Understanding the Law of Demand in US Law: A Detailed Explanation
Hello and welcome to this informative article on the Law of Demand in US Law. It’s great to have you here!
Before we dive into the exciting world of US law, I want to stress the importance of cross-referencing information with other reliable sources and consulting legal professionals. While I will do my best to provide a comprehensive explanation, it is always wise to seek multiple perspectives and advice when it comes to legal matters.
📋 Content in this article
Now, let’s get started on our journey of exploring the Law of Demand in US Law. This concept forms the foundation of many economic and legal principles, and understanding it is crucial for comprehending how our legal system operates. So, let’s break it down step by step.
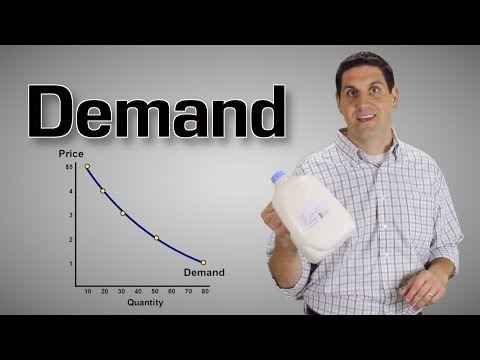
The Law of Demand, in a nutshell, states that as the price of a good or service increases, the quantity demanded by consumers decreases, and vice versa. This simple yet powerful principle has far-reaching implications in various aspects of US law, particularly in the realm of economics and business.
To delve deeper into this concept, let’s highlight a few key points:
1. Price and Quantity Relationship: The Law of Demand establishes a direct relationship between price and quantity demanded. As prices rise, people tend to purchase less of a product or service, while lower prices stimulate demand and encourage consumption.
2. Consumer Behavior: This law is rooted in consumer behavior and decision-making processes. Consumers typically seek the greatest satisfaction or utility for their spending. When prices increase, they often substitute with alternative products or reduce their overall consumption.
3. Market Equilibrium: The Law of Demand plays a crucial role in determining market equilibrium. Supply and demand intersect at a point where the quantity demanded equals the quantity supplied. Understanding the demand side is essential for analyzing market dynamics and making informed legal decisions.
4. Legal Implications: Lawmakers and legal professionals consider the
Understanding the Law of Demand: A Detailed Explanation with an Example
Understanding the Law of Demand in US Law: A Detailed Explanation
The law of demand is a fundamental concept in economics that also plays a crucial role in US law. It explains the relationship between the price of a good or service and the quantity demanded by consumers. By understanding this law, individuals and businesses can make informed decisions regarding pricing, production, and consumer behavior. In this article, we will delve into the intricacies of the law of demand and its significance within the context of US law.
1. The Law of Demand Explained:
According to the law of demand, there is an inverse relationship between the price of a product or service and the quantity demanded by consumers, all other factors being constant. In simpler terms, as the price of a good or service increases, the quantity demanded decreases, and vice versa. This concept is based on the assumption that consumers generally seek to maximize their utility or satisfaction while minimizing their costs.
2. The Role of Price:
Price serves as a critical determinant of demand. When the price of a product is high, consumers tend to demand less of it because it becomes relatively more expensive compared to alternative goods or services. On the other hand, when prices are low, consumers are more willing to purchase larger quantities. This relationship is commonly depicted through a downward-sloping demand curve.
3. Factors Affecting Demand:
While price is a significant factor in determining demand, several other factors can influence consumer behavior. These include:
Understanding the Law of Demand: Exploring its Mechanics and Observing Real-Life Examples
Understanding the Law of Demand in US Law: A Detailed Explanation
The concept of the law of demand is a fundamental aspect of US law that governs economic behavior. It is important to have a clear understanding of this concept as it affects many aspects of our daily lives, from prices of goods and services to consumer behavior and market dynamics. In this article, we will delve into the mechanics of the law of demand and provide real-life examples to help illustrate its application.
What is the Law of Demand?
The law of demand states that as the price of a good or service increases, the quantity demanded for that good or service decreases, and vice versa. In simpler terms, when the price of a product goes up, people tend to buy less of it, and when the price goes down, people tend to buy more.
How does the Law of Demand Work?
The law of demand is based on the idea that as prices increase, people have to allocate their limited resources more carefully. When a product becomes more expensive, consumers may choose to substitute it with a cheaper alternative or forego purchasing it altogether. This inverse relationship between price and quantity demanded forms the backbone of the law of demand.
Factors Influencing Demand:
Several factors influence the demand for a product or service. These factors include:
Understanding the Law of Demand in US Law: A Detailed Explanation
Introduction:
The law of demand is a fundamental concept in economics that also has relevance in the field of US law. It plays a crucial role in various legal areas, including antitrust, labor, and consumer protection laws. As such, it is essential for legal professionals and individuals interested in the law to have a solid understanding of this concept. In this article, we will provide a detailed explanation of the law of demand in the context of US law and emphasize the importance of staying current on this topic.
The Law of Demand:
The law of demand states that, all other factors being equal, as the price of a product or service decreases, the quantity demanded by consumers will increase, and vice versa. This inverse relationship between price and quantity demanded forms the basis for understanding consumer behavior and market dynamics.
Application in US Law:
1. Antitrust Law:
In the realm of antitrust law, the law of demand helps determine whether certain practices or agreements are anti-competitive. If a company or group of companies employs strategies that significantly reduce competition and increase prices, it may be deemed a violation of antitrust laws. Understanding the law of demand is essential for assessing whether such practices have an adverse impact on consumer welfare.
2. Labor Law:
In labor law, the law of demand comes into play when analyzing wage levels and employment. According to this principle, when the demand for labor decreases (such as during an economic downturn), employers may reduce wages or lay off workers. Conversely, when the demand for labor increases (during economic growth), employers may raise wages to attract and retain employees. Understanding the dynamics between labor demand and wages is crucial for navigating labor disputes and negotiating fair employment terms.
3. Consumer Protection Law:
Consumer protection laws aim to safeguard consumers from unfair or deceptive practices in the marketplace. The law of demand helps identify instances where businesses engage in price gouging or engage in fraudulent pricing schemes.
