Welcome to our informative article on the origins of law-making in England. In this piece, we will delve into the fascinating history of England’s first legislative body, shedding light on its formation and significance. Let’s dive right in and uncover the roots of this influential institution.
The Evolution of England’s Law-Making Body: A Comprehensive Overview
A Brief Guide to England’s First Legislative Body: Unraveling the Origins of Law-Making
📋 Content in this article
In order to understand the present-day legal system in England, it is crucial to examine the historical development of its law-making body. The origins of England’s first legislative body can be traced back to the early medieval period, specifically to the reign of King Edward I in the 13th century.
1. The Emergence of the Great Council:
– During this time, the monarch held significant power and authority in governing the realm. However, they often sought advice and assistance from prominent individuals, including nobles and clergy.
– This informal gathering of trusted advisors gradually evolved into a more structured and formal assembly known as the Great Council. The Great Council consisted of high-ranking officials, bishops, and influential barons who provided counsel to the king.
2. The Evolution into Parliament:
– Over time, the Great Council transformed into a more powerful institution that played a crucial role in law-making. This evolution marked the birth of what would eventually become known as Parliament.
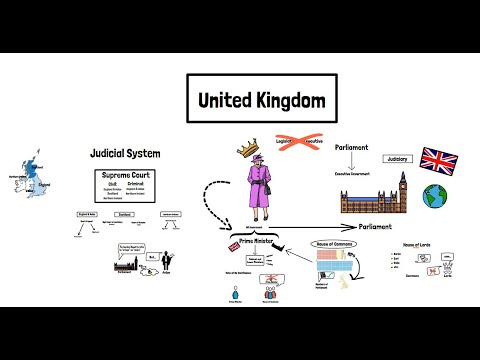
– Parliament initially consisted of two parts: the House of Lords and the House of Commons. The House of Lords comprised of bishops and nobles, while the House of Commons represented the common people.
– The primary function of Parliament was to advise the monarch on matters of governance, including legislation and taxation.
3. The Magna Carta and the Expansion of Parliamentary Power:
– One significant milestone in the development of England’s law-making body was the signing of the Magna Carta in 1215. This historic document limited the king’s authority and established certain rights and liberties for the nobility.
– The Magna Carta also paved the way for increased participation of the nobility in law-making processes. It granted them the right to consent to certain taxes and laws, effectively expanding parliamentary power.
– Subsequent monarchs, such as King Edward I, recognized the importance of seeking consent from the nobles and began summoning them to Parliament to participate in decision-making.
4. Parliament’s Role as a Law-Making Body:
– By the 14th century, Parliament had solidified its position as the primary law-making body in England. It gained the authority to enact statutes that applied to the entire realm.
– Parliament’s legislative power stemmed from its representative nature. The House of Commons, in particular, played a vital role in the law-making process by voicing the concerns and interests of the common people.
– Over time, Parliament’s jurisdiction expanded to cover various areas of governance, including taxation, justice, and foreign affairs.
5. Continuity and Adaptation:
– The structure and functions of Parliament have evolved over centuries, adapting to societal changes and political developments. Today, it consists of two houses: the House of Lords and the House of Commons.
– While the monarchy’s role in law-making has diminished significantly, the British Parliament retains its status as the supreme legislative authority in the United Kingdom.
– The development and evolution of England’s first legislative body have shaped the modern legal system and democratic governance in the country.
In conclusion, understanding the origins and evolution of England’s law-making body is essential for comprehending how the legal system operates today. The transformation from the Great Council to Parliament marked a significant shift in power and paved the way for a more representative and accountable system of governance.
The Evolution of Lawmaking in England: Unveiling the Government Body Responsible for Enacting Laws
A Brief Guide to England’s First Legislative Body: Unraveling the Origins of Law-Making
In order to understand the evolution of lawmaking in England, it is crucial to delve into the origins of the country’s first legislative body. This body, known as the Witan, played a fundamental role in shaping Britain’s legal system and laid the foundation for the modern law-making process. Let’s explore the origins and significance of the Witan in this brief guide.
1. Origins of the Witan
The Witan, also referred to as the Witenagemot or the Council of the Wise, can be traced back to Anglo-Saxon England. It emerged during the early medieval period and consisted of influential individuals such as nobles, bishops, and high-ranking officials. The exact origins of the Witan are not clear, but it is believed to have evolved from pre-existing Germanic tribal assemblies.
2. Role and Functions
The Witan served as an advisory body to the monarch, providing counsel on matters of governance, legislation, and law enforcement. It played a crucial role in decision-making processes and contributed to the formulation of laws and policies. The Witan also had the power to elect and advise the king, making it a significant political institution.
3. Law-Making in the Witan
One of the key functions of the Witan was its involvement in law-making. While there was no formal legislative process as we understand it today, the Witan had the authority to enact laws and regulations. These laws were often based on customary practices and traditions observed within the Anglo-Saxon society. The decisions made by the Witan had a significant impact on the legal landscape of England.
4. Evolution and Decline
Over time, the role and influence of the Witan underwent significant changes. With the arrival of the Norman Conquest in 1066, the Witan gradually transformed into a more centralized body known as the Great Council. This transition marked the beginning of the evolution of England’s law-making process, which would eventually lead to the establishment of Parliament.
