Greetings!
As an experienced attorney in the United States, I have been called upon to shed light on the nuanced distinction between a regulation and a law in the context of the United Kingdom. While the legal systems of different countries may vary, understanding this fundamental difference is crucial for comprehending the framework within which legal rules operate.
📋 Content in this article
In the UK, a law is a rule that has been formally enacted by the legislative body of the country. In other words, it is a written command that carries the full force and effect of the legal system. Laws are typically created by Parliament and are officially known as Acts of Parliament. These Acts undergo a rigorous process of debate, amendment, and voting before they are finally enacted and become binding on individuals and entities within the UK.
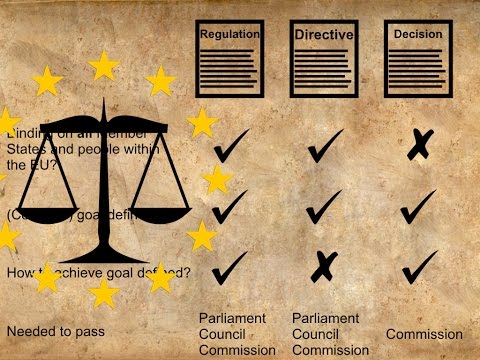
On the other hand, a regulation in the UK refers to a rule or requirement that is formulated and enforced by an administrative agency or governmental body. Unlike laws, regulations are not created by Parliament. Instead, they are developed and implemented by specialized agencies or departments to fulfill specific purposes authorized by existing laws. Regulations are generally more detailed than laws, outlining specific procedures, standards, or guidelines that must be adhered to in order to comply with the law effectively.
To summarize, laws in the UK are formal legal rules enacted by Parliament, while regulations are additional rules created by administrative agencies to support and implement those laws. Understanding this distinction is crucial because failing to comply with either laws or regulations can have legal consequences and may result in penalties or other forms of enforcement action.
I hope this clarifies the difference between a regulation and a law in the UK. If you have any further questions or require additional information, please do not hesitate to ask.
Understanding the Distinction: Law vs. Regulation Explained
Understanding the Distinction: A Regulation vs. a Law in the UK
When navigating the legal landscape, it is essential to understand the distinction between a regulation and a law. While these terms are often used interchangeably, they have distinct meanings and implications. In the United Kingdom (UK), as in many other legal systems, regulations and laws play crucial roles in governing society. Let’s delve into the differences between these two concepts to gain a clearer understanding.
What is a Law?
A law, also known as legislation or statute, is a formal rule that is created and enacted by a legislative body, such as the UK Parliament. Laws are broad in scope and cover a wide range of issues, from criminal offenses to civil procedures, employment rights to consumer protection. They establish legal obligations and rights for individuals and organizations and are enforced by the courts.
In the UK, laws typically go through a rigorous process before being enacted. They are proposed as bills, scrutinized by both Houses of Parliament, and ultimately receive Royal Assent from the monarch. Once a law comes into effect, it applies to all individuals or entities within its jurisdiction.
What is a Regulation?
Regulations, on the other hand, are rules that are created by government agencies or bodies under the authority granted by a law. These agencies are responsible for administering and enforcing specific areas of law. Regulations provide more detailed guidelines on how to comply with the overarching laws and often focus on technical aspects or specific industries.
Unlike laws, regulations do not go through the same legislative process. Instead, they are developed by experts within the relevant government agency. This allows for flexibility and efficiency in responding to changing circumstances or advancements within a particular field. However, regulations must still be consistent with the underlying legislation and cannot contradict or exceed the authority granted by the law.
The Relationship Between Laws and Regulations
Laws and regulations are interconnected, with regulations serving as a subsidiary to the laws they are derived from. Regulations provide the necessary details and specific requirements for compliance with the broader laws. They serve as a means of operationalizing and implementing the laws in practice.
It is important to note that regulations cannot create new legal obligations or rights beyond what is set out in the underlying law. They are meant to clarify and provide guidance on the application of the law, ensuring consistency and uniformity in its interpretation and enforcement.
