Greetings!
Today, we will delve into the topic of ‘Understanding the Distinctions: EU Directive vs Regulation’. As a seasoned attorney, I aim to provide you with a clear and informative explanation of these two important legal concepts.
📋 Content in this article
EU Directive:
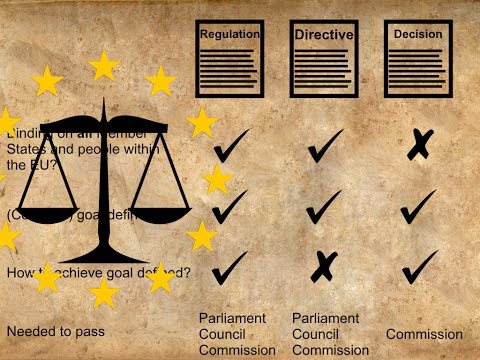
An EU Directive is a legislative act issued by the European Union that sets out specific objectives for member states to achieve within a given timeframe. It provides guidance and outlines the general principles that need to be implemented into national laws. However, it does not automatically become law in member states. Each member state is given flexibility in how they implement the Directive into their own legal system.
Here are a few key points about EU Directives:
EU Regulation:
On the other hand, an EU Regulation is a binding legislative act that applies directly to all member states. Unlike Directives, Regulations do not require further implementation into national law. They are automatically applicable and enforceable as soon as they come into effect.
Here are a few key points about EU Regulations:
Distinguishing Between EU Directives and Regulations:
To summarize, the main distinction between EU Directives and Regulations lies in their legal nature and the way they affect member states. Directives provide guidelines for member states to achieve specific objectives, granting them flexibility in implementation, while Regulations are directly applicable and binding in their entirety.
It is important to note that both Directives and Regulations play a crucial role in shaping the legal framework within the European Union. They contribute to the harmonization of laws among member states and facilitate cooperation and coordination within the EU.
I hope this article has shed some light on the distinctions between EU Directives and Regulations. Should you have any further questions or require legal advice specific to your situation, it is recommended to consult with a qualified legal professional.
Best regards,
[Your Name]
Seasoned U.S.
Understanding the Distinction: EU Directive vs. EU Regulation
Understanding the Distinction: EU Directive vs. EU Regulation
When navigating the complexities of European Union (EU) law, it is crucial to understand the distinctions between an EU Directive and an EU Regulation. While both are legislative acts that have binding legal force, they differ in their scope, applicability, and implementation.
EU Directive:
1. Scope: An EU Directive sets out the objectives that EU member states must achieve within a certain timeframe. It provides a framework for national legislation by establishing the desired results, leaving the specific means of achieving those results to each member state.
2. Applicability: Directives are addressed to member states, requiring them to adopt national legislation that complies with the directive’s objectives. Member states have discretion regarding the form and methods of implementation.
3. Implementation: Member states typically have a certain amount of time, usually a few years, to transpose an EU Directive into their national laws. During this period, member states can adapt the directive’s provisions to their legal systems, taking into account their specific circumstances.
One important aspect of directives is that they do not have direct effect. This means that individuals and businesses cannot rely on directives alone to claim rights or challenge actions before national courts. However, if a member state fails to implement a directive within the prescribed timeframe, individuals may be able to rely on the directive against the state itself.
EU Regulation:
1. Scope: An EU Regulation is a law that applies directly and uniformly across all EU member states without the need for national legislation. It is immediately binding and becomes part of the national legal systems of member states.
2. Applicability: Regulations are addressed to individuals, businesses, and public authorities within the EU. They are self-executing and do not require any additional steps for implementation at the national level.
3. Implementation: Member states do not have discretion when it comes to implementing EU regulations. They are obliged to apply the regulation as it is and cannot modify its provisions or deviate from them.
Regulations have direct effect, which means that individuals can rely on them before national courts to claim their rights or challenge actions that violate the regulation. This is because regulations are directly applicable, complete, and do not need further action from member states.
Understanding the distinction between an EU Directive and an EU Regulation is essential for individuals and businesses operating within the EU. It enables them to navigate the legal landscape effectively, ensuring compliance with applicable laws and benefiting from the rights and obligations established by EU legislation.
In summary, while both EU Directives and EU Regulations have binding legal force, directives require member states to achieve certain objectives through national legislation, whereas regulations directly apply to individuals and businesses without the need for additional implementation measures. Being aware of these distinctions allows individuals and businesses to make informed decisions and effectively engage with EU law.
Understanding the Distinction between a Standard and a Directive: An In-depth Comparison
Understanding the Distinctions: EU Directive vs Regulation
In the European Union (EU), directives and regulations are two important types of legislative instruments. While both aim to harmonize laws across member states, there are distinct differences between them. This article will provide an in-depth comparison of EU directives and EU regulations, highlighting their unique features and implications.
EU Directive:
1. Purpose: A directive is a legal instrument that sets out certain objectives to be achieved by member states within a specified timeframe.
2. Implementation: Member states are responsible for implementing directives into their national laws, which allows for flexibility in adapting the legislation to fit their specific legal systems.
3. Result: Once a directive is implemented, it becomes binding as national law in each member state, but the form and methods of implementation can vary between countries.
4. Flexibility: Member states have some discretion in how they achieve the directive’s objectives, which can lead to variations in the laws across the EU.
5. Timing: Directives typically provide a deadline for implementation, giving member states time to make necessary adjustments to their domestic legislation.
