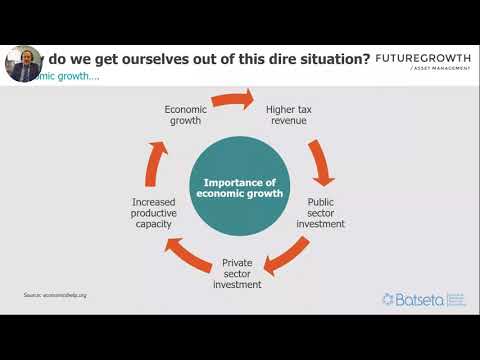
Greetings, readers!
Today, we will embark on a journey to explore and understand the intricacies of Regulation 28. This comprehensive overview will provide you with a solid foundation and a clear understanding of the regulations in question.
📋 Content in this article
But first, let’s clarify what Regulation 28 is all about. In essence, Regulation 28 refers to a set of rules established by South Africa’s Pension Funds Act. These regulations aim to ensure that pension funds are managed in a prudent and responsible manner, with the goal of safeguarding the long-term financial well-being of pension fund members.
Now that we have a general idea of what Regulation 28 entails, let’s delve into its key elements and concepts:
It is important to note that Regulation 28 is subject to periodic review and amendments. This ensures that the regulations remain relevant and effective in a changing economic and financial landscape.
In conclusion, understanding Regulation 28 is crucial for anyone involved in the management or oversight of pension funds in South Africa. By adhering to these regulations, pension funds can mitigate risks, safeguard retirement savings, and protect the interests of their members.
Stay tuned for more articles that will delve deeper into the specific aspects of Regulation 28. Until then, remember to always seek professional advice when dealing with legal and financial matters.
Understanding Regulation 28: A Beginner’s Guide to Financial Regulations and Investments
Understanding Regulation 28: A Comprehensive Overview of the Regulations
Introduction:
Regulation 28 is an important aspect of financial regulations and investments in the United States. It plays a crucial role in ensuring the stability and protection of investors’ interests. In this article, we will provide you with a comprehensive overview of Regulation 28 and its key provisions.
1. What is Regulation 28?
Regulation 28 refers to a set of rules established by regulatory bodies such as the Securities and Exchange Commission (SEC) and the Financial Industry Regulatory Authority (FINRA). These regulations govern various aspects of investment activities, aiming to maintain fair and transparent practices in the financial industry.
2. Why is Regulation 28 Important?
Regulation 28 is crucial for protecting investors from fraudulent practices, ensuring market integrity, and promoting investor confidence. It establishes guidelines that financial institutions, brokers, and investment advisors must adhere to when managing clients’ funds.
3. Key Provisions of Regulation 28:
4. Compliance and Enforcement:
Regulatory bodies like the SEC and FINRA are responsible for monitoring and enforcing compliance with Regulation 28. Financial institutions, brokers, and investment advisors must establish robust internal controls and regularly report their compliance to these regulatory bodies. Non-compliance can result in penalties, fines, or even the revocation of licenses.
Understanding Regulation 28 Policy: A Comprehensive Guide
Understanding Regulation 28: A Comprehensive Overview of the Regulations
Regulation 28 is an important part of the legal framework governing investments in South Africa. It sets out guidelines regarding the investment limits and asset allocation for pension funds, retirement annuities, and other long-term insurance policies. This article aims to provide a comprehensive overview of Regulation 28 and its significance.
1. What is Regulation 28?
2. Investment Limits under Regulation 28:
3. Prudent Investment Principle:
4. Governance and Reporting:
5. Impact on Investors:
In conclusion, Regulation 28 is a crucial regulatory framework that governs investment practices in South Africa’s retirement funds. It aims to protect the interests of fund members by setting investment limits and promoting prudent investment principles. Compliance with Regulation 28 ensures that retirement funds are managed in a balanced and responsible manner, safeguarding the long-term financial security of members.
Understanding the Offshore Limit for Regulation 28: A Comprehensive Guide
Understanding Regulation 28: A Comprehensive Overview of the Regulations
In the realm of financial investments, it is crucial to have a thorough understanding of the regulations that govern these activities. One such important regulation is Regulation 28, which applies to pension funds and other institutional investors in South Africa. This regulation sets out certain limitations and guidelines on the types and amounts of assets that can be held by these investors. In this comprehensive guide, we will focus on a specific aspect of Regulation 28 – the offshore limit.
What is Regulation 28?
