Understanding the Hierarchy: Unveiling the Highest Source of Federal Law in the United States
Welcome to this informative article, where we will delve into the complex world of the hierarchy of federal law in the United States. Before we begin, it is important to note that while this article aims to provide a comprehensive overview, it is always wise to cross-reference with other authoritative sources or consult legal professionals for specific guidance.
Law is the bedrock of any society, providing structure and order. In the United States, this foundation is built upon a hierarchy of laws, with each level serving a distinct purpose. At the apex of this legal pyramid lies the highest source of federal law, wielding unparalleled authority and influence.
📋 Content in this article
1. The United States Constitution:
At the very pinnacle of the hierarchy stands the United States Constitution. This remarkable document, drafted by the Founding Fathers, embodies the fundamental principles upon which our nation is built. It establishes the structure of government, outlines the powers of its branches, and safeguards individual rights. The Constitution represents the supreme law of the land and any law inconsistent with its provisions is deemed unconstitutional.
2. Acts of Congress:
Just below the Constitution, we find Acts of Congress. These are laws passed by both houses of Congress (the Senate and the House of Representatives) and signed by the President. Acts of Congress cover a vast array of issues, such as civil rights, taxation, commerce, and national defense. They have the power to shape and influence our daily lives and carry significant weight within our legal system.
3. Treaties:
Treaties occupy a special place in our hierarchy, as they are agreements made between the United States and other nations. Negotiated by the President and consented to by two-thirds of the Senate, treaties address matters of global importance, such as trade, human rights, and international cooperation.
Understanding the Hierarchy of the USA Legal System: Exploring the Highest Source of Law
Understanding the Hierarchy: Unveiling the Highest Source of Federal Law in the United States
In the United States, the legal system is a complex web of laws and regulations that govern our society. To ensure clarity and consistency, the legal system follows a hierarchical structure, which means that certain laws hold greater authority than others. Understanding this hierarchy is crucial for anyone seeking to navigate the legal landscape effectively.
At the highest level of the legal system in the United States, we find the United States Constitution. The Constitution is the supreme law of the land and serves as the foundation for all other laws. It outlines the basic structure of our government, establishes fundamental rights for individuals, and sets limits on governmental power. As the ultimate authority, any law or action that contradicts the Constitution can be challenged and declared unconstitutional by the courts.
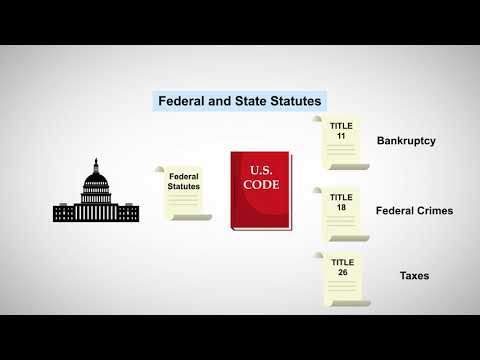
Below the Constitution, we have federal statutes, which are laws passed by Congress. These laws are created to address specific issues that fall under federal jurisdiction, such as interstate commerce, national defense, and civil rights. Federal statutes cover a wide range of topics and serve as an important source of law in the United States.
Next in line are federal regulations. These regulations are created by executive agencies to implement and enforce federal statutes. Executive agencies, such as the Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) or the Federal Communications Commission (FCC), have been granted authority by Congress to make rules and regulations within their respective areas of expertise. These regulations provide detailed guidance on how federal statutes should be interpreted and applied in practice.
Key Points:
Moving further down the hierarchy, we encounter state constitutions and state statutes.
Understanding the Hierarchy of Law in the United States
Understanding the Hierarchy of Law in the United States: Unveiling the Highest Source of Federal Law
In the United States, the legal system operates under a hierarchical structure, which means that laws are arranged in a specific order of authority. This hierarchy helps to ensure that conflicts between laws are resolved in a consistent and orderly manner. At the top of this hierarchy is the highest source of federal law, which holds the utmost authority in the legal system.
To better understand this hierarchical structure, it is important to grasp the concept that not all laws are created equal. Some laws carry more weight than others, and they are considered to be superior in authority. The hierarchy of law in the United States can be categorized into three main levels: constitutional law, statutory law, and administrative regulations.
1. Constitutional Law: At the pinnacle of this hierarchy lies the United States Constitution. The Constitution is the supreme law of the land, and all other laws must conform to its provisions. It establishes the fundamental principles and framework for governance in the United States. Any law that conflicts with the Constitution can be declared unconstitutional and therefore null and void.
2. Statutory Law: The second level of the hierarchy consists of statutes enacted by Congress. Statutory law includes federal laws passed by both houses of Congress and signed by the President. These laws cover a wide range of topics, such as criminal offenses, civil rights, taxation, and commerce. Statutory law can sometimes be influenced by constitutional principles and must align with them to remain valid.
3. Administrative Regulations: The third level of the hierarchy is made up of regulations promulgated by administrative agencies. These agencies are created by Congress to implement and enforce laws within specific areas. They have the authority to create regulations that carry the force of law.
Understanding the Hierarchy: Unveiling the Highest Source of Federal Law in the United States
In the complex world of U.S. law, it is crucial to stay current and knowledgeable about the hierarchy of federal law. The highest source of federal law holds significant importance in shaping the legal landscape of the United States. Whether you are an aspiring lawyer, a law student, or simply interested in understanding how laws are made and interpreted, grasping this concept is essential.
The hierarchy of federal law refers to the order of precedence that different sources of law hold. It determines which laws take precedence over others and helps establish legal authority and decision-making processes. At the top of this hierarchy is the United States Constitution, which is considered the supreme law of the land.
The United States Constitution:
The Constitution serves as the foundation upon which all other laws are built. It establishes the structure of the federal government and delineates its powers and limitations. Any law that contradicts the Constitution is considered unconstitutional and can be struck down by the courts. This document ensures that the government operates within defined boundaries and protects individual rights.
Federal Statutes:
Federal statutes are laws enacted by Congress. They cover a wide range of subjects, including criminal offenses, civil rights, taxation, and commerce. Statutes are passed through a deliberate legislative process, which involves both houses of Congress (the House of Representatives and the Senate) and requires presidential approval. Once signed into law, federal statutes are binding throughout the United States.
Regulations:
Regulations are rules created by administrative agencies to implement and enforce federal statutes. These agencies are authorized by Congress to make regulations within specific areas of expertise, such as the Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) or the Federal Communications Commission (FCC). While regulations may not carry the same weight as statutes, they play a significant role in shaping how laws are applied and enforced.
Case Law:
Case law, also known as common law or
