Greetings readers,
Welcome to this informative article on the new tax code for 2023 to 2024. In this comprehensive overview, we will dive into the key concepts and changes that you need to know about. So sit back, relax, and let’s explore the world of taxes together.
📋 Content in this article
1. Background:
The tax code is a set of laws and regulations that govern how individuals and businesses are taxed by the government. It outlines the rules for calculating and paying taxes, as well as any exemptions, deductions, or credits that may apply.
2. The New Tax Code:
The new tax code for 2023 to 2024 refers to the latest set of changes made to the existing tax laws. These changes are enacted by the government to ensure fairness, promote economic growth, and address any loopholes or inefficiencies in the previous code.
3. Key Changes:
The new tax code may introduce several key changes that impact individuals and businesses alike. Some of these changes may include:
– Tax Rates: The tax rates for different income brackets may be adjusted, potentially resulting in higher or lower taxes for certain individuals or entities.
– Deductions and Exemptions: The availability and scope of deductions and exemptions may change, affecting the amount of taxable income that can be reduced.
– Tax Credits: The eligibility criteria and amount of tax credits may be modified, impacting the ability of individuals and businesses to reduce their overall tax liability.
– Business Provisions: The new tax code may introduce specific provisions that address business-related matters such as depreciation rules, capital gains taxes, and other industry-specific regulations.
4. Implications:
Understanding the new tax code is crucial as it can have significant implications on your financial planning and obligations. By staying informed, you can make informed decisions regarding your income, investments, and overall tax strategy.
5. Seeking Professional Advice:
Given the complexity of tax laws, it is often advisable to seek professional advice from a tax accountant or attorney. They can provide personalized guidance based on your unique circumstances and help you navigate the intricacies of the new tax code.
In conclusion, familiarizing yourself with the new tax code for 2023 to 2024 is essential for maintaining compliance and optimizing your tax situation. By staying informed and seeking professional advice when needed, you can ensure that you are making the most of the available tax provisions while avoiding any potential pitfalls.
Thank you for joining us on this journey through the world of taxes. Stay tuned for more informative articles on legal matters in the future.
Disclaimer: The information provided in this article is for educational purposes only and should not be considered legal or tax advice. Always consult with a qualified professional regarding your specific situation.
Understanding the Extra Standard Deduction for Seniors over 65 in 2023
Understanding the New Tax Code for 2023 to 2024: A Comprehensive Overview
The new tax code for 2023 brings several changes that may affect individuals and businesses. It is crucial to understand these changes to ensure compliance and make informed financial decisions. In this article, we will focus on the extra standard deduction for seniors over 65 as one of the key provisions of the new tax code.
What is the extra standard deduction for seniors over 65?
The extra standard deduction is an additional amount that seniors over the age of 65 can claim on their tax returns. This deduction is meant to provide older individuals with some relief by reducing their taxable income.
How does the extra standard deduction work?
For taxpayers who are 65 years or older, the extra standard deduction is added to their regular standard deduction. The amount of the extra deduction varies depending on the taxpayer’s filing status.
For the tax year 2023, the extra standard deduction for single filers and married individuals filing separately is $1,700. For married couples filing jointly, the extra standard deduction is $1,350 per spouse, totaling $2,700.
To claim this additional deduction, seniors must meet certain criteria. First, they must be at least 65 years old by the end of the tax year. Second, they must not be claimed as a dependent on someone else’s tax return. Finally, they must have a filing status that allows them to claim the standard deduction.
Why was the extra standard deduction for seniors over 65 implemented?
The extra standard deduction for seniors recognizes that older individuals may have higher medical and healthcare expenses compared to younger taxpayers. By providing an additional deduction, the tax code aims to alleviate some of the financial burdens faced by seniors.
Other considerations for seniors under the new tax code
While the extra standard deduction is a valuable benefit for seniors, it’s important to note that other tax provisions may also impact older individuals. For example, changes to the tax brackets, capital gains rates, and retirement account contribution limits may influence how seniors plan their financial affairs.
Additionally, seniors should be aware of potential deductions and credits that they may be eligible for. These could include deductions for medical expenses, long-term care premiums, and credits for the elderly or disabled.