Enforcement and Penalties
Both laws and regulations come with consequences for non-compliance. Failure to adhere to laws may result in criminal charges, fines, or other legal repercussions. Regulations, being more specific in nature, often outline administrative penalties, such as fines or revocation of licenses. The severity of the penalties will depend on the nature and seriousness of the violation.
In conclusion, understanding the distinction between a regulation and a law is crucial for navigating the legal landscape in the UK. Laws provide the overarching framework, while regulations offer detailed guidance for compliance. By adhering to both, individuals and organizations can ensure they are operating within the boundaries of the law and avoid potential legal consequences.
Understanding the Distinction: Rules vs Laws in the UK
Understanding the Distinction: A Regulation vs. a Law in the UK
When it comes to understanding the legal system in the United Kingdom, it’s essential to grasp the distinction between regulations and laws. While both play a crucial role in governing society, they have some significant differences. This article aims to shed light on the contrast between regulations and laws in the UK, providing you with a comprehensive understanding of these two concepts.
1. What is a Regulation?
A regulation is a set of rules developed by a governmental body or an administrative agency to enforce laws. It serves as a detailed framework that outlines how a law should be implemented and followed. Regulations are more specific and precise than laws, often providing guidance on specific procedures, requirements, or standards. They are designed to ensure compliance with the overarching law and promote order and fairness in various sectors such as finance, healthcare, employment, and environmental protection.
Regulations are created by administrative agencies or bodies that have been granted specific authority by the legislature. These agencies have the expertise and knowledge to develop rules that align with the objectives of the law. In the UK, regulations are typically made by secondary legislation, which means they are authorized by an Act of Parliament, but the detailed rules are left to be determined by the relevant administrative agency.
2. What is a Law?
A law, on the other hand, refers to a broader set of legal principles and rules that are enacted by the legislative body. These principles are more general and abstract compared to regulations. Laws are usually passed by Parliament in the UK and aim to establish fundamental rights, obligations, and prohibitions that apply to all members of society.
Laws are drafted to provide a framework for governance and regulate various aspects of public and private life. They establish fundamental rights and responsibilities, criminal offenses, penalties, and legal procedures. Laws are enforced by the courts and can be challenged or interpreted through the legal system.
3. Key Differences between Regulations and Laws
Now that we have a basic understanding of regulations and laws, let’s explore some key differences between the two:
– Authority: Regulations are developed by administrative agencies or bodies that are authorized by primary legislation. Laws, on the other hand, are enacted by the legislative body itself, such as Parliament in the UK.
– Specificity: Regulations are more specific and detailed, outlining the procedures and standards required to comply with the law. Laws are more general and provide a broader framework for governance.
– Enforcement: Regulations are enforced by the administrative agency responsible for their creation. Laws, on the other hand, are enforced by the courts and can result in legal consequences if violated.
– Amendment: Regulations can be amended or repealed by the administrative agency that created them, subject to certain limitations. Laws can only be amended or repealed by the legislative body through the enactment of new legislation.
– Scope: Regulations typically apply to specific sectors or industries, providing detailed guidelines for compliance. Laws, on the other hand, have a broader application and affect all members of society.
Understanding the Distinction: Act vs. Law in the UK
Understanding the Distinction: Act vs. Law in the UK
When it comes to legal matters, it is crucial to have a clear understanding of the terminology and concepts involved. One common source of confusion pertains to the distinction between an Act and a Law in the United Kingdom.
1. Acts:
An Act, also known as a statute, is a piece of legislation that has been passed by the UK Parliament. It is a formal written document that sets out rules, regulations, and procedures that must be followed by individuals and organizations. Acts cover a wide range of areas, including criminal law, civil law, employment law, and more. They are highly authoritative and carry significant legal weight.
