Hello readers,
Welcome to this informative article where we will be diving into the fascinating world of legal terminology. In particular, we will explore the distinction between two important concepts: Mens Rea and Actus Reus.
📋 Content in this article
Mens Rea and Actus Reus are Latin terms that are commonly used in the field of law to describe different elements of a crime. Understanding these concepts is crucial for anyone studying or practicing law, as they form the foundation for criminal liability.
1. Mens Rea:
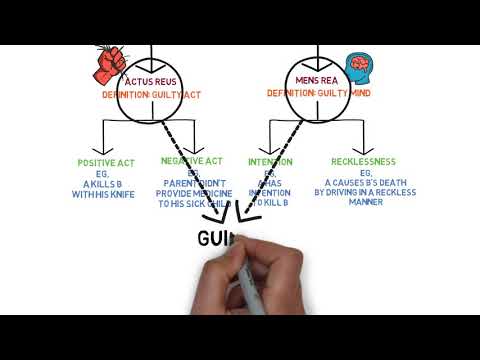
Mens Rea, loosely translated as “guilty mind,” refers to the mental state or intention of an individual when committing a crime. It focuses on the mental element of an offense and seeks to ascertain whether the accused had the necessary intention, knowledge, or recklessness to commit the crime.
Mens Rea is divided into different levels based on the degree of intention or knowledge involved. These levels include:
– Intention: This is the highest level of Mens Rea and involves a deliberate desire to bring about a specific result. For example, if someone intentionally causes harm to another person, they have committed a crime with intent.
– Knowledge: This level of Mens Rea involves the awareness that one’s actions will likely result in a certain outcome. For instance, if someone knows that their reckless driving could potentially harm others, they may be held criminally liable for their actions.
– Recklessness: Recklessness refers to consciously disregarding a substantial and unjustifiable risk. If someone acts with reckless disregard for the safety of others and causes harm, they may be held accountable under this level of Mens Rea.
– Negligence: Negligence is a lower level of Mens Rea that focuses on a lack of reasonable care. If someone fails to exercise the care that a reasonable person would in a similar situation and causes harm, they may be held legally responsible.
2. Actus Reus:
Actus Reus, meaning “guilty act,” refers to the physical act or conduct that constitutes a crime. It concentrates on the external and observable elements of an offense, such as actions, omissions, or a specific state of affairs.
To establish criminal liability, it is generally required to prove both Mens Rea and Actus Reus. In other words, it must be shown that the accused had the necessary mental element (Mens Rea) and also engaged in the prohibited conduct (Actus Reus).
It is important to note that not every act committed with Mens Rea is necessarily a crime. Certain defenses, such as self-defense or necessity, can negate criminal liability even if the accused had the requisite Mens Rea and Actus Reus.
In conclusion, understanding the distinction between Mens Rea and Actus Reus is critical in the field of law. While Mens Rea focuses on the mental state or intention of an individual, Actus Reus refers to the physical act or conduct that constitutes a crime. Both elements are essential in determining criminal liability.
Thank you for joining us on this exploration of legal terminology. We hope this article has shed some light on these important concepts.
Understanding the Distinction: Actus Reus vs. Mens Rea
Understanding the Distinction: Mens Rea vs. Actus Reus in Legal Terminology
In the field of law, it is essential to have a clear understanding of certain concepts and terminologies. One such distinction that holds great significance is between Mens Rea and Actus Reus. These Latin terms are often used in criminal law to differentiate between the mental element and the physical act of a crime. Let’s dive deeper into these two concepts to gain a better understanding of their importance and how they are applied in legal proceedings.
Mens Rea, which translates to “guilty mind,” refers to the mental state or intention of an individual when committing a crime. It focuses on the mindset of the person accused of the offense. Mens Rea is crucial in determining criminal liability as it establishes whether the accused had the necessary mental state to commit the crime. It helps differentiate between accidental conduct and intentional wrongdoing.
There are various levels or degrees of Mens Rea, depending on the jurisdiction and the specific offense in question. Some common types of Mens Rea include:
On the other hand, Actus Reus, meaning “guilty act,” refers to the physical act or conduct that constitutes a crime. It focuses on the external behavior of the accused rather than their mental state. Actus Reus encompasses all elements of a criminal offense that are not related to the accused’s state of mind, such as the actual physical act, omission, or possession of prohibited items.
