.