2. Laws:
In contrast, the term “law” is a broader concept that encompasses various sources of legal rules and principles. Laws can be derived from Acts, as well as from other sources such as common law, equity, and European Union law. While Acts are specific pieces of legislation, laws refer to the overall body of legal rules that govern society.
3. Relationship between Acts and Laws:
Acts are the primary means by which laws are created in the UK. When an Act is passed by Parliament, it becomes part of the legal framework and contributes to the body of laws in that jurisdiction. Acts can modify, amend, or repeal existing laws, or introduce entirely new laws.
4. Role of Acts and Laws:
Acts provide the specific rules and regulations that individuals and organizations must adhere to. They set out the rights and obligations of parties involved in legal matters. Laws, on the other hand, provide a more comprehensive framework within which legal disputes are resolved and societal order is maintained.
5. Importance of Understanding the Distinction:
Understanding the distinction between an Act and a Law is essential for several reasons. Firstly, it allows individuals to know the precise legal provisions that apply to their situation. Secondly, it enables legal professionals to interpret and apply the law correctly in court proceedings. Finally, it provides clarity and transparency in the legal system, ensuring that everyone can access and understand their legal rights and obligations.
In conclusion, while Acts are specific pieces of legislation passed by the UK Parliament, laws encompass the broader body of legal rules. Acts play a vital role in creating and modifying laws, while laws provide the overall framework within which legal disputes are resolved. Understanding this distinction is crucial for individuals and legal professionals alike, as it ensures compliance, fairness, and access to justice.
Understanding the Distinction: A Regulation vs. a Law in the UK
As a seasoned attorney, it is important to stay up-to-date on various legal concepts and principles, even those that may be specific to different countries. One such concept that warrants attention is the distinction between a regulation and a law in the United Kingdom (UK).
In the UK legal system, there is a clear distinction between regulations and laws, and it is crucial for legal practitioners and individuals involved in legal matters to understand this difference. While both regulations and laws serve as legal instruments, they have distinct characteristics and functions.
1. Regulations: Regulations are rules created by government agencies or other delegated authorities. They are designed to provide specific guidance and impose requirements in relation to a particular law. Regulations are more detailed and specific than laws and often outline the practical steps necessary to comply with the overarching legislative framework. They are typically enacted to implement and supplement laws passed by the UK Parliament.
2. Laws: Laws, on the other hand, are broader legal provisions enacted by the UK Parliament. They are generally more overarching and establish legal principles and rights that govern various aspects of society. Laws are typically created through a democratic legislative process and apply to everyone within the jurisdiction. They lay down the fundamental rules and principles that govern conduct, rights, obligations, and penalties.
It is important to note that regulations are subordinate to laws. In other words, regulations are created under the authority of laws and are legally binding because they have been authorized by an existing law. Regulations cannot go beyond the scope of the parent legislation and must align with its objectives.
Importance of Staying Up-to-Date
Staying up-to-date with the distinction between regulations and laws is crucial for several reasons:
1. Compliance: Understanding regulations is essential for individuals and organizations to ensure compliance with the law. Ignorance of relevant regulations can lead to unintentional non-compliance and potential legal consequences.
2. Legal Advice: As legal practitioners, it is important to provide accurate and reliable advice to clients. By staying informed about the distinction between regulations and laws, attorneys can better guide their clients and help them navigate the complexities of the legal system.
3. Advocacy: Advocates, whether representing individuals or organizations, should be aware of the relevant regulations and laws to effectively argue their case. Knowledge of both can help in building stronger legal arguments and presenting persuasive evidence.
4. Public Interest: Staying abreast of legal developments and understanding the distinction between regulations and laws allows attorneys to contribute to public debates, engage in legal scholarship, and inform policy discussions.
While this article provides an overview of the distinction between regulations and laws in the UK, it is essential for readers to verify and contrast the information provided with primary legal sources such as legislation, regulations, case law, and legal commentary. The legal landscape is constantly evolving, and it is always prudent to consult authoritative sources when dealing with specific legal issues or seeking professional advice.
