Understanding Regulation 12 of the Waste Regulations 2011: An In-Depth Explanation
Greetings,
📋 Content in this article
In today’s article, we will delve into the intricacies of Regulation 12 of the Waste Regulations 2011. This regulation plays a crucial role in waste management practices in the United States. Our aim is to provide you with a comprehensive understanding of this regulation, its purpose, and its implications.
Regulation 12 of the Waste Regulations 2011 pertains to the duty of care for waste. It places responsibilities on those who produce, transport, store, or treat waste. The primary objective of this regulation is to ensure that waste is handled and managed properly, minimizing any adverse impacts on the environment and public health.
To help you navigate through the details, we have compiled a list of key points related to Regulation 12 of the Waste Regulations 2011:
It is essential for waste producers, carriers, and managers to familiarize themselves with the requirements and obligations set forth in Regulation 12 of the Waste Regulations 2011. Compliance not only ensures legal adherence but also contributes to a cleaner, safer, and more sustainable environment for all.
Please note that this article provides a general overview and should not be considered legal advice. For specific guidance related to your situation, it is advisable to consult with a qualified legal professional.
We hope this article has shed light on the complexities of Regulation 12 of the Waste Regulations 2011. By understanding and adhering to these regulations, we can collectively make a positive impact on waste management practices in our country.
Best regards,
[Your Name]
Seasoned U.S.
Understanding Regulation 12 of the Waste Management Guidelines: A Comprehensive Overview
Understanding Regulation 12 of the Waste Regulations 2011: An In-Depth Explanation
Introduction:
Regulation 12 of the Waste Regulations 2011 is a critical provision that plays a key role in waste management in the United States. It sets forth important requirements and obligations for businesses and individuals involved in the generation, transportation, storage, treatment, and disposal of waste. This article aims to provide a comprehensive overview of Regulation 12, outlining its main provisions and highlighting its significance in the waste management industry.
Key provisions of Regulation 12:
1. Duty of care:
Regulation 12 imposes a duty of care on anyone who produces, imports, carries, keeps, treats, or disposes of waste. This duty requires these individuals or businesses to take all reasonable measures to ensure that waste is managed properly and does not cause harm to human health or the environment. Failure to fulfill this duty can result in significant penalties and legal consequences.
2. Waste classification:
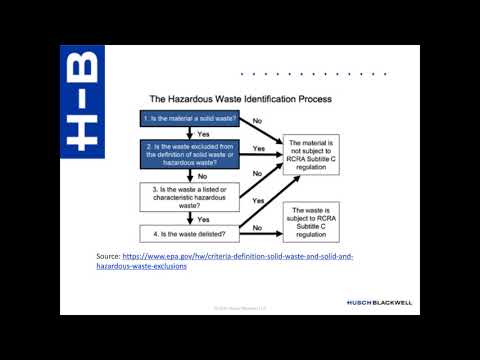
One essential aspect of Regulation 12 is the classification of waste. Waste is classified based on its properties and potential risks to human health and the environment. The regulation provides detailed guidance on how to classify waste, including specific criteria for hazardous waste. This classification is crucial for determining appropriate handling, storage, transportation, and disposal methods.
3. Waste management hierarchy:
Regulation 12 promotes the waste management hierarchy, which prioritizes waste prevention, minimization, reuse, recycling, recovery, and finally, safe disposal. The hierarchy serves as a guideline for waste management decision-making, encouraging individuals and businesses to choose the most environmentally-friendly option at each stage of the waste management process.
4. Record-keeping requirements:
To ensure compliance with Regulation 12, individuals and businesses must maintain accurate records of their waste management activities. These records should include details such as the types and quantities of waste generated, transfer notes for waste transportation, and consignment notes for waste disposal. Proper record-keeping is crucial for demonstrating compliance and facilitating effective waste tracking.
Significance of Regulation 12:
Regulation 12 plays a crucial role in protecting human health and the environment by establishing a comprehensive framework for waste management. By imposing a duty of care and promoting effective waste management practices, the regulation aims to prevent pollution, reduce the environmental impact of waste, and ensure the safe handling and disposal of hazardous materials. Compliance with Regulation 12 is not only a legal requirement but also a moral responsibility to safeguard our planet for future generations.
Understanding the Controlled Waste Regulation: A Comprehensive Guide
Understanding Regulation 12 of the Waste Regulations 2011: An In-Depth Explanation
Regulation 12 of the Waste Regulations 2011 is a crucial provision that governs the handling, storage, and disposal of controlled waste. It is essential for businesses and individuals to have a solid understanding of this regulation to avoid legal repercussions and contribute to a healthier environment.
The Scope of Regulation 12
Regulation 12 applies to anyone who produces, imports, carries, keeps, treats, or disposes of controlled waste. Controlled waste refers to any waste listed in Schedule 2 of the Environmental Protection Act 1990 and includes hazardous waste, clinical waste, and industrial waste. It is important to note that this regulation applies to both businesses and individuals.
