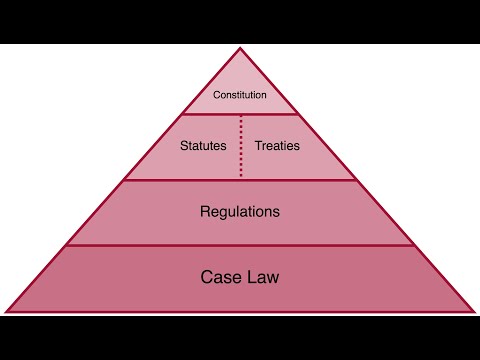
Understanding Minor Violations of State Statutes or Local Ordinances: Exploring Fines, Tickets, and Penalties
Greetings, dear readers! Today, we embark on a journey to demystify the world of minor violations of state statutes or local ordinances. We will delve into the fascinating realm of fines, tickets, and penalties, and guide you through the intricate web of legal consequences for these minor transgressions.
📋 Content in this article
When it comes to minor violations, such as jaywalking, parking violations, or littering, it’s important to understand that these offenses are typically considered less serious than major crimes. While they may not result in jail time or extensive legal proceedings, they can still pack a punch in the form of fines, tickets, or other penalties.
Fines: A fine is a monetary penalty imposed by a court or other legal authority as punishment for committing a minor offense. The amount of the fine depends on the specific violation and can vary widely. For example, a speeding ticket may come with a fine of $100, while a littering violation could result in a fine of $500. The purpose of fines is twofold: to punish the offender and to deter them from engaging in similar behavior in the future.
Tickets: Tickets are often issued on the spot by law enforcement officers for minor violations. They serve as notice that an offense has been committed and typically require the person receiving the ticket to either pay a fine or appear in court to contest the charges. It’s crucial to remember that receiving a ticket does not automatically mean you are guilty of the offense. You have the right to challenge it in court and present your defense.
Penalties: In addition to fines and tickets, minor violations can carry other penalties. These penalties can include community service, probation, mandatory classes or programs (such as traffic school), or even the suspension of certain privileges (such as a driver’s license). The specific penalties will depend on the nature of the offense and the laws of the jurisdiction where it occurred.
It’s important to note that while minor violations may not have the same gravity as major crimes, they should not be taken lightly. Ignoring a ticket or failing to pay a fine can lead to more serious consequences, such as license suspension, increased fines, or even arrest warrants.
In conclusion, understanding minor violations of state statutes or local ordinances is crucial for navigating the legal landscape. Fines, tickets, and penalties serve as means to enforce compliance with the law and discourage future transgressions. So, the next time you find yourself facing a minor violation, approach it with knowledge and awareness, and remember that seeking legal advice is always a wise course of action.
Thank you for joining us on this enlightening exploration!
Understanding Traffic Violations: Exploring Minor Offenses and Terminology
Understanding Traffic Violations: Exploring Minor Offenses and Terminology
Traffic violations are infractions of laws that regulate the operation of motor vehicles on public roads. These violations can range from minor offenses to more serious crimes. In this article, we will focus on understanding minor violations of state statutes or local ordinances, with a particular emphasis on fines, tickets, and penalties.
1. Minor Offenses:
Minor offenses, also known as non-criminal traffic violations, are generally less serious infractions that do not carry the risk of imprisonment. These offenses are typically punishable by fines, points on your driving record, or traffic school. Examples of minor offenses include:
2. Fines:
Fines are monetary penalties imposed by the court for committing a traffic violation. The amount of the fine is usually determined by the severity of the offense and can vary from one jurisdiction to another. It is important to remember that fines for traffic violations can add up quickly, especially if you have multiple offenses on your record.
3. Tickets:
When you commit a traffic violation, law enforcement officers may issue you a ticket or citation. A ticket serves as a formal notice that you have violated a traffic law and typically contains information such as the date, time, and location of the offense, as well as the details of the violation. It is crucial to read the ticket carefully and follow any instructions provided, such as paying the fine or appearing in court on a specified date.
4. Penalties:
In addition to fines, traffic violations can result in other penalties that can impact your driving privileges and insurance rates. These penalties may include:
In conclusion, understanding minor violations of state statutes or local ordinances is crucial to navigate through traffic law. Being familiar with the terminology, fines, tickets, and penalties associated with traffic violations can help you make informed decisions and potentially minimize the negative consequences of these offenses. If you find yourself facing a traffic violation charge, consulting with an attorney who specializes in traffic law can provide valuable guidance and representation.
Understanding Traffic Violation Punishments: What You Need to Know
Understanding Minor Violations of State Statutes or Local Ordinances: Exploring Fines, Tickets, and Penalties
When it comes to traffic violations, it is important to understand the potential punishments that can arise from minor infractions of state statutes or local ordinances. This article aims to provide you with a comprehensive understanding of the fines, tickets, and penalties associated with these types of violations.
Fines:
Fines are monetary penalties imposed for traffic violations. The amount of the fine varies depending on the nature of the violation and the jurisdiction in which it occurred. Minor violations such as speeding, running a red light, or failure to yield typically result in fines ranging from $50 to $300. However, keep in mind that fines can be higher for more serious offenses or if the violation caused property damage or injury.
Tickets:
When you commit a traffic violation, you may receive a ticket from a law enforcement officer. A ticket serves as a notice to appear in court or pay the specified fine within a certain timeframe. It usually includes details about the violation, such as the date, time, location, and the specific statute or ordinance violated. Ignoring a ticket or failing to respond can lead to additional penalties, including suspension of your driving privileges.
