Greetings!
Today, we will embark on a journey to demystify the intricacies of understanding electricity billing for 500 units in Delhi. This subject may seem daunting at first, but fear not! By the end of this article, you will have a comprehensive understanding of how electricity billing works in this context.
📋 Content in this article
So, let’s dive in and unravel the mysteries of electricity billing for 500 units in Delhi!
Understanding Electricity Bill Calculation for 500 Units in Delhi
Understanding Electricity Billing for 500 Units in Delhi: A Detailed Explanation
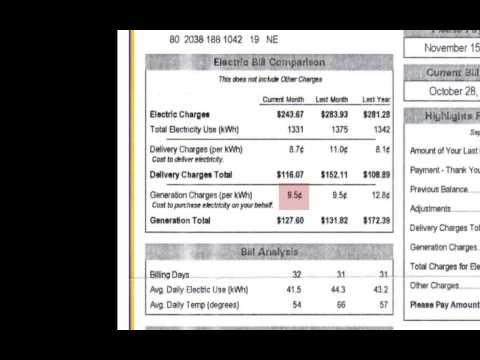
In Delhi, the calculation of electricity bills for residential consumers can often be confusing and puzzling. Many consumers struggle to understand how their bills are calculated and what factors contribute to the final amount. This article aims to provide a comprehensive explanation of how electricity bills for 500 units are calculated in Delhi.
Electricity consumption is measured in units, also known as kilowatt-hours (kWh). One unit is equivalent to one kilowatt-hour, which represents the amount of electricity consumed when a device with a power rating of one kilowatt is used for one hour. It is important to keep track of the number of units consumed to properly understand the billing process.
Electricity bills in Delhi consist of two main components – fixed charges and energy charges. Fixed charges are the cost associated with providing electricity infrastructure and services to consumers. These charges remain constant regardless of the amount of electricity consumed. It is important to note that fixed charges vary depending on the category of the consumer, such as domestic or commercial.
Energy charges are based on the actual units of electricity consumed. The rate per unit may vary depending on the slabs set by the electricity distribution company. In Delhi, the energy charges are typically divided into different slabs. As the consumption increases, the rate per unit may also increase.
To calculate the electricity bill for 500 units in Delhi, let’s assume there are three slabs:
– The first 100 units are charged at Rs. X per unit.
– The next 200 units are charged at Rs. Y per unit.
– Any units beyond 300 are charged at Rs. Z per unit.
To calculate the energy charges, we need to determine the consumption in each slab:
– First 100 units: 100 units x Rs. X per unit.
– Next 200 units: 200 units x Rs. Y per unit.
– Remaining 200 units: 200 units x Rs. Z per unit.
The total energy charges will be the sum of these three calculations.
Apart from the fixed charges and energy charges, electricity bills may also include taxes and other additional charges. These can vary based on government regulations and policies. It is important to carefully review the bill to understand the complete breakdown of charges.
To ensure accurate billing, it is crucial to keep track of the electricity meter readings. Consumers should regularly check their meter readings and compare them with the readings mentioned on the bill. Discrepancies should be reported to the electricity distribution company for rectification.
Understanding the Per Unit Charge of Electricity in Delhi: A Comprehensive Guide
Understanding Electricity Billing for 500 Units in Delhi: A Detailed Explanation
In Delhi, like in many other places, electricity consumption is measured and billed using a unit-based system. The per unit charge of electricity refers to the cost of each unit of electricity consumed. It is important to understand how this charge is calculated and how it affects your electricity bill.
Here is a comprehensive guide to help you understand the concept of per unit charge and how it applies to your electricity billing in Delhi:
1. What is a unit of electricity?
– A unit of electricity, also known as a kilowatt-hour (kWh), is a standard measurement of energy consumption.
– It represents the amount of energy consumed when a device with a power rating of one kilowatt (kW) operates for one hour.
2. How is the per unit charge determined?
– The per unit charge of electricity is determined by the electricity distribution company (DISCOM) in Delhi.
– DISCOMs take into account various factors such as generation costs, transmission costs, distribution costs, and regulatory charges when setting the per unit charge.
– The per unit charge may vary for different consumer categories, such as residential, commercial, and industrial.
3. Understanding the billing components:
– Fixed charges: Apart from the per unit charge, your electricity bill may also include fixed charges. These charges are a fixed amount that you have to pay regardless of your actual consumption.
– Energy charges: The energy charges are calculated by multiplying the number of units consumed by the per unit charge.
– Additional charges: Your bill may also include additional charges like taxes, levies, fuel surcharge, and other regulatory charges.
4. Calculating electricity bill for 500 units:
– To understand how the per unit charge affects your electricity bill, let’s consider an example of consuming 500 units of electricity.
– Suppose the per unit charge is ₹5.00 (hypothetical value) and there are no fixed charges or additional charges applied.
– In this case, the energy charges would be ₹5.00 x 500 units = ₹2,500.00.
5. Factors affecting the per unit charge:
– The per unit charge of electricity may vary from time to time based on factors such as fuel prices, inflation, government policies, and changes in the cost of generation and distribution.
– DISCOMs may revise the per unit charge periodically to reflect these factors and maintain a sustainable electricity supply.
Understanding the per unit charge of electricity is crucial for managing your electricity consumption and budgeting. By monitoring your usage and being aware of the per unit charge, you can make informed decisions to reduce your electricity bill.