Duty of Care
Regulation 12 imposes a duty of care on those involved in the management of controlled waste. The duty of care requires that every reasonable step is taken to prevent unauthorized or harmful disposal of waste. This includes ensuring that waste is properly stored, transported, and disposed of at authorized facilities.
Key Obligations
To comply with Regulation 12, it is important to be aware of the following key obligations:
1. Waste Transfer Notes: When any controlled waste is transferred from one party to another, a written Waste Transfer Note must be completed and retained for a minimum of two years. The note should include details about the waste, the parties involved, and the intended destination.
2. Carriers’ Registration: Businesses involved in the transportation of controlled waste must register as a waste carrier with the appropriate regulatory authority. This ensures that carriers meet certain standards and can be held accountable for any improper handling or disposal of waste.
3. Storage Requirements: Controlled waste must be stored in a manner that prevents pollution and poses no risk to human health. This includes using appropriate containers, labeling them correctly, and ensuring that any hazardous waste is securely stored.
4. Disposal: When disposing of controlled waste, it is vital to use authorized facilities such as landfill sites, incinerators, or recycling centers. Illegal disposal can result in severe penalties and harm the environment.
Enforcement and Penalties
Failure to comply with Regulation 12 can lead to serious consequences. The regulatory agencies responsible for enforcing this regulation have the power to issue fines, revoke licenses, and even initiate criminal proceedings in cases of deliberate or negligent non-compliance. It is crucial to understand that ignorance of the law is not a valid defense.
Seek Professional Advice
Navigating the complexities of Regulation 12 can be challenging, especially for businesses. To ensure compliance, it is advisable to seek professional legal advice from qualified attorneys experienced in environmental law. They can provide guidance tailored to your specific circumstances and help safeguard against legal issues related to controlled waste management.
In conclusion, a thorough understanding of Regulation 12 of the Waste Regulations 2011 is vital for anyone involved in the handling and disposal of controlled waste. By fulfilling the duty of care and complying with the key obligations, businesses and individuals can contribute to a cleaner and safer environment while avoiding potential legal pitfalls.
Understanding the Five Stages of Waste Hierarchy: A Comprehensive Overview
Understanding the Five Stages of Waste Hierarchy: A Comprehensive Overview
In order to fully comprehend Regulation 12 of the Waste Regulations 2011, it is crucial to first understand the concept of the Five Stages of Waste Hierarchy. This hierarchy serves as a framework for waste management and places an emphasis on waste prevention and minimization, as well as resource recovery.
The Five Stages of Waste Hierarchy, in descending order of priority, are as follows:
Regulation 12 of the Waste Regulations 2011 builds on the principles outlined in the Five Stages of Waste Hierarchy, emphasizing the need for waste producers to apply these principles in their waste management practices. It requires waste producers to take all reasonable steps to apply the waste hierarchy when transferring waste.
By understanding the Five Stages of Waste Hierarchy and how Regulation 12 of the Waste Regulations 2011 aligns with it, waste producers can make informed decisions about their waste management practices. Compliance with these regulations not only helps protect the environment but also ensures sustainable use of resources and promotes a circular economy.
In conclusion, familiarizing oneself with the Five Stages of Waste Hierarchy provides a comprehensive overview of waste management practices. Regulation 12 of the Waste Regulations 2011 further enforces the importance of applying this hierarchy in waste management activities.
Understanding Regulation 12 of the Waste Regulations 2011: An In-Depth Explanation
As a seasoned attorney in the United States, I have come across numerous regulations and legal frameworks that govern various aspects of our society. One such regulation that I believe is of utmost importance to understand is Regulation 12 of the Waste Regulations 2011. In this article, I will provide an in-depth explanation of this regulation and emphasize the significance of staying up-to-date on this topic.
Regulation 12 of the Waste Regulations 2011 pertains to the duty of care that individuals and businesses have in relation to waste management. This regulation places a legal obligation on anyone who produces, imports, carries, keeps, treats, or disposes of waste to ensure that it is managed properly and does not cause harm to human health or the environment.
Key points to consider when understanding Regulation 12:
It is essential to stay up-to-date on Regulation 12 and other relevant waste management regulations. The legal landscape is constantly evolving, and regulations may be subject to amendments or updates. By regularly reviewing the latest information provided by the appropriate regulatory bodies, individuals and businesses can ensure they are fully compliant and avoid any legal complications.
However, it is important to note that this article serves as a general overview of Regulation 12 of the Waste Regulations 2011 and should not be considered legal advice. To fully understand the specific requirements and implications of this regulation, it is advisable to consult with a qualified attorney or seek guidance from relevant regulatory authorities.
In conclusion, understanding Regulation 12 of the Waste Regulations 2011 is crucial for individuals and businesses involved in waste management. Staying up-to-date on this topic allows for informed decision-making, compliance with legal obligations, and the promotion of environmentally sustainable practices. Always remember to verify and contrast the content of this article with authoritative sources to ensure accurate and reliable information.