5. Legacy and Significance
The legacy of the Witan is not to be underestimated. It was a precursor to the modern parliamentary system and laid the groundwork for representative governance in England. The Witan’s influence on law-making helped shape the legal traditions and principles that are still prevalent in the English legal system today.
In conclusion, understanding the origins and role of the Witan provides valuable insights into the evolution of lawmaking in England. By exploring this first legislative body, we gain a deeper appreciation for the historical development of England’s legal system and the significant impact it continues to have on modern governance.
The Historical Development of the British Parliament: A Comprehensive Overview
A Brief Guide to England’s First Legislative Body: Unraveling the Origins of Law-Making
The concept of the historical development of the British Parliament is a complex and fascinating topic. To truly understand the origins of law-making in England, it is crucial to delve into the roots of the country’s first legislative body. This article aims to provide a comprehensive overview of the origins of law-making in England, focusing on the establishment and evolution of England’s first legislative body.
1. The Witan: The Precursor to England’s First Legislative Body
The Witan, also known as the Witenagemot, was a council of advisors to the early English kings. It originated in Anglo-Saxon times and acted as a consultative assembly. While not a legislative body in the modern sense, the Witan played a pivotal role in law-making by advising the king on matters of governance and serving as a forum for discussion.
2. The Norman Conquest and the Development of the Curia Regis
With the Norman Conquest in 1066, England underwent significant political and legal changes. The curia regis, meaning “royal court” in Latin, emerged as the central governing body. Initially composed of the king’s closest advisors, it gradually evolved into a more structured assembly that included representatives from different regions.
3. Magna Carta and the Emergence of Parliament
The signing of Magna Carta in 1215 marked a turning point in English history. This historic document established certain rights and liberties and limited the powers of the monarch. It also paved the way for the development of Parliament as a separate entity from the king’s council.
4. The Model Parliament of 1295
Under Edward I, the concept of Parliament took a significant step forward with the calling of the Model Parliament in 1295. This assembly consisted of representatives from different counties and boroughs, including commoners and clergy. It marked the beginning of Parliament as a legislative body with the power to enact laws.
5. The Evolution of Parliament
Over the centuries, Parliament evolved into a bicameral institution with the House of Commons representing the commoners and the House of Lords composed of nobles and clergy. The powers and functions of Parliament expanded, including overseeing the finances of the nation, passing legislation, and providing a forum for debate and discussion.
In conclusion, understanding the historical development of the British Parliament is essential to comprehend the origins of law-making in England. From its roots in the Witan to the establishment of England’s first legislative body, Parliament has played a crucial role in shaping the country’s legal system. The evolution of Parliament has resulted in a robust legislative process that continues to influence English law to this day.
A Brief Guide to England’s First Legislative Body: Unraveling the Origins of Law-Making
As a seasoned attorney in the United States, it is crucial to stay up-to-date on legal concepts and developments not only within our own jurisdiction but also around the world. One particular area of interest is the origins of law-making, which can provide valuable insights and historical context that may influence our interpretation and application of laws today.
In this article, we will explore a brief guide to England’s first legislative body, shedding light on its significance and unraveling the roots of law-making in the country. However, it is important to note that while this guide provides a solid foundation for understanding the history of law-making in England, readers should always verify and contrast the content with additional reliable sources before drawing any firm conclusions.
1. The Witenagemot
The Witenagemot was England’s first legislative body, dating back to the early medieval period. The name “Witenagemot” roughly translates to “meeting of wise men” and was composed of the king, nobles, bishops, and other influential individuals. It played a crucial role in advising the king on matters of governance and law-making.
2. The Development of Common Law
The Witenagemot played a pivotal role in the development of common law in England. Common law refers to legal principles and rules derived from judicial decisions rather than statutes. It emerged as a way to standardize legal practices across different regions of the country and to ensure consistency and fairness in the administration of justice.
3. The Magna Carta
One of the most significant documents in English legal history is the Magna Carta. Signed in 1215, it was a landmark agreement between King John and his barons that limited the power of the monarchy and established certain rights and liberties for the English people. The Magna Carta marked a significant step towards constitutional governance and the protection of individual rights.
4. The Role of Parliament
The evolution of law-making in England eventually led to the establishment of Parliament, a representative body composed of the House of Commons and the House of Lords. Parliament became a central institution for law-making, enacting statutes that had the force of law throughout the kingdom. Over time, Parliament’s powers expanded, and it became a key player in shaping the legal landscape of England.
5. Continuing Influence
While the Witenagemot no longer exists and England’s legal system has evolved significantly over the centuries, understanding the origins of law-making in the country remains important. The principles and precedents established during the early stages continue to influence legal thought and practice to this day. For legal professionals, having a grasp of this historical context can enhance our understanding of the law and our ability to interpret and apply it effectively.
In conclusion, exploring the origins of law-making in England provides valuable insights into the development of legal systems and practices around the world. However, it is essential to approach this topic with caution, and readers should verify and contrast the information provided in this guide with reliable sources to ensure accuracy and comprehensive understanding. By staying up-to-date on this topic and continuously expanding our knowledge, we can become more effective and well-rounded legal professionals.