Remember, it is always advisable to check the official website or contact your local DISCOM for the most up-to-date information on electricity tariffs and billing practices in Delhi.
What Happens if Electricity Consumption Exceeds 400 Units in Delhi?
Understanding Electricity Billing for 500 Units in Delhi: A Detailed Explanation
When it comes to electricity consumption, it is essential to understand how it affects your billing. In the city of Delhi, India, electricity billing follows a specific process. This article aims to provide a detailed explanation of electricity billing for 500 units in Delhi, highlighting the main factors that influence the final amount on your bill.
1. Electricity Consumption and Units:
– Electricity consumption is measured in units (kWh) and represents the amount of energy consumed by electrical appliances over a specific period.
– One unit is equivalent to consuming 1 kilowatt of power for one hour.
2. The Slab System:
– In Delhi, electricity consumption is divided into slabs, with each slab having a different rate per unit.
– The slab system encourages efficient electricity usage by charging higher rates for higher consumption.
3. Slab Rates for Domestic Consumers:
– For domestic consumers in Delhi, the current slab rates are as follows:
– Up to 200 units: Rs. X per unit (for example)
– 201-400 units: Rs. Y per unit (for example)
– 401-800 units: Rs. Z per unit (for example)
– Above 800 units: Rs. A per unit (for example)
4. Calculating the Bill:
– To understand how your bill is calculated, let’s consider a consumption of 500 units.
– The first 200 units will be charged at the rate of Rs. X per unit.
– The subsequent 200 units (201-400) will be charged at the rate of Rs. Y per unit.
– The remaining 100 units (401-500) will be charged at the rate of Rs. Z per unit.
– Add up these charges to determine the total amount for the consumption of 500 units.
5. Additional Charges:
– Apart from the slab rates, your electricity bill may include other charges, such as:
– Fixed charges: A monthly fee for the connection.
– Electricity duty: A percentage of the total bill amount.
– Taxes: Applicable taxes imposed by the government.
– Meter rent: In some cases, a rental fee for the electricity meter.
6. Tips for Efficient Consumption:
– To reduce your electricity bill, consider implementing these energy-saving practices:
– Use energy-efficient appliances.
– Turn off lights and appliances when not in use.
– Opt for natural lighting during the day.
– Insulate your home to minimize heat loss or gain.
– Regularly maintain and clean your electrical appliances.
By understanding the concept of electricity billing for 500 units in Delhi, you can gain better control over your consumption and effectively manage your electricity expenses. It is always advisable to review your bill carefully and reach out to the relevant authorities or experts for any clarification or assistance you may need.
Understanding Electricity Billing for 500 Units in Delhi: A Detailed Explanation
Staying up-to-date on the topic of electricity billing is crucial, as it directly affects individuals and businesses alike. In this article, we will dive into the intricacies of understanding electricity billing for 500 units in Delhi, providing a detailed explanation of the process. However, it is important to remember that laws and regulations regarding electricity billing can vary by jurisdiction and may be subject to change. Therefore, readers should always verify and contrast the information provided in this article with the relevant local authorities or utility companies.
1. Electricity Units: Electricity consumption is measured in units (kWh). A unit represents the amount of electrical energy consumed within a specific period.
2. Electricity Tariffs: Tariffs are the rates at which electricity is charged. They can vary depending on the consumer category (residential, commercial, industrial) and the level of consumption. Tariffs may include charges for energy consumption, fixed charges, fuel surcharges, taxes, and other fees.
3. 500 Units: When we refer to 500 units, we are discussing the amount of electricity consumed during a particular billing cycle. It is essential to monitor your consumption to understand your usage patterns and anticipate your bill.
4. Fixed Charges: Fixed charges are a set amount that consumers have to pay regardless of their actual electricity consumption. These charges cover the fixed costs incurred by utility companies to maintain infrastructure and provide essential services.
5. Energy Charges: Energy charges are calculated based on the number of units consumed during a billing cycle. Different slabs or tiers may exist, where the rate per unit increases as consumption levels rise.
6. Fuel Surcharge: Fuel surcharges are additional charges levied to compensate for fluctuations in the cost of fuel used to generate electricity. These charges are subject to change as fuel prices fluctuate.
7. Taxes and Other Fees: Electricity bills often include various taxes and fees imposed by the government or regulatory bodies. These charges may include GST (Goods and Services Tax), electricity duty, and others.
8. Peak and Off-Peak Hours: Some utility companies have different rates for electricity consumed during peak and off-peak hours. Peak hours are typically times when electricity demand is high, such as evenings or weekends. Understanding your utility company’s peak and off-peak hours can help you plan your electricity usage more efficiently.
9. Meter Readings: Meter readings are taken periodically to measure the units of electricity consumed. It is crucial to keep track of these readings and ensure they are accurate, as they directly impact your bill.
10. Billing Cycle: The billing cycle refers to the period for which your electricity consumption is calculated. It can vary from monthly to quarterly, depending on your region and utility company.
To fully understand electricity billing for 500 units in Delhi, it is essential to review the specific tariff structure provided by the utility company serving your area. The tariff structure will outline the charges for different components, such as fixed charges, energy charges, fuel surcharge, and taxes.
Remember, this article serves as a general guide and should not replace verifying the information with reliable sources or seeking professional advice.
