Understanding the Power Law of Electricity: A Comprehensive Explanation
Greetings to all readers! Today, we delve into the fascinating world of electricity and unravel the mysteries behind the power law. In this article, we will provide a detailed explanation of this fundamental concept without embellishing any credentials. So, let’s dive right in!
📋 Content in this article
1. What is the Power Law?
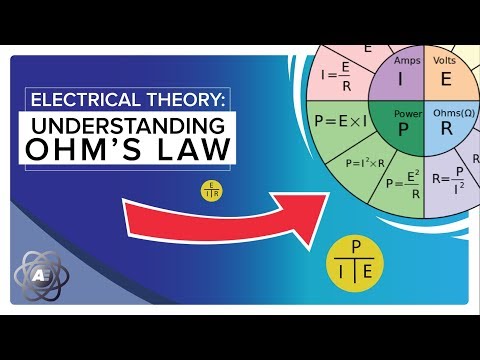
The power law, also known as Ohm’s law, is a basic principle in electrical engineering that describes the relationship between voltage, current, and resistance in an electrical circuit. It states that the current passing through a conductor between two points is directly proportional to the voltage across the two points, while inversely proportional to the resistance.
2. The Formula:
The mathematical representation of the power law is expressed as I = V/R, where:
– I is the current flowing through the circuit, measured in amperes (A).
– V is the voltage difference across the two points in the circuit, measured in volts (V).
– R is the resistance of the conductor, measured in ohms (Ω).
3. Understanding Voltage:
Voltage refers to the electric potential difference between two points in a circuit. It can be thought of as the force that drives electrons to flow through a conductor. The higher the voltage, the more electrons are pushed through the circuit.
4. Grasping Current:
Current is the flow of electric charge through a conductor. It represents the rate at which electrons pass through a specific point in a circuit. Current flows from a higher voltage to a lower voltage and is measured in amperes (A).
5. Unveiling Resistance:
Resistance is the opposition encountered by an electric current when it flows through a material or device. It determines how much current will flow through a circuit for a given voltage. Resistance is influenced by factors such as the material’s properties and its dimensions.
6. Applying Ohm’s Law:
Using Ohm’s law, we can solve for any of the three variables. For example, if we know the voltage and resistance, we can calculate the current using the formula I = V/R. Similarly, if we know the current and resistance, we can find the voltage using V = I * R.
7. Implications of Ohm’s Law:
Understanding Ohm’s law is crucial in various electrical applications. It helps engineers design circuits and determine the appropriate components to use. Ohm’s law also allows us to predict the behavior of electrical circuits and troubleshoot any issues that may arise.
In summary, the power law, or Ohm’s law, is a fundamental principle in electrical engineering that explains the relationship between voltage, current, and resistance in a circuit. By understanding this law, we gain insights into how electricity behaves and can apply this knowledge in practical applications.
Remember, it is always essential to consult qualified professionals for specific electrical needs or legal advice.
Understanding the Power Law: A Comprehensive Explanation
Understanding the Power Law of Electricity: A Comprehensive Explanation
In today’s technologically advanced world, electricity plays a crucial role in our daily lives. From powering our homes to fueling industries, the demand for electricity is ever-growing. However, it is essential to have a comprehensive understanding of the power law that governs the production, distribution, and consumption of electricity.
1. What is the Power Law?
The power law, also known as Ohm’s Law, is a fundamental principle in electrical engineering and physics that defines the relationship between voltage, current, and resistance in an electric circuit. It states that the current flowing through a conductor is directly proportional to the voltage applied across it and inversely proportional to the resistance of the conductor.
Key Point: The power law can be expressed using the formula: I = V/R, where I represents the current in amperes (A), V denotes the voltage in volts (V), and R signifies the resistance in ohms (Ω).
2. Understanding Voltage:
Voltage, often referred to as electric potential difference, is the driving force that pushes the electric charge through a circuit. It is typically measured in volts and can be thought of as the pressure or potential energy difference between two points in an electrical system.
Key Point: Voltage is responsible for creating an electric field that induces the flow of current.
3. Exploring Current:
Current is the rate at which electric charge flows through a conductor. It is measured in amperes and is influenced by both voltage and resistance. Higher voltages result in increased current flow, whereas higher resistances hinder the flow of current.
