Greetings!
Welcome to this informative article on understanding non-excludable liabilities in UK law. It is important to note that while this text aims to provide you with a comprehensive introduction to the topic, it is always advisable to cross-reference information with other reliable sources or consult legal advisors for a comprehensive understanding of the subject matter.
Now, let’s delve into the fascinating world of non-excludable liabilities in UK law. To fully grasp this concept, we must first understand what non-excludable liabilities are and how they function within the legal framework.
📋 Content in this article
In simple terms, non-excludable liabilities refer to legal obligations that cannot be waived or excluded through contractual agreements. These liabilities arise from laws and regulations that have been put in place to protect individuals, consumers, and the general public. They serve as safeguards, ensuring that certain rights and protections cannot be compromised or disregarded.
To further illustrate this, let’s explore a few key characteristics of non-excludable liabilities:
1. Protection of Consumer Rights: Non-excludable liabilities often come into play when dealing with consumer-related matters. They ensure that consumers are not left at a disadvantage due to unfair contract terms, misleading advertising, or faulty products. These liabilities hold businesses accountable for their actions and provide recourse for consumers who have suffered harm or loss.
2. Public Safety and Health: Non-excludable liabilities also extend to matters of public safety and health. For example, laws may dictate that certain safety standards must be met in the manufacturing of goods or the provision of services. Failure to adhere to these standards can result in legal consequences to ensure the wellbeing of individuals and communities.
3. Statutory Protections: Non-excludable liabilities often stem from statutory laws enacted by the government. These laws define the rights and obligations of individuals and organizations in various contexts, such as employment, tenancy, and consumer protection.
Understanding Liabilities That Cannot be Excluded by Law in the UK
Understanding Non-Excludable Liabilities in UK Law
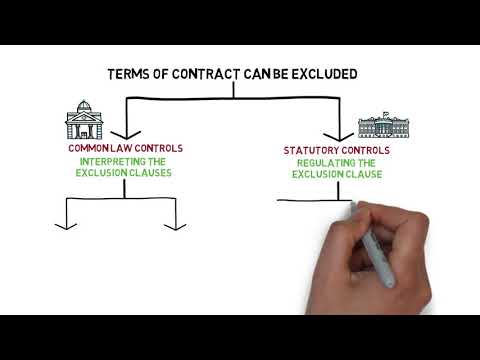
In the realm of UK law, liabilities can vary greatly. While it is common practice for parties to include clauses in contracts to limit their liability, there are certain liabilities that cannot be excluded by law. These non-excludable liabilities are of significant importance and must be fully understood by all parties involved in any legal agreement.
When entering into a contract or agreement, it is crucial to be aware that some liabilities cannot be limited or excluded, regardless of the language used in the contract. These non-excludable liabilities are established to protect certain rights and interests, ensuring fairness and justice in legal relationships.
To shed light on this topic, it is essential to highlight some key non-excludable liabilities in UK law:
It is important to note that non-excludable liabilities can differ depending on the nature of the contract or the specific industry involved. For instance, construction contracts often have specific provisions regarding liabilities for defects or damages to property.
To further illustrate this concept, let’s consider an example. Suppose a consumer purchases a faulty electrical appliance from a retailer.
Understanding Exclusion of Liability for Negligence in the UK
Understanding Exclusion of Liability for Negligence in the UK
In UK law, the concept of exclusion of liability for negligence is an important aspect to understand. It refers to the ability of parties to limit or exclude their liability for any losses or damages caused by their own negligence. However, it is important to note that not all liabilities can be excluded or limited, and there are certain non-excludable liabilities that parties must be aware of.
Non-Excludable Liabilities in UK Law
While parties have the freedom to negotiate and include exclusion clauses in their contracts, there are certain liabilities that cannot be excluded or limited. These non-excludable liabilities are established to protect the interests of the public and ensure fairness in contractual relationships.
One of the key non-excludable liabilities in UK law is liability for death or personal injury caused by negligence. This means that regardless of any exclusion clauses in a contract, a party cannot escape liability if their negligence results in someone’s death or personal injury. This is considered a fundamental public policy consideration and cannot be contracted out of.
Another non-excludable liability is liability for fraud or misrepresentation. If one party deliberately makes false statements or misrepresents facts to induce the other party into the contract, they cannot exclude or limit their liability for any resulting damages. This is because fraud undermines the integrity of the contractual relationship and is not permitted to be excluded.
Liability for breach of certain contractual terms may also be non-excludable. For example, if a contract contains terms that are implied by law, such as terms regarding quality or fitness for purpose of goods, any attempt to exclude or limit liability for breaching these terms may be unenforceable.
Title: Understanding Non-Excludable Liabilities in UK Law: Staying Informed and Verified
Introduction:
In the complex realm of UK law, it is essential to stay current on the concept of non-excludable liabilities. This article aims to provide a comprehensive understanding of this topic, emphasizing the importance of verifying and cross-referencing the content herein.
Defining Non-Excludable Liabilities:
Non-excludable liabilities refer to legal obligations that cannot be waived or excluded by contractual agreements or other means. These liabilities arise from certain fundamental legal principles and public policy considerations, which prioritize protecting the rights and interests of individuals in a fair and balanced manner.
Categories of Non-Excludable Liabilities:
1. Personal Injury:
– Instances where individuals suffer harm due to the negligent or intentional actions of others generally fall under non-excludable liabilities.
– These may include bodily harm, emotional distress, or damage to reputation caused by defamation.
2. Consumer Rights:
– Non-excludable liabilities in the realm of consumer rights aim to safeguard individuals from unfair trade practices.
– These may include misrepresentation, false claims, or the sale of unsafe products.
3. Employment Law:
– Certain workplace obligations cannot be excluded by contractual agreements, ensuring fairness and protection for employees.
– Examples include protection against unfair dismissal, discrimination, and breach of health and safety regulations.
4. Statutory Rights:
– Non-excludable liabilities often arise from statutory rights granted by legislation.
– These may include rights such as access to public services, protection against discrimination, or entitlements related to housing and welfare.
Importance of Staying Current:
Staying informed about non-excludable liabilities in UK law is crucial for various reasons:
1. Legal Compliance:
– Maintaining awareness of non-excludable liabilities helps individuals and organizations ensure they are operating within the boundaries of the law.
