An Introduction to the Role of a Principal Lawyer in the UK Legal System
Welcome, dear reader, to this informative article that aims to shed light on the important role of a Principal Lawyer within the UK legal system. It is crucial to note that while this article strives to provide a comprehensive understanding of the topic, it is always advisable to cross-reference with other reliable sources or seek guidance from qualified legal professionals.
Now, let us embark on a journey to explore the realm of Principal Lawyers in the UK legal system. In order to understand their role, it is essential to grasp the foundations of the legal system itself.
📋 Content in this article
The UK Legal System: An Overview
The United Kingdom operates under a common law legal system, which means that legal principles are derived from court decisions and precedents rather than solely from statutes. This system emphasizes the importance of case law and relies on judicial interpretations to shape and develop the law.
Within this legal framework, Principal Lawyers play a central role by upholding and interpreting the law in their respective areas of expertise. They are highly skilled individuals who possess a deep understanding of legal principles, statutes, regulations, and case law.
The Role of a Principal Lawyer
A Principal Lawyer is an experienced legal professional who takes on a leadership role within a law firm or organization. They are recognized for their exceptional knowledge and expertise in a specific area of law, which allows them to guide and advise clients on complex legal matters.
Responsibilities and Duties
Principal Lawyers have a wide range of responsibilities and duties that can vary depending on their area of specialization. Some common duties include:
Understanding the Fundamentals: Principles of the UK Legal System
Understanding the Fundamentals: Principles of the UK Legal System
The UK legal system is a complex and fascinating institution, with its roots dating back centuries. It is crucial for anyone involved in legal matters in the UK to have a solid understanding of the fundamental principles that underpin the system. This article aims to provide a detailed explanation of these principles, with a focus on the role of a principal lawyer.
The Rule of Law
At the core of the UK legal system lies the principle of the rule of law. This principle ensures that every person, regardless of their background or social status, is subject to the same laws and regulations. It means that no one is above the law and that everyone is entitled to equal legal protection.
The Doctrine of Precedent
Another key principle of the UK legal system is the doctrine of precedent. This doctrine, also known as stare decisis, means that judges are bound to follow the decisions of higher courts in similar cases. This creates consistency and predictability in the law, allowing individuals and businesses to understand and rely on legal principles established in previous cases.
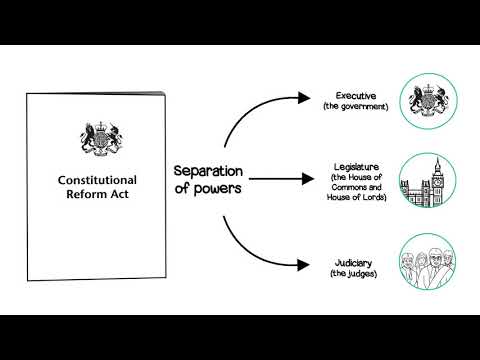
The Separation of Powers
The UK legal system operates on the principle of the separation of powers. This means that powers are divided among three branches of government: the legislative, executive, and judicial branches. The legislative branch makes laws, the executive branch enforces laws, and the judicial branch interprets laws and resolves disputes. This separation ensures a system of checks and balances, preventing any one branch from becoming too powerful.
The Role of a Principal Lawyer
Within the UK legal system, a principal lawyer holds a significant role. A principal lawyer, also known as a solicitor or barrister, is a qualified legal professional who provides legal advice and representation to clients. They have extensive knowledge in various areas of law and can specialize in specific fields such as criminal law, family law, or commercial law.
Responsibilities of a
Understanding the Distinction Between Barristers and Solicitors in the UK
Understanding the Distinction Between Barristers and Solicitors in the UK
In the United Kingdom legal system, there is a clear distinction between two types of legal professionals: barristers and solicitors. While both barristers and solicitors are lawyers, they have separate roles and responsibilities within the legal system. Understanding their distinction is crucial for individuals seeking legal representation or advice in the UK.
Role of a Solicitor:
A solicitor is the first point of contact for clients seeking legal assistance. They provide a wide range of legal services, including advisory and transactional work. Solicitors handle a variety of matters such as drafting legal documents, negotiating contracts, and providing general legal advice. They are often involved in non-contentious matters and act as intermediaries between clients and other legal professionals.
Role of a Barrister:
On the other hand, barristers are specialist advocates who represent clients in court proceedings. They are typically called upon by solicitors to provide expert advice and representation in matters that require advocacy, such as litigation and appeals. Barristers are highly skilled in presenting legal arguments and cross-examining witnesses in court. They focus on the preparation and presentation of cases rather than client interaction.
The Distinction:
The key distinction between barristers and solicitors lies in their respective functions within the legal system. Solicitors primarily handle the day-to-day legal affairs of clients, while barristers specialize in courtroom advocacy. Solicitors are often involved in the initial stages of a legal matter, gathering information, advising clients, and preparing cases for court. If a case proceeds to trial, solicitors enlist the services of barristers to represent their clients.
Education and Training:
The educational path to becoming a solicitor or barrister also differs. To become a solicitor, individuals must complete a law degree followed by the Legal Practice Course (LPC) and a two-year training contract at a law firm.
Title: Understanding the Role of a Principal Lawyer in the UK Legal System
Introduction:
In this article, we will explore the crucial role of a principal lawyer in the UK legal system. This discussion aims to provide an overview of their responsibilities and shed light on the importance of staying up-to-date with this topic. It is essential to note that readers should always verify and cross-reference the content of this article, as the legal landscape may undergo changes over time.
1. Defining the Role of a Principal Lawyer:
A principal lawyer, also known as a solicitor, plays a central role in the UK legal system. They are legal professionals who provide legal advice, guidance, and representation to individuals, businesses, and organizations. Principal lawyers possess an in-depth knowledge of various areas of law and are licensed to practice law in England and Wales.
2. Responsibilities of a Principal Lawyer:
a. Client Consultation: Principal lawyers engage in thorough consultations with clients to understand their legal needs, objectives, and concerns. This process includes gathering relevant information, assessing the strengths and weaknesses of a case, and providing tailored advice.
b. Legal Research and Analysis: To effectively represent their clients, principal lawyers must conduct extensive legal research and analysis. This ensures they have a comprehensive understanding of relevant statutes, case law, and legal precedents that may impact a client’s case.
c. Document Preparation: Principal lawyers are responsible for drafting and reviewing legal documents such as contracts, agreements, wills, and court pleadings. Attention to detail is crucial to ensure accuracy and compliance with legal requirements.
d. Negotiation and Mediation: Principal lawyers often engage in negotiation and mediation processes on behalf of their clients to seek favorable outcomes without resorting to litigation. Their skills in resolving disputes through alternative means can save time, costs, and maintain amicable relationships.
e. Court Representation: When necessary, principal lawyers represent their clients in various courts, including submitting legal
