Understanding the Ecodesign for Energy-Related Products Regulations 2010: A Comprehensive Overview
Greetings,
📋 Content in this article
In this article, we will dive into the realm of the Ecodesign for Energy-Related Products Regulations 2010. These regulations are designed to promote energy efficiency and environmental sustainability in the European Union (EU). While I am not a specialist in EU law, I will provide you with a comprehensive overview of the key concepts and principles involved in these regulations.
1. What is Ecodesign?
Ecodesign is an approach that aims to integrate environmental considerations into the design and development of products. The goal is to reduce the environmental impact of products throughout their entire lifecycle, from raw material extraction to disposal.
2. Energy-Related Products (ErPs)
Energy-Related Products refer to a wide range of goods that have an impact on energy consumption during their use. This includes appliances such as refrigerators, washing machines, and televisions, as well as heating systems, ventilation units, and insulation materials.
3. The Ecodesign Directive
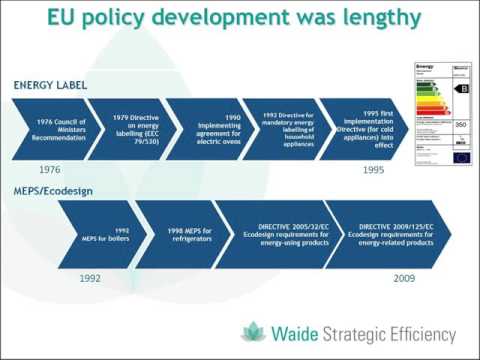
The Ecodesign for Energy-Related Products Regulations 2010 is based on the Ecodesign Directive (Directive 2009/125/EC). This directive establishes a framework for setting eco-design requirements for energy-related products in the EU market.
4. Key Objectives
The primary objectives of the Ecodesign Regulations are to:
– Improve the energy efficiency of products.
– Promote the use of renewable energy.
– Reduce greenhouse gas emissions.
– Enhance resource efficiency.
– Encourage technological innovation.
5. Scope of Application
The Ecodesign Regulations apply to specific product groups that have a significant impact on energy consumption and the environment in the EU market. These product groups are identified and prioritized based on their potential for energy savings and their environmental impact.
6. Minimum Efficiency Requirements
The Ecodesign Regulations set minimum efficiency requirements that energy-related products must meet to be placed on the EU market. These requirements are periodically updated to reflect technological advancements and changes in environmental priorities.
7. Standardization and Testing
To ensure compliance with the Ecodesign Regulations, standardized testing methods and measurement procedures are established. These methods allow for accurate and consistent assessment of product performance and energy efficiency.
8. Energy Labels
Energy labels provide consumers with information about the energy efficiency and performance of products. These labels use a standardized scale and symbols to make it easier for consumers to compare different products and make informed choices.
9. Market Surveillance
Member States of the EU are responsible for market surveillance, ensuring that energy-related products comply with the Ecodesign Regulations. They carry out inspections and take appropriate measures to address non-compliant products.
10. Benefits and Impacts
The Ecodesign Regulations have several benefits, including:
– Energy savings and reduced energy costs.
– Environmental protection and reduced greenhouse gas emissions.
– Improved product quality and performance.
– Enhanced competitiveness and innovation in the market.
In conclusion, the Ecodesign for Energy-Related Products Regulations 2010 plays a vital role in promoting energy efficiency and environmental sustainability in the EU. By setting minimum efficiency requirements, establishing standardized testing methods, and providing energy labels, these regulations empower consumers to make informed choices and drive innovation in the market.
Please note that this overview is intended to provide general information and should not be considered legal advice. It is always recommended to consult with a qualified legal professional for specific guidance on compliance with the Ecodesign Regulations or any other legal matter.
Thank you for reading.
Understanding the Ecodesign for Energy-Related Products Regulations 2010: An In-Depth Overview
Understanding the Ecodesign for Energy-Related Products Regulations 2010: A Comprehensive Overview
The Ecodesign for Energy-Related Products Regulations 2010 is a set of regulations enacted in the United States with the aim of promoting energy efficiency and reducing the environmental impact of energy-related products. These regulations are an important tool in the government’s efforts to address climate change and achieve sustainability goals.