Penalties:
In addition to fines and tickets, traffic violations can result in various other penalties. These penalties can include points on your driving record, license suspension or revocation, mandatory traffic school, increased insurance premiums, and even potential jail time for more serious offenses. Accumulating too many points on your driving record can lead to license suspension or higher insurance rates.
Points on Your Driving Record:
Many states operate on a point system to track driving violations. Each violation is assigned a certain number of points depending on its severity. For example, a minor speeding violation may result in two points, while a more serious offense like reckless driving could result in six points. If you accumulate a certain number of points within a specific period, your driving privileges may be suspended or revoked.
Importance of Legal Representation:
When facing a traffic violation, it is crucial to consider seeking legal representation. An experienced attorney can help you understand your rights, navigate the legal process, and potentially mitigate the penalties associated with the violation. They can review the circumstances of your case, identify any potential defenses, and negotiate with prosecutors to achieve the best possible outcome.
In conclusion, understanding the fines, tickets, and penalties associated with minor violations of state statutes or local ordinances is essential when dealing with traffic violations. It is important to be aware of the potential consequences and to seek legal representation to protect your rights and interests.
Understanding Infraction Tickets in California: A Comprehensive Guide
Understanding Minor Violations of State Statutes or Local Ordinances: Exploring Fines, Tickets, and Penalties
When it comes to minor violations of state statutes or local ordinances, it is important to have a clear understanding of the potential consequences and legal processes involved. In this comprehensive guide, we will delve into the intricacies of infraction tickets in California and provide valuable insights into fines, tickets, and penalties.
What is an Infraction Ticket?
An infraction ticket is a legal document issued by law enforcement officers for minor offenses that are not considered crimes. These offenses are typically non-criminal violations, such as traffic infractions, parking violations, or certain ordinance violations. Unlike misdemeanors or felonies, infractions generally do not carry the risk of jail time.
The Process of Receiving an Infraction Ticket
1. Issuance of the Ticket: When an officer observes a violation, they may issue an infraction ticket to the individual responsible. The ticket includes details such as the date, time, location, and nature of the violation.
2. Options for Responding: Upon receiving an infraction ticket, individuals have several options for responding. They can choose to pay the fine indicated on the ticket, contest the ticket in court, or in some cases, complete a traffic school or other diversion program.
3. Paying the Fine: If individuals decide to pay the fine, they can typically do so online, by mail, or in person at a designated government office. It is important to note that paying the fine is an admission of guilt and may result in points being added to your driving record or other negative consequences.
4. Contesting the Ticket: If individuals believe they are not guilty of the violation, they have the right to contest the infraction ticket. This involves appearing in court and presenting evidence to support their case. It is advisable to seek legal representation to navigate the complexities of the legal process.
Fines, Tickets, and Penalties
The fines associated with infraction tickets can vary depending on the nature of the violation. Common examples include speeding tickets, red light violations, and parking tickets. These fines can range from a few dollars to several hundred dollars, depending on the severity of the offense.
In addition to fines, infraction tickets can result in other penalties such as:
– Points on Driving Record: Certain traffic violations can result in points being added to your driving record. Accumulating too many points within a specified period may lead to a suspended or revoked driver’s license.
– Increased Insurance Rates: Some violations may result in increased insurance rates as insurers consider them indicators of higher risk.
– Required Traffic School: In specific cases, individuals may be required to complete a traffic school or defensive driving course as part of their penalty. Successful completion of such programs can help mitigate or dismiss the offense.
– Community Service: In some instances, individuals may be required to perform community service as a penalty for certain violations.
It is important to understand that each violation and jurisdiction may have its own specific rules and penalties. Consulting with a legal professional can provide tailored guidance based on your circumstances.
Understanding Minor Violations of State Statutes or Local Ordinances: Exploring Fines, Tickets, and Penalties
As a seasoned attorney in the United States, I understand the importance of staying up-to-date on the topic of minor violations of state statutes or local ordinances. In this article, I aim to provide a comprehensive understanding of the fines, tickets, and penalties associated with such violations. However, it is crucial for readers to verify and contrast the content of this article with current laws and regulations as they can vary by jurisdiction.
Fines:
Fines are monetary penalties imposed on individuals who have committed minor violations of state statutes or local ordinances. These fines serve as a form of punishment and deterrent to discourage individuals from engaging in similar conduct in the future. The amount of the fine is typically determined by the jurisdiction and may vary depending on the severity of the violation.
Tickets:
Tickets are commonly issued for minor violations of state statutes or local ordinances. They serve as formal notices to individuals who have committed such violations. Tickets provide information about the offense committed and the corresponding penalty that will be imposed. In some cases, tickets may require individuals to appear in court to address the violation.
Penalties:
Penalties refer to the consequences individuals face as a result of committing minor violations of state statutes or local ordinances. These penalties can range from fines and tickets to other forms of punishment, such as community service or probation. The specific penalty imposed will depend on the nature and severity of the violation, as well as any prior offenses.
It is important for individuals to familiarize themselves with the specific statutes or ordinances in their jurisdiction to understand the potential fines, tickets, and penalties associated with certain offenses. This knowledge can help individuals make informed decisions and avoid unnecessary legal trouble.
To stay up-to-date on this topic, individuals should regularly review and verify the statutes or ordinances relevant to their jurisdiction. Local government websites, legal databases, and consulting with legal professionals can provide accurate and current information. It is crucial to remember that laws and regulations can change over time, so regular updates are necessary.
In conclusion, understanding minor violations of state statutes or local ordinances, including fines, tickets, and penalties, is essential for individuals to navigate the legal system responsibly. Staying informed about the specific laws and regulations in one’s jurisdiction is crucial for making informed decisions and avoiding unnecessary legal consequences. To ensure accuracy, individuals should always verify and contrast the content of this article with current laws and regulations in their jurisdiction.
