Welcome to this informative article on understanding the Local Government Code and its relevance to the Local Development Council (LDC). In this guide, we will explore the key concepts and functions of the Local Development Council under the Local Government Code of the United States. Let’s dive in and discover more about this important aspect of local governance.
Understanding the Local Government Code: A Comprehensive Guide to the Local Development Council
Understanding the Local Government Code: A Comprehensive Guide to the Local Development Council
📋 Content in this article
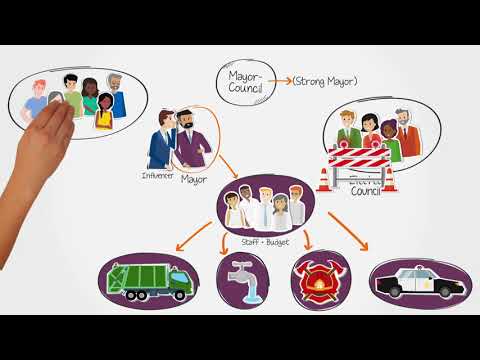
The Local Government Code is a crucial piece of legislation that governs the local government units (LGUs) in the United States. It provides a framework for the allocation of powers and responsibilities between the national government and the LGUs. One important facet of the Local Government Code is the establishment of the Local Development Council (LDC). In this comprehensive guide, we will delve into the concept of the LDC and its significance in local governance.
What is the Local Development Council?
The Local Development Council is a mandated body created under the provisions of the Local Government Code. Its main function is to serve as the primary planning and policy-making body at the local level. The LDC is composed of key stakeholders, including representatives from the LGU, non-government organizations, business sector, and other concerned groups within the region.
The Role of the Local Development Council
The primary role of the LDC is to formulate development plans and policies for the LGU. These plans and policies aim to address the various social, economic, and environmental issues within the local community. The LDC takes into consideration the needs and aspirations of the constituents, as well as the available resources and opportunities for development. By involving various sectors and stakeholders in the planning process, the LDC seeks to ensure that development initiatives are inclusive, participatory, and sustainable.
Functions and Responsibilities of the Local Development Council
1. Formulating and adopting a Comprehensive Development Plan (CDP): The LDC is responsible for crafting a CDP that outlines the long-term development goals and strategies for the LGU. This plan serves as a blueprint for development programs, projects, and activities within the local community.
2. Coordination and monitoring of development programs: The LDC facilitates coordination among different government agencies, private organizations, and other stakeholders involved in the implementation of development projects. It also monitors the progress and impact of these programs to ensure their effectiveness.
3. Budgeting and resource allocation: The LDC plays a crucial role in the budgeting process by identifying priority programs and projects for funding. It ensures that resources are allocated efficiently and effectively to address the needs of the community.
4. Advocacy and mobilization: The LDC acts as an advocate for local development, promoting awareness and mobilizing support for various initiatives. It engages the community through consultations, workshops, and other activities to gather inputs and foster a sense of ownership among the constituents.
The Importance of Understanding the Local Development Council
Understanding the Local Development Council is essential for both LGUs and the general public. For LGUs, a comprehensive understanding of the LDC enables effective planning and governance. It allows them to align their development strategies with the needs and aspirations of the community, fostering sustainable growth and progress. For the public, familiarity with the LDC provides opportunities for active participation and engagement in local decision-making processes. It empowers individuals to contribute to shaping their communities and ultimately improve their quality of life.
In conclusion, the Local Development Council is a vital component of local governance under the Local Government Code. Its establishment and functions promote inclusive and participatory development at the grassroots level. By understanding the role of the LDC, LGUs and the general public can actively contribute to the growth and well-being of their communities.
Understanding the Core Purpose of the Local Government Code: An In-depth Analysis
Understanding the Core Purpose of the Local Government Code: An In-depth Analysis
Introduction:
The Local Government Code is a crucial piece of legislation that guides the operation and governance of local government units in the United States. It sets forth the powers, functions, and responsibilities of these local entities, ensuring efficient delivery of public services and fostering local development. To truly comprehend the Local Government Code and its impact, it is essential to delve into its core purpose. This article provides an in-depth analysis of the core purpose of the Local Government Code.
1. Devolution of Power:
The primary objective of the Local Government Code is to devolve power from the national government to local government units. This decentralization allows for more effective decision-making processes that are tailored to the specific needs and circumstances of local communities. By empowering local government units, the Local Government Code seeks to enhance local autonomy and promote democratic governance at the grassroots level.
2. Local Development:
Promoting local development is another central aspect of the Local Government Code. It recognizes that each local government unit possesses unique resources, potential, and challenges. The Code mandates the creation of Local Development Councils (LDCs) as a means to facilitate participatory and comprehensive development planning at the local level. LDCs serve as forums for collaboration among various stakeholders, including government officials, civil society organizations, and community members, to identify priorities, set goals, and strategize for sustainable development within their respective jurisdictions.
3. Fiscal Autonomy:
The Local Government Code also aims to provide local government units with fiscal autonomy. This means that they have the power to generate their own revenue through taxation, fees, charges, and other sources. By allowing local government units to have control over their finances, the Code empowers them to address local needs more efficiently and effectively.