Key Point: Current can be either direct current (DC), which flows in one direction, or alternating current (AC), which periodically reverses its direction.
4. Resistance and its Impact:
Resistance refers to the opposition encountered by the flow of current in a conductor. It depends on various factors such as the material, length, cross-sectional area, and temperature of the conductor. The unit of resistance is the ohm (Ω).
Key Point: Resistance acts as a limiting factor in a circuit, affecting the amount of current that can flow through it.
5. Power and Energy:
Power is the rate at which work is done or energy is transferred or converted. In an electrical context, it can be calculated using the formula: P = IV, where P denotes power in watts (W), I represents current in amperes, and V signifies voltage in volts.
Key Point: Energy, on the other hand, is the capacity to do work and is typically measured in joules (J) or kilowatt-hours (kWh).
Understanding the power law is essential for various reasons, including designing electrical systems, troubleshooting electrical issues, and ensuring the efficient use of electricity. It forms the foundation for comprehending how electricity behaves in different circuits and devices.
In conclusion, gaining a comprehensive understanding of the power law of electricity is crucial to navigate the complex realm of electrical engineering. By grasping the interplay between voltage, current, and resistance, individuals can better appreciate how electricity powers our modern world.
Understanding the Power Law of Electricity: A Comprehensive Overview
Understanding the Power Law of Electricity: A Comprehensive Explanation
Electricity is an essential part of our daily lives, powering our homes, businesses, and industries. However, understanding the complexities of electricity and its legal implications can be quite challenging. In this comprehensive explanation, we will delve into the power law of electricity and break it down into understandable terms.
1. The Power Law and Electricity Generation:
Electricity is generated through various sources such as fossil fuels, nuclear energy, and renewable resources like solar and wind. The power law relates to the amount of electric power generated and consumed. It encompasses the principles of supply, demand, and transmission of electricity.
2. Understanding Power Generation and Distribution:
Power plants generate electricity, which is then transmitted through a network of power lines, transformers, and substations. The power law governs how electricity is distributed from power plants to consumers. It ensures a steady and reliable supply of electricity while maintaining grid stability.
3. The Role of Regulatory Authorities:
Regulatory authorities play a crucial role in overseeing the power industry. They establish policies and regulations to ensure fair competition, consumer protection, and the efficient operation of the electricity market. These authorities enforce compliance with the power law to maintain a balance between supply and demand.
4. Power Purchase Agreements:
Power purchase agreements (PPAs) are contracts between electricity generators and consumers. PPAs define the terms of electricity sale and purchase, including pricing, quantity, and duration. They provide legal protection for both parties involved and ensure a stable supply of electricity.
5. Understanding Rate Structures:
Rate structures determine how consumers are charged for their electricity usage. They vary based on factors such as usage patterns, time of day, and demand levels. Understanding rate structures is crucial for managing electricity costs and optimizing consumption.
6. Energy Conservation and Efficiency:
The power law also emphasizes the importance of energy conservation and efficiency. By using energy-efficient appliances, adopting sustainable practices, and reducing waste, individuals and businesses can contribute to a more sustainable energy future while saving on electricity costs.
7. The Role of Renewable Energy:
Renewable energy sources are gaining prominence as a cleaner and more sustainable alternative to traditional fossil fuel-based power generation. The power law encourages the integration of renewable energy sources into the electricity grid, promoting a greener and more environmentally friendly energy landscape.
In conclusion, understanding the power law of electricity is essential for individuals, businesses, and policymakers. It provides a framework for the generation, distribution, and consumption of electricity while ensuring fair competition and consumer protection. By comprehending the intricacies of the power law, you can make informed decisions regarding your electricity usage and contribute to a more sustainable energy future.
Understanding the Three Formulas for Electric Power: A Comprehensive Guide
Understanding the Power Law of Electricity: A Comprehensive Explanation
Electricity is a fundamental force that powers our modern world. Whether we are using it to light our homes, operate machinery, or charge our devices, understanding the power law of electricity is essential. In this comprehensive guide, we will explore the three formulas for electric power and how they relate to this fundamental concept.
1. Power (P) Formula: The power formula represents the rate at which electric energy is converted or consumed. It is calculated by multiplying the voltage (V) by the current (I). The formula is as follows:
P = V * I
Power is measured in watts (W), and a watt is equivalent to one joule of energy per second. This formula allows us to determine how much power is being used or generated in a given electrical circuit.