Understanding the Key Tax Changes for 2023: A Comprehensive Overview
Understanding the New Tax Code for 2023 to 2024: A Comprehensive Overview
The tax landscape is constantly evolving, and as we enter 2023, it is crucial to stay informed about the key tax changes that may affect you. In this article, we will provide a comprehensive overview of the new tax code for 2023 to 2024, highlighting important concepts and key points to help you navigate these changes.
1. Tax Rates:
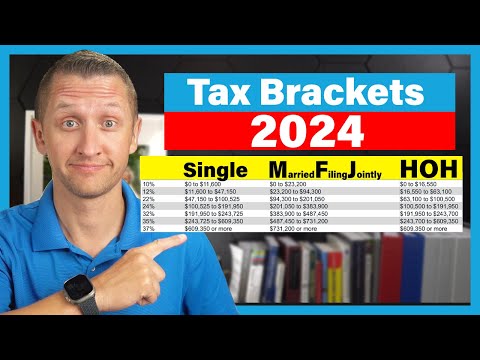
– The tax rates for individuals have been adjusted for 2023. There are now seven tax brackets, ranging from 10% to 37%. It is important to know which bracket you fall into, as it will determine the amount of tax you owe.
2. Standard Deduction:
– The standard deduction has increased for both single and married taxpayers in 2023. Single taxpayers can now claim a standard deduction of $12,950, while married taxpayers filing jointly can claim a deduction of $25,900. This increase in the standard deduction means that more taxpayers may choose to take the standard deduction rather than itemizing their deductions.
3. Child Tax Credit:
– The child tax credit has been expanded for 2023. Eligible taxpayers can now claim a credit of up to $3,000 per qualifying child between the ages of 6 and 17, and up to $3,600 per qualifying child under the age of 6. This credit is fully refundable for many taxpayers, which means that even if you have no tax liability, you may still receive a refund.
4. Capital Gains Tax:
– The capital gains tax rates have changed for 2023. The maximum tax rate on long-term capital gains and qualified dividends is now 20% for individuals in the highest tax bracket. For individuals in the lower tax brackets, the capital gains tax rate remains at 0% or 15%.
5. Retirement Contributions:
– The contribution limits for retirement accounts have increased for 2023. The maximum contribution limit for 401(k) plans is now $20,500, and for individual retirement accounts (IRAs), the limit is $6,000. These increased limits provide an opportunity for individuals to save more for retirement on a tax-advantaged basis.
6. Estate Tax:
– The estate tax exemption has increased for 2023. The exemption amount is now $12.06 million per individual or $24.12 million for married couples. This means that estates below these values will not be subject to federal estate tax.
7. Affordable Care Act (ACA) Penalties:
– The individual mandate penalty under the Affordable Care Act (ACA) has been reduced to zero starting from 2019. This means that individuals who do not have health insurance will not face a penalty on their federal tax return.
It is important to note that this overview provides a general understanding of the new tax code for 2023 to 2024. Individual circumstances may vary, and it is advisable to consult with a qualified tax professional to fully understand how these changes may impact your unique situation.
In conclusion, staying informed about the key tax changes for 2023 is crucial to ensure compliance and make strategic financial decisions. By understanding the new tax code and how it affects you, you can effectively manage your tax obligations and take advantage of any available opportunities.
Understanding the Taxation of Social Security Benefits: Age at Which it Ceases
Understanding the Taxation of Social Security Benefits: Age at Which it Ceases
As we dive into the complexities of the new tax code for 2023 to 2024, one important aspect to consider is the taxation of Social Security benefits and the age at which these benefits cease to be taxed. It is crucial to understand how these rules apply to your specific situation, as it can greatly impact your overall tax liability.
1. Taxation of Social Security Benefits
When it comes to Social Security benefits, not all beneficiaries are subject to taxation. The amount of your benefits that may be subject to income tax depends on your provisional income. Provisional income is calculated by combining your adjusted gross income (AGI), any non-taxable interest, and 50% of your Social Security benefits.
2. Age at Which Social Security Benefits Cease to be Taxed
Prior to the enactment of the new tax code for 2023 to 2024, there was a specific age at which Social Security benefits ceased to be taxed. However, under the new tax code, there is no longer a designated age at which benefits become tax-free. Instead, the taxation of Social Security benefits depends on your provisional income as mentioned earlier.