Regulation 28 is a set of rules issued by the South African government’s Financial Services Board (FSB) under the Pension Funds Act. It aims to protect pension fund members by promoting responsible investment practices and ensuring the long-term sustainability of these funds. The regulation covers a wide range of investment activities, including asset allocation, diversification, risk management, and prudential limits.
Understanding the Offshore Limit
One key aspect of Regulation 28 is the offshore limit. This refers to the maximum percentage of assets that can be invested in foreign markets or held in foreign currencies. The rationale behind this limit is to manage the potential risks associated with investments in foreign jurisdictions while still allowing for diversification and access to international markets.
The current offshore limit in Regulation 28 is set at 30% for pension funds. This means that pension funds can allocate up to 30% of their assets to investments outside of South Africa or denominated in foreign currencies. It is important to note that this limit applies to the total assets of the fund and not to individual investments.
Factors Influencing the Offshore Limit
The offshore limit set by Regulation 28 is not arbitrary; it takes into consideration various factors to strike a balance between risk and opportunity. Some of the factors that may influence the offshore limit include:
1. Economic Factors: The stability and growth prospects of the domestic economy and currency play a significant role in determining the offshore limit. If the local economy is strong and the currency stable, there may be less need for excessive offshore investments.
2. Political Factors: The regulatory environment, political stability, and geopolitical risks can impact the offshore limit. Higher risks in the local political landscape may necessitate a higher offshore limit to mitigate potential losses.
3. Market Factors: The depth, liquidity, and efficiency of the local financial markets are also considered when determining the offshore limit. If the local markets provide sufficient opportunities for investment, there may be a lower need for offshore exposure.
Complying with the Offshore Limit
Pension funds and institutional investors must carefully monitor their investment portfolios to ensure compliance with the offshore limit set by Regulation 28. This involves regular monitoring of investment allocations, performance evaluation, and taking appropriate actions to rebalance the portfolio if necessary.
It is important for investors to engage qualified and experienced financial advisors or asset managers who have a deep understanding of Regulation 28 and its implications. These professionals can help navigate the complexities of offshore investments and ensure compliance with the regulations.
In conclusion, Regulation 28 is a crucial aspect of the South African investment landscape. The offshore limit is an important consideration for pension funds and institutional investors when constructing their portfolios. By understanding the regulations and working with knowledgeable professionals, investors can navigate the complexities of Regulation 28 while maximizing potential returns and managing risks effectively.
Understanding Regulation 28: A Comprehensive Overview of the Regulations
As an attorney, it is crucial to stay informed and up-to-date on various regulations that govern our society. One such regulation that holds significant importance in the financial sector is Regulation 28. This article aims to provide a comprehensive overview of Regulation 28 and highlight its significance in today’s regulatory landscape.
Regulation 28 is a directive that falls under the Pension Funds Act of South Africa. Its main purpose is to establish prudential investment guidelines for retirement funds such as pension funds, retirement annuities, and preservation funds. These guidelines aim to ensure the long-term sustainability and financial soundness of these funds by setting limits and restrictions on their investment activities.
The primary objective of Regulation 28 is to protect pension fund members and their retirement savings by promoting responsible and prudent investment practices. It achieves this by imposing limits on asset allocation, concentration risk, and exposure to certain asset classes. By doing so, the regulation aims to strike a balance between risk and return, ensuring that retirement funds are not unduly exposed to excessive risk.
Some key provisions of Regulation 28 include:
1. Asset Allocation Limits: Regulation 28 sets maximum limits on the percentage of assets that can be invested in different asset classes. These asset classes include equities, property, bonds, cash, and alternative investments. These limits vary depending on the type of fund and the risk profile of its members.
2. Concentration Risk: The regulation also aims to mitigate concentration risk by limiting exposure to a single issuer or counterparty. This ensures that pension funds are not overly reliant on a single investment or entity, reducing the potential impact of defaults or financial distress.
3. Environmental, Social, and Governance (ESG) Factors: Regulation 28 recognizes the importance of considering ESG factors in investment decision-making. It encourages pension funds to integrate ESG considerations into their investment processes, promoting sustainable and responsible investing practices.
It is important to note that while this article provides a comprehensive overview of Regulation 28, it is crucial for readers to verify and contrast the information presented. Regulations and guidelines are subject to change over time, and it is essential to consult the latest legislation, official publications, and professional advice to ensure accurate understanding and compliance.
In conclusion, understanding and staying up-to-date on Regulation 28 is of utmost importance for attorneys and professionals in the financial sector. Compliance with this regulation not only ensures the protection of retirement fund members but also promotes responsible investment practices. By adhering to the guidelines of Regulation 28, attorneys can play a crucial role in safeguarding the financial well-being of their clients and the wider community.