2. Ohm’s Law: Ohm’s Law is a fundamental principle in understanding the relationship between voltage, current, and resistance in an electrical circuit. It states that the current flowing through a conductor between two points is directly proportional to the voltage across the two points and inversely proportional to the resistance.
The formula for Ohm’s Law is as follows:
I = V / R
Where I represents the current in amperes (A), V represents the voltage in volts (V), and R represents the resistance in ohms (Ω). Ohm’s Law allows us to calculate the current flowing through a circuit when the voltage and resistance are known.
3. Electrical Energy Formula: The electrical energy formula allows us to determine the amount of electrical energy consumed or generated over a certain period. It is calculated by multiplying the power by the time (t) for which it is applied.
The formula for electrical energy is as follows:
E = P * t
Where E represents the electrical energy in joules (J), P represents the power in watts (W), and t represents the time in seconds (s). This formula is used to calculate the total energy consumption of an electrical appliance or the amount of energy generated by a power source over a specific period.
Understanding these three formulas for electric power is crucial in various applications, such as designing electrical circuits, calculating energy usage and costs, and ensuring the efficient use of electrical resources.
In conclusion, comprehending the power law of electricity and the three formulas for electric power provides a solid foundation for understanding and manipulating electrical systems. By grasping these concepts, individuals can make informed decisions about power consumption, troubleshoot electrical issues, and optimize the efficiency of their electrical devices and systems.
Understanding the Power Law of Electricity: A Comprehensive Explanation
As technology continues to advance, electricity plays an increasingly vital role in our everyday lives. From powering our homes and businesses to fueling our devices, it has become an essential part of modern society. In order to comprehend the intricacies of electricity and its regulation, it is important to understand the concept of the power law.
The power law of electricity refers to the legal framework that governs the generation, transmission, and distribution of electrical power. It encompasses a wide range of regulations and statutes that are designed to ensure the safe and reliable delivery of electricity to consumers.
One key aspect of the power law is the regulation of electric utilities. Electric utilities are entities responsible for generating and distributing electricity to consumers. They are subject to extensive regulations to ensure that they provide reliable service at reasonable rates. These regulations often involve oversight from state or federal regulatory agencies, such as the Federal Energy Regulatory Commission (FERC) or state public utility commissions.
Another critical component of the power law is the principle of rate-making. Rate-making refers to the process by which electric utilities determine the rates they charge consumers for electricity. This process involves balancing the costs of generating and delivering electricity with the need to provide affordable service. Rate-making is often subject to review and approval by regulatory agencies to ensure that rates are just and reasonable.
In addition, the power law addresses electricity markets and competition. In some jurisdictions, there are deregulated electricity markets where multiple suppliers can compete to provide electricity to consumers. These markets are governed by specific rules and regulations to promote fair competition and protect consumers’ interests. Understanding these rules is crucial for businesses and individuals who want to navigate the complexities of purchasing electricity from alternative suppliers.
Furthermore, the power law also encompasses energy conservation and environmental considerations. As society becomes more aware of the environmental impact of electricity generation, there is a growing emphasis on promoting energy conservation and the use of renewable energy sources. Various laws and regulations exist to encourage energy efficiency, incentivize renewable energy development, and mitigate the environmental effects of traditional energy sources.
Staying up-to-date on the power law is essential for both businesses and individuals. Changes in regulations can have significant impacts on electricity costs, availability, and sustainability. By keeping abreast of the latest developments in the power law, consumers can make informed decisions about their electricity usage, explore alternative energy options, and advocate for policies that align with their interests.
It is important to note that while this article provides a comprehensive explanation of the power law, readers should always verify and contrast the content with reputable sources and consult with legal professionals when necessary. The power law can vary from state to state and is subject to interpretation by courts and regulatory agencies. Therefore, it is crucial to seek guidance from qualified experts to ensure compliance with applicable laws and regulations.
In conclusion, understanding the power law of electricity is crucial in navigating the complex landscape of electricity regulation. From utility regulation to rate-making, electricity markets, energy conservation, and environmental considerations, the power law encompasses various aspects that directly impact consumers. Staying informed about these regulations empowers individuals and businesses to make informed decisions and advocate for their interests in an ever-evolving energy landscape.