3. Income Thresholds for Taxation
To determine whether your Social Security benefits will be subject to income tax, you need to compare your provisional income to certain thresholds. These thresholds differ depending on your filing status. Here are the income thresholds for the 2023 to 2024 tax year:
– Single filers: If your provisional income is below $25,000, your Social Security benefits will not be subject to taxation. If your provisional income falls between $25,000 and $34,000, up to 50% of your benefits may be taxable. If your provisional income exceeds $34,000, up to 85% of your benefits may be taxable.
– Married filing jointly: If your provisional income is below $32,000, your Social Security benefits will not be subject to taxation. If your provisional income falls between $32,000 and $44,000, up to 50% of your benefits may be taxable. If your provisional income exceeds $44,000, up to 85% of your benefits may be taxable.
– Married filing separately: In general, if you are married filing separately and lived with your spouse at any time during the tax year, up to 85% of your Social Security benefits may be taxable.
4. Considerations for Future Tax Years
It is important to note that these income thresholds and taxation rules may change in future tax years. The new tax code for 2023 to 2024 sets the current guidelines, but Congress has the ability to amend these rules in the future.
5. Seek Professional Advice
Given the intricate nature of tax laws and the potential impact on your personal finances, it is always advisable to consult with a qualified tax professional. They can help you navigate the complexities of the tax code, assess your individual circumstances, and provide personalized guidance to minimize your tax liability.
In conclusion, understanding the taxation of Social Security benefits and the age at which it ceases is an essential component of comprehending the new tax code for 2023 to 2024. By knowing how your provisional income compares to the income thresholds outlined in this article, you can better gauge the potential tax implications of your Social Security benefits. Remember to consult with a tax professional for personalized advice tailored to your specific situation.
Understanding the New Tax Code for 2023 to 2024: A Comprehensive Overview
As we enter the year 2023, it is essential to stay up-to-date with changes in the tax code that may impact individuals and businesses alike. The tax code is an intricate and ever-evolving set of laws and regulations that determine how taxes are assessed and collected. Staying informed about these changes is crucial to ensure compliance and make informed financial decisions.
The tax code affects everyone: from individuals earning income, to businesses of all sizes, to estates and trusts. It dictates the rules by which income is taxed, deductions and credits that can be claimed, and the procedures for filing tax returns. Failure to understand and adhere to the tax code can result in penalties, fines, or even legal action.
Why Stay Informed?
Staying up-to-date on the new tax code is important for several reasons:
1. Compliance: The tax code is not optional. It is a legal requirement for individuals and businesses to accurately report their income and pay the appropriate amount of taxes. Ignorance of the law is not a valid defense. By staying informed, you can ensure that you are meeting your legal obligations.
2. Maximizing Deductions and Credits: The tax code provides numerous opportunities for individuals and businesses to minimize their tax liability through deductions and credits. Changes in the tax code may introduce new deductions or modify existing ones. By remaining informed, you can identify potential deductions and credits that can help reduce your tax burden.
3. Planning Opportunities: Knowledge of the tax code allows individuals and businesses to engage in strategic tax planning. By understanding how specific transactions or actions may be treated under the law, you can make informed decisions that minimize your tax liability. Staying informed ensures that you are aware of any changes that may impact your tax planning strategies.
4. Avoiding Penalties and Audits: Failing to comply with the tax code can lead to penalties, fines, and even audits by tax authorities. By staying informed, you can avoid inadvertently violating tax laws and mitigate the risk of facing penalties or audits.
Verifying and Contrasting Information
It is important to note that the tax code is complex and subject to interpretation. While this article aims to provide a comprehensive overview of the new tax code for 2023 to 2024, it is essential to verify and contrast the information presented here with official sources.
The Internal Revenue Service (IRS) is the authoritative source for tax laws and regulations in the United States. Their website, www.irs.gov, provides official publications, forms, and guidance that can help you navigate the tax code. Additionally, consulting with a qualified tax professional can provide personalized advice and guidance based on your specific situation.
In conclusion, understanding the new tax code for 2023 to 2024 is crucial for individuals and businesses alike. Staying informed allows you to comply with the law, maximize deductions and credits, identify planning opportunities, and avoid penalties or audits. However, it is essential to independently verify and contrast the information presented here with official sources to ensure accuracy and applicability to your unique circumstances.