1. What are Ecodesign Regulations?
Ecodesign regulations set mandatory requirements for the design and performance of energy-related products. These regulations are applicable to a wide range of products, including household appliances, heating and cooling equipment, lighting products, and industrial machinery. The goal is to ensure that these products are produced and operated in a more environmentally friendly manner.
2. How do Ecodesign Regulations work?
Ecodesign regulations specify minimum energy efficiency requirements that products must meet in order to be sold on the market. These requirements are aimed at reducing energy consumption, minimizing greenhouse gas emissions, and promoting resource efficiency. The regulations also cover other aspects such as product labeling, information provision, and conformity assessment procedures.
3. Benefits of Ecodesign Regulations
The Ecodesign for Energy-Related Products Regulations 2010 brings several benefits for both consumers and the environment. By requiring manufacturers to produce more energy-efficient products, these regulations help consumers save on their energy bills while reducing their carbon footprint. Additionally, they foster innovation and promote the development of new technologies that are more sustainable.
4. Key provisions of the Ecodesign for Energy-Related Products Regulations 2010
The Ecodesign for Energy-Related Products Regulations 2010 encompasses various provisions that contribute to its comprehensive nature. Some of the key provisions include:
5. Role of attorneys in Ecodesign Compliance
Attorneys play a crucial role in helping businesses understand and comply with the Ecodesign for Energy-Related Products Regulations 2010. They provide legal advice and guidance on the complex requirements of the regulations, assist in reviewing and drafting compliance documentation, and represent clients in regulatory proceedings or enforcement actions.
In conclusion, the Ecodesign for Energy-Related Products Regulations 2010 is a comprehensive set of regulations aimed at promoting energy efficiency and reducing the environmental impact of energy-related products. These regulations have a wide-ranging impact on manufacturers, consumers, and the environment, and attorneys play a vital role in ensuring compliance and helping businesses navigate the complexities of these regulations.
Understanding the Ecodesign Directive: A Comprehensive Overview for Energy-related Products
Understanding the Ecodesign for Energy-Related Products Regulations 2010: A Comprehensive Overview
The Ecodesign for Energy-Related Products (ErP) Regulations 2010 is a set of laws implemented in the European Union (EU) with the goal of reducing the environmental impact of energy-related products. These regulations are important for businesses and consumers alike to understand, as they have a significant impact on the design, manufacturing, and sale of various products.
What are Energy-Related Products?
Energy-related products, as defined by the ErP Regulations, include a wide range of goods used for energy consumption or energy-saving purposes. This includes household appliances (e.g., refrigerators, washing machines), heating and cooling systems, lighting products, computers, and televisions, among others. The ErP Regulations aim to improve the energy efficiency and environmental performance of these products.
The Objectives of the ErP Regulations
The primary objective of the ErP Regulations is to reduce the overall energy consumption and environmental impact of energy-related products throughout their lifecycle. This is achieved by setting specific requirements and standards for product design, energy efficiency, labeling, and information provision.
Product Requirements and Standards
Under the ErP Regulations, manufacturers and suppliers are obligated to comply with specific requirements and standards for energy-related products. These requirements typically relate to energy efficiency, standby power consumption, noise levels, and other environmental aspects. Compliance with these standards ensures that products on the market meet certain minimum efficiency criteria.
Energy Labels
One key aspect of the ErP Regulations is the requirement for energy labeling. Products covered by the regulations must display an energy label that provides consumers with information on their energy efficiency rating. These labels help consumers make informed choices by comparing the energy efficiency of different products.
Information Provision
In addition to energy labeling, the ErP Regulations also require manufacturers and suppliers to provide consumers with relevant product information. This includes information on energy consumption, performance, and features that may affect energy efficiency. By providing this information, consumers can make more informed decisions based on their energy-saving needs.
The Role of Market Surveillance
To ensure compliance with the ErP Regulations, market surveillance authorities monitor the market and enforce the requirements. They have the power to conduct inspections, carry out tests, and take appropriate measures against non-compliant products or businesses. Market surveillance is crucial in maintaining a level playing field and ensuring the effectiveness of the regulations.