EU Regulation:
1. Purpose: A regulation is a legislative act that is directly applicable and binding on all member states, without the need for national implementation.
2. Implementation: Regulations are automatically enforceable as soon as they come into force, and member states are obliged to apply them uniformly without any modifications.
3. Result: Regulations have a direct effect, meaning they create rights and obligations for individuals and organizations throughout the EU.
4. Uniformity: Unlike directives, regulations ensure a higher degree of harmonization because they are uniformly applied across all member states.
5. Timing: Regulations usually come into force on a specific date specified within the regulation itself.
Key Differences:
1. Legal Nature: The main distinction between a directive and a regulation lies in their legal nature. Directives require national implementation, while regulations are directly applicable.
2. Flexibility: Directives provide member states with some discretion in implementation, allowing them to adapt the legislation to their national legal systems. Regulations, on the other hand, are binding and enforceable without modifications.
3. Uniformity: Regulations ensure uniform application across the EU, while directives may result in variations in national laws due to implementation differences.
4. Timing: Directives set deadlines for implementation, providing member states with a certain timeframe for compliance. Regulations come into force on a specified date mentioned within the regulation itself.
Understanding EU Directives: An In-Depth Explanation and Interpretation
Understanding the Distinctions: EU Directive vs Regulation
The European Union (EU) is a supranational organization comprised of member states that have come together to establish a common framework for economic and political cooperation. One of the key instruments used by the EU to achieve its objectives is legislation, which is enacted in the form of EU Directives and EU Regulations. While both Directives and Regulations serve as legislative instruments of the EU, they differ in terms of their legal nature and the manner in which they are implemented by member states.
EU Directives:
Directives are legal acts that set out particular objectives which must be achieved by member states. They do not have direct effect and require implementation into national law by each member state. This means that member states have flexibility in terms of how they transpose the Directive into their national legal systems, taking into account their own legal traditions and structures. Member states typically have a specified timeframe within which they must implement the Directive, failing which they may face legal consequences.
Key points regarding EU Directives include:
EU Regulations:
Regulations, on the other hand, are legal acts that have direct effect and are immediately applicable in all member states. This means that they become part of the national legal systems of member states without any further action required on their part. Regulations are uniform and directly applicable, ensuring a high level of harmonization and legal certainty within the EU.
Key points regarding EU Regulations include:
In summary, while both EU Directives and Regulations are important legislative instruments of the EU, they differ in terms of their legal nature and implementation. Directives require member states to achieve certain objectives, while leaving them discretion as to the form and means of implementation. In contrast, Regulations are directly applicable and binding on all member states, ensuring uniformity and legal certainty within the EU. Understanding these distinctions is crucial for individuals and businesses operating within the EU to ensure compliance with EU law.
Understanding the Distinctions: EU Directive vs Regulation
Staying up-to-date with the ever-changing landscape of European Union (EU) law is of utmost importance for anyone involved in international business, trade, or legal matters. Two key legal instruments that shape the EU legal framework are directives and regulations. Understanding the distinctions between these instruments is crucial for navigating the complexities of EU law.
1. Definition and Legal Force:
– Directive: A directive is a legal act issued by the EU that sets out specific objectives that member states must achieve within a certain timeframe. However, it allows member states flexibility in implementing the objectives into their national laws. Directives require transposition into national legislation through acts or laws passed by the member states.
– Regulation: A regulation is a binding legislative act that is directly applicable in all member states without the need for national implementation. It is immediately enforceable and creates legal obligations that are directly applicable to individuals, businesses, and public authorities across the EU.
2. Binding Nature:
– Directive: Directives are binding as to the result to be achieved. Member states have discretion regarding the form and means of achieving those results. The member states are responsible for implementing directives by enacting laws to comply with the objectives set out in the directive.
– Regulation: Regulations are binding in their entirety and are directly applicable in all member states without any national implementation. Member states cannot deviate from the regulations and must ensure compliance from the moment they come into effect.
3. Flexibility vs Uniformity:
– Directive: Directives allow member states some flexibility in deciding how to achieve the objectives set out in the directive. This means that while the ultimate goal is the same, there may be variations in the way each member state implements the directive into their domestic legislation. This flexibility can lead to variations in the legal frameworks between member states.
– Regulation: Regulations provide uniformity across all member states as they are directly applicable and binding. They create a level playing field by ensuring that the same rules apply to all EU member states and their citizens, businesses, and organizations.
4. Legal Effect:
– Directive: Directives do not have direct legal effect in member states until they are implemented into national law. Individuals cannot rely on the directives alone to challenge actions or decisions of public authorities or private entities.
– Regulation: Regulations have direct legal effect in all member states as soon as they enter into force. Individuals can rely on regulations directly to challenge actions or decisions of public authorities or private entities.
Staying up-to-date on EU directives and regulations is essential due to their significant impact on various aspects of law and business within the EU. It is important to verify and contrast the content of any article or resource, as EU law is subject to frequent updates and amendments. Consulting official EU sources, legal professionals, and relevant stakeholders will ensure accurate and current information is obtained.
In conclusion, understanding the distinctions between EU directives and regulations is vital for anyone dealing with EU law. Directives allow member states flexibility in implementation, while regulations are directly applicable and binding on all member states. Staying informed and verifying information from reliable sources is key to navigating the complexities of EU law successfully.