4. Decentralization of Service Delivery:
Efficient delivery of public services is a key concern of the Local Government Code. It recognizes that the needs of communities can vary significantly, and local government units are better positioned to identify and address these needs. The Code delegates the responsibility for delivering basic services such as health, education, and infrastructure to the local government units. This decentralization not only ensures better service provision but also promotes accountability and responsiveness from local government officials.
Understanding the 5 Sectors of Corporate Data Privacy
Understanding the 5 Sectors of Corporate Data Privacy
In today’s digital age, data privacy has become a critical concern for corporations of all sizes and industries. Protecting sensitive information is not only essential for maintaining a company’s reputation and customer trust, but also for complying with various laws and regulations. To effectively safeguard corporate data, it is crucial to understand the 5 sectors of corporate data privacy.
1. Data Collection and Storage:
The first sector of corporate data privacy involves the collection and storage of data. Companies collect a vast amount of information from their customers, employees, and other stakeholders. This data may include personal identifiable information (PII), financial records, transaction history, and more. It is important to establish robust protocols for collecting, storing, and securing this data to prevent unauthorized access or breaches.
2. Data Processing and Usage:
Once data is collected and stored, it often goes through various processing stages within a company. Data processing involves activities such as analyzing, manipulating, and extracting insights from the collected information. However, it is crucial to ensure that these processes are conducted in compliance with applicable privacy laws and regulations. Companies must have proper consent mechanisms in place and adhere to data usage policies to respect individual privacy rights.
3. Data Transmission and Sharing:
The third sector of corporate data privacy focuses on the transmission and sharing of data. In today’s interconnected world, organizations frequently exchange data with partners, vendors, clients, and government agencies. It is essential to establish secure channels for transmitting data to prevent interception or unauthorized access. Additionally, companies must have clear policies and contracts in place when sharing data with third parties to protect against misuse or unauthorized disclosure.
4. Data Retention and Disposal:
Data retention refers to the practice of storing data for a specified period as required by law or business needs. Companies must have well-defined retention policies that outline how long different types of data should be retained. Once the retention period ends, it is crucial to dispose of the data securely to prevent unauthorized access or potential breaches. Proper data disposal methods include secure deletion, shredding physical documents, or using data destruction services.
5. Data Governance and Compliance:
The final sector of corporate data privacy revolves around data governance and compliance. This involves establishing a framework of policies, procedures, and controls to ensure the proper handling and protection of data. Data governance includes assigning responsibilities, conducting regular audits, and monitoring compliance with relevant laws and regulations. Compliance with industry-specific standards and regulations, such as the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) or the California Consumer Privacy Act (CCPA), is critical for avoiding penalties and maintaining trust with stakeholders.
In conclusion, understanding the 5 sectors of corporate data privacy is essential for any organization aiming to protect sensitive information effectively. By implementing robust procedures in data collection, processing, transmission, retention, and governance, companies can mitigate the risk of data breaches and safeguard the privacy of individuals. It is vital to stay informed about evolving privacy laws and regulations to ensure continued compliance and maintain a strong reputation in today’s data-driven business landscape.
Understanding the Local Government Code: A Guide to the Local Development Council
As a seasoned attorney in the U.S., it is crucial to stay up-to-date on all areas of the law, including local government codes. These codes play a vital role in governing the actions and decisions of local authorities, and having a comprehensive understanding of them is essential for any lawyer practicing in the realm of local government law.
One important aspect of local government codes is the establishment and functioning of the Local Development Council (LDC). The LDC is a crucial body that exists at the local level and is responsible for formulating development plans and policies within its jurisdiction. The purpose of the LDC is to ensure that development initiatives are implemented in a systematic and coordinated manner, taking into account the needs and aspirations of the local community.
To truly understand the workings of the LDC and its role in local governance, it is imperative to delve into the Local Government Code that governs its establishment and operation. The Local Government Code is a comprehensive statute that outlines the powers and responsibilities of local government units, including cities, municipalities, and provinces, in the United States.
To navigate through this code effectively, it is important to pay attention to several key provisions. Some important sections to consider include:
1. Article X: Local Development Councils: This section provides an in-depth understanding of the structure, composition, and functions of the LDC. It outlines the roles of various stakeholders, such as local government officials, sectoral representatives, and non-governmental organizations, in contributing to the development planning process.
2. Article XI: Administrative Organization: This section delves into the administrative structure of local government units and their relationship with the LDC. It explains how the local chief executive interacts with the LDC and provides guidance on the appointment and removal of LDC members.
3. Article XIII: Local Government Budget and Fiscal Administration: This section is essential for lawyers practicing in local government law, as it provides insights into the budgeting process and financial management of local government units. Understanding this section is crucial for comprehending the financial aspects of development planning and the role of the LDC in budget formulation.
To ensure accuracy and reliability, it is important to verify and contrast the information provided in this article with the actual Local Government Code. While this article aims to provide a comprehensive understanding of the Local Development Council and its legal framework, it is always advisable to refer directly to the relevant statutory provisions for precise interpretation and application.
In conclusion, staying up-to-date on the Local Government Code, particularly in relation to the establishment and functioning of the Local Development Council, is essential for any attorney practicing in the field of local government law. By familiarizing yourself with the relevant provisions, such as those mentioned above, you can confidently navigate the legal landscape and effectively advocate for your clients in matters involving local governance and development planning.