Impact on Businesses and Consumers
The ErP Regulations have a significant impact on both businesses and consumers. For manufacturers and suppliers, compliance with the regulations is mandatory to legally market their products in the EU. Non-compliance can result in penalties, product recalls, or even loss of market access. For consumers, the regulations provide valuable information to make informed choices about energy-related products that are both efficient and environmentally friendly.
In conclusion, the Ecodesign for Energy-Related Products Regulations 2010 play a vital role in promoting energy efficiency and reducing the environmental impact of energy-related products in the EU. Understanding these regulations is crucial for businesses operating in the EU market and for consumers seeking energy-efficient products. Compliance with the regulations ensures that products meet minimum efficiency criteria and helps consumers make informed choices for a greener future.
Understanding Ecodesign Regulations: A Comprehensive Guide
Understanding the Ecodesign for Energy-Related Products Regulations 2010: A Comprehensive Overview
Introduction:
The Ecodesign for Energy-Related Products (ERP) Regulations 2010 is an important legislation in the field of environmental protection and energy efficiency. These regulations were created by the European Union (EU) with the aim of reducing the environmental impact of energy-related products throughout their lifecycle. This comprehensive overview will provide you with a clear understanding of the ERP Regulations and its significance.
Key Objectives:
The ERP Regulations have two main objectives:
Scope of the Regulations:
The ERP Regulations cover a wide range of energy-related products, including but not limited to:
Compliance Requirements:
To comply with the ERP Regulations, manufacturers must meet certain requirements, such as:
Benefits:
Complying with the ERP Regulations offers several benefits, including:
Enforcement and Penalties:
The enforcement of the ERP Regulations lies with national authorities within each EU member state. Non-compliance can result in penalties, including fines and the removal of non-compliant products from the market.
Understanding the Ecodesign for Energy-Related Products Regulations 2010: A Comprehensive Overview
As a seasoned attorney in the United States, I understand the importance of staying up-to-date on various legal topics to effectively advise clients and navigate the complex legal landscape. One such area that warrants attention is the Ecodesign for Energy-Related Products Regulations 2010. This comprehensive regulatory framework governs the energy efficiency requirements for a wide range of products sold in the European Union (EU).
The Ecodesign for Energy-Related Products Regulations 2010 aims to promote energy efficiency, reduce greenhouse gas emissions, and enhance environmental protection. It establishes minimum energy efficiency standards for a diverse array of products, including household appliances, lighting products, heating and cooling equipment, and many others.
It is crucial for attorneys and legal professionals to have a firm grasp of these regulations for several reasons. Firstly, businesses operating in the EU or exporting products to EU member states must comply with these requirements. Failure to do so can result in legal consequences, including fines and restrictions on market access.
Secondly, understanding these regulations enables attorneys to assist clients in complying with their obligations and avoiding potential legal pitfalls. By staying informed about the latest developments and amendments to the regulations, attorneys can provide accurate advice on compliance strategies, product labeling requirements, and potential energy efficiency improvements.
Furthermore, familiarity with the Ecodesign for Energy-Related Products Regulations 2010 allows attorneys to advise on potential business opportunities and risks. They can help clients identify innovative ways to enhance energy efficiency in their products, which can result in cost savings and increased market competitiveness.
To fully comprehend the Ecodesign for Energy-Related Products Regulations 2010, attorneys should consult primary sources such as the official EU legislation website or reliable legal databases. These sources provide detailed information on the scope of the regulations, product-specific requirements, and any updates or amendments.
It is essential to remember that laws and regulations can evolve over time. Attorneys should regularly verify the accuracy and currency of the information they rely on by referring to official sources and consulting with trusted experts or colleagues. Additionally, it is crucial to compare and contrast information from multiple sources to ensure a comprehensive understanding of the regulations and their practical implications.
In conclusion, staying up-to-date on the Ecodesign for Energy-Related Products Regulations 2010 is crucial for attorneys practicing in or advising clients operating in the European Union. Familiarity with these regulations enables attorneys to provide accurate advice on compliance, identify business opportunities, and mitigate potential risks. However, it is important to verify the information and consult reliable sources to ensure the accuracy and currency of the content.