To establish guilt, it is generally necessary to prove both Mens Rea and Actus Reus. The prosecution must demonstrate that the accused not only committed the physical act (Actus Reus) but also possessed the requisite mental state (Mens Rea) at the time of the offense. This principle ensures that individuals are not held criminally liable solely based on their thoughts or intentions without any corresponding criminal behavior.
Understanding the distinction between Mens Rea and Actus Reus is crucial in criminal law as it helps shape legal principles surrounding culpability, punishment, and defenses. It allows for a fair and balanced assessment of criminal conduct and ensures that individuals are held accountable for their actions while considering their mental state at the time.
In conclusion, Mens Rea and Actus Reus are fundamental concepts in criminal law that play a significant role in determining criminal liability. Mens Rea focuses on the mental element or intention of the accused, while Actus Reus relates to the physical act or conduct constituting a crime. Both elements must be proven to establish guilt beyond a reasonable doubt. By understanding these distinctions, individuals can navigate the complexities of criminal law with greater clarity and comprehension.
Understanding the 4 Essential Components of Mens Rea in Legal Contexts
Understanding the Distinction: Mens Rea vs Actus Reus in Legal Terminology
In legal terminology, two essential elements form the foundation of criminal liability: mens rea and actus reus. While both concepts are crucial in determining a person’s guilt or innocence, it is important to understand their distinct roles and how they interact within the legal system.
Mens rea, Latin for “guilty mind,” refers to the mental state or intent of the accused at the time the offense was committed. It focuses on the defendant’s state of mind and whether they possessed the necessary mental elements required to commit a particular crime. Mens rea can vary depending on the specific offense and is generally categorized into four components:
1. Intention: This component involves a deliberate desire or purpose to engage in conduct that is prohibited by law. It applies when a person acts with the conscious objective of achieving a particular result.
2. Knowledge: Knowledge refers to the awareness that certain circumstances exist or that certain consequences will occur as a result of one’s actions. It implies that the defendant was aware of the nature and probable consequences of their conduct.
3. Recklessness: Recklessness occurs when an individual disregards a substantial and unjustifiable risk that their actions may cause harm to others. It involves consciously taking a chance that harm will result from one’s conduct.
4. Negligence: Negligence refers to the failure to exercise reasonable care in one’s actions or omissions, resulting in harm to another person. It involves a departure from the standard of care that a reasonable person would exercise in similar circumstances.
In contrast, actus reus, meaning “guilty act” in Latin, focuses on the physical element of a crime. It refers to the actual conduct or behavior that constitutes the offense. Actus reus includes both affirmative acts and certain omissions that are legally required to establish criminal liability.
To secure a conviction, the prosecution must establish beyond a reasonable doubt both the mens rea and actus reus of the crime. This means proving that the accused not only committed the prohibited act but also possessed the required mental state.
It is important to note that different crimes require different levels of mens rea. Some offenses, such as murder, may require a higher level of intent, while other offenses, such as strict liability crimes, may not require any specific mental state. Understanding these distinctions is crucial in mounting an effective defense or evaluating the strength of the prosecution’s case.
In conclusion, mens rea and actus reus are essential components in criminal law. While mens rea focuses on the mental state or intent of the accused, actus reus pertains to the physical act or behavior that constitutes the offense. Both elements must be proven beyond a reasonable doubt to establish criminal liability.
Understanding Actus Reus and Mens Rea: When Two Legal Elements Unite
Understanding the Distinction: Mens Rea vs Actus Reus in Legal Terminology
In the field of law, there are two crucial elements that a prosecutor must establish beyond a reasonable doubt in order to prove that a person has committed a crime. These elements are known as actus reus and mens rea. Although they may sound complex, understanding their meanings is essential for comprehending the different aspects of criminal liability.
1. Actus Reus: The term ‘actus reus’ derives from Latin and translates to “guilty act” or “wrongful act.” It refers to the physical element or conduct of a crime. In other words, actus reus focuses on the external actions or behavior of an individual that is deemed illegal under the law. To establish actus reus, the prosecution must prove that the defendant committed a voluntary act or omission that resulted in harm or violated a legal duty.
2. Mens Rea: Similarly, ‘mens rea,’ also originating from Latin, means “guilty mind” or “criminal intent.” This concept centers on the mental state or intention of the perpetrator at the time of committing the criminal act. Mens rea emphasizes the moral culpability of an individual, as it seeks to determine whether they had the necessary mental state to commit the crime. This mental state can range from intentionally causing harm to acting recklessly or negligently.
It is important to note that not all crimes require both actus reus and mens rea. Some offenses, known as strict liability crimes, only require proof of the guilty act without any consideration of the defendant’s mental state. These typically involve offenses that are considered inherently dangerous or involve public welfare, such as traffic violations or certain environmental regulations.
However, most crimes do require the presence of both actus reus and mens rea. The combination of these two elements demonstrates the complete criminal liability of an individual. To illustrate this, let’s consider an example of a theft crime:
Example: John takes his neighbor’s bicycle without permission. He knows it belongs to his neighbor but takes it anyway, intending to use it temporarily. In this scenario, the actus reus is John physically taking the bicycle without permission. The mens rea is John’s knowledge that he is taking someone else’s property without authorization, which indicates his intent to commit the crime.
To convict John of theft, the prosecution would need to prove both elements. They would have to establish that John physically took the bicycle (actus reus) and that he knew it belonged to his neighbor and still took it (mens rea).
In summary, actus reus and mens rea are crucial concepts in the field of criminal law. Actus reus focuses on the physical actions or omissions that constitute a crime, while mens rea deals with the mental state or intention of the perpetrator. Understanding these elements is essential for comprehending criminal liability and determining whether a person can be held accountable for their actions.
Understanding the Distinction: Mens Rea vs Actus Reus in Legal Terminology
Introduction:
Legal terminology can be complex and understanding the nuances of different concepts is crucial for practicing law. Two important terms that often come up in criminal law cases are ‘Mens Rea’ and ‘Actus Reus’. These Latin phrases refer to the mental state and the physical act, respectively, required to establish criminal liability. It is essential for attorneys to have a clear understanding of these terms, as they play a significant role in determining guilt or innocence.
The Distinction:
1. Mens Rea:
Mens Rea refers to the mental state or intention of the person accused of a crime. It is derived from the Latin phrase “guilty mind” and focuses on the state of mind at the time the crime was committed. Mens Rea encompasses various mental states, ranging from purposefully intending to commit a crime to acting with negligence or recklessness. The specific mens rea required for a particular offense varies depending on the jurisdiction and the elements of the crime.
2. Actus Reus:
Actus Reus, on the other hand, refers to the physical act or conduct that constitutes a crime. Derived from the Latin phrase “guilty act,” actus reus involves any voluntary bodily movement that results in a prohibited outcome. It is important to note that not all acts are considered criminal, and actus reus must satisfy the elements outlined in the relevant statute or common law.
The Importance of Understanding the Distinction:
Understanding the distinction between mens rea and actus reus is vital for practicing attorneys for several reasons:
1. Building a Strong Defense:
Knowledge of mens rea and actus reus allows attorneys to craft a robust defense strategy for their clients. By analyzing the mental state and physical actions involved in a case, attorneys can identify weaknesses in the prosecution’s arguments and present counterarguments effectively.
2. Assessing Criminal Liability:
Different crimes require different levels of mens rea, and understanding these distinctions enables attorneys to evaluate the strength of the prosecution’s case. It allows them to determine whether their client’s mental state aligns with the required mens rea for the offense charged, potentially leading to reduced charges or acquittal.
3. Navigating Legal Precedents:
Familiarity with the concepts of mens rea and actus reus is essential for comprehending legal precedents and case law. Many court decisions hinge on the interpretation and application of these two terms. Lawyers who stay up-to-date on relevant cases can use them as persuasive authority to support their arguments.
Verifying and Contrasting Information:
While this article provides a general explanation of mens rea and actus reus, it is crucial for readers to independently verify and contrast the information provided with authoritative legal sources. The application of these concepts may vary based on jurisdiction and specific circumstances. Consulting legal texts, statutes, case law, and seeking advice from legal professionals will ensure a comprehensive understanding of these concepts.
Conclusion:
Understanding the distinction between mens rea and actus reus is vital for attorneys practicing in the criminal law domain. By grasping these fundamental concepts, attorneys can build robust defenses, assess criminal liability accurately, and navigate legal precedents effectively. Staying up-to-date on relevant case law and consulting reliable legal sources will further enhance their understanding and application of these concepts.
