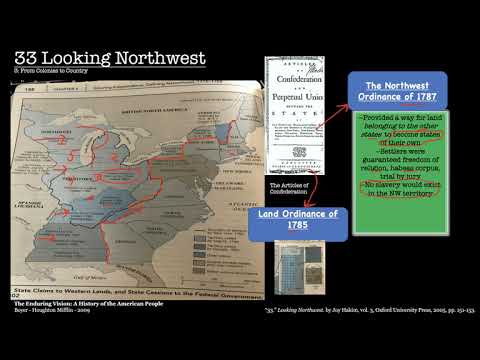
Understanding the Land Ordinance of 1785: Its Purpose and Impact on United States Citizens
Greetings! Today, we will delve into the intriguing topic of the Land Ordinance of 1785. This historic legislation played a significant role in shaping the United States as we know it today. In this article, we will explore the purpose behind this ordinance and the impact it had on American citizens. So, let’s dive in!
📋 Content in this article
What is the Land Ordinance of 1785?
The Land Ordinance of 1785 was a law passed by the United States Congress that established a systematic way to survey and distribute land in the newly formed territories of the United States. This ordinance was a critical step in organizing and developing the vast territories acquired by the United States after the Revolutionary War.
The Purpose of the Land Ordinance
The primary purpose of the Land Ordinance of 1785 was to provide a fair and efficient system for distributing land to settlers and generating revenue for the federal government. The government aimed to avoid the chaos and disputes that had arisen in previous land distribution efforts. The orderly settlement of these territories was seen as crucial to the success and stability of the young nation.
The Impact on United States Citizens
1. Land Surveying: The Land Ordinance called for a standardized system for surveying land, leading to the creation of the Public Land Survey System (PLSS). This system divided land into a grid-like pattern of townships, sections, and ranges, simplifying land ownership records and providing an efficient way to locate and describe parcels of land.
2. Land Sales: Under the Land Ordinance, land was to be sold in townships, with each township containing 36 sections, and each section encompassing 640 acres. This provided opportunities for individuals to purchase affordable land directly from the government, encouraging westward expansion and promoting economic growth.
3. Educational Funding: Another significant impact of the Land Ordinance was the provision for setting aside one section of land in each township for public education. This foresight ensured that future generations would have access to education, highlighting the importance the founders placed on knowledge and civic participation.
4. Land Use Planning: The Land Ordinance of 1785 also included provisions for reserving sections of land for specific purposes, such as supporting religious institutions or assisting veterans of the Revolutionary War. This demonstrated a deliberate effort to balance individual land ownership with communal needs and societal goals.
In conclusion, the Land Ordinance of 1785 was a landmark legislation that laid the foundation for organized land distribution and development in the United States. It provided a systematic approach to surveying, selling, and utilizing land, setting the stage for westward expansion, economic opportunity, and access to education. The impact of this ordinance can still be seen today in the PLSS system and the legacy of public lands across the nation.
The Impact of the Land Ordinance of 1785 on the United States: A Comprehensive Analysis
Understanding the Land Ordinance of 1785: Its Purpose and Impact on United States Citizens
The Land Ordinance of 1785 was a crucial piece of legislation that shaped the development of the United States. This comprehensive analysis aims to provide a clear understanding of the purpose and impact of this historic ordinance.
1. The Purpose of the Land Ordinance:
The Land Ordinance of 1785 was enacted by the Continental Congress as a means to organize and sell western lands acquired through the Treaty of Paris in 1783. The primary goal was to establish a systematic process for surveying, dividing, and selling these lands.
The ordinance introduced the Rectangular Survey System, also known as the Public Land Survey System (PLSS). This system divided land into square townships, each measuring six miles by six miles. Each township was further divided into 36 sections, each measuring one square mile.
Under this method, townships were numbered from north to south and ranges were numbered from east to west. This facilitated the identification and location of specific tracts of land.
The ordinance specified that four sections within each township would be reserved for public use. One section was reserved for schools, while three others were set aside for future sale or lease to support public education.
2. The Impact on United States Citizens:
The Land Ordinance of 1785 had a profound impact on the development and settlement of the United States.
By establishing a clear framework for surveying and selling western lands, the ordinance encouraged westward migration and settlement. It provided an opportunity for individuals and families to acquire land at affordable prices, leading to the expansion of agricultural activities and the growth of new communities.
The reservation of one section of each township for schools helped promote education in newly settled areas. The revenue generated from the sale or lease of the other three reserved sections supported the establishment and maintenance of public schools, contributing to the overall growth of education in the United States.
The Land Ordinance enabled citizens to acquire land and establish ownership rights. This ownership not only provided a sense of stability and security but also acted as a catalyst for economic growth. Landowners could use their property as collateral for loans, invest in agriculture or other ventures, and contribute to the expansion of the national economy.
The Purpose and Significance of the Land Ordinance of 1787: A Comprehensive Analysis
Understanding the Land Ordinance of 1785: Its Purpose and Impact on United States Citizens
The Land Ordinance of 1785 was a pivotal piece of legislation that played a significant role in the development and expansion of the United States. This comprehensive ordinance established a systematic method for surveying and selling land in the newly acquired western territories. It laid the foundation for westward expansion and the distribution of land to settlers, thereby shaping the future of the nation.
The Purpose of the Land Ordinance of 1785:
– The primary purpose of the Land Ordinance of 1785 was to create a standardized system for surveying and selling public land. The United States government needed to establish an organized way of distributing these lands to finance the growing nation’s debts incurred during the Revolutionary War.
– The ordinance aimed to provide a fair and transparent process for private individuals or groups to purchase the public lands, encouraging settlement and economic growth in the western territories.
– By setting clear guidelines for surveying and numbering plots of land, the ordinance intended to prevent disputes over property boundaries and establish a reliable system for land ownership.
The Impact on United States Citizens:
– The Land Ordinance of 1785 opened up vast opportunities for ordinary citizens to acquire and own land in the western territories. It allowed for the purchase of land in units known as townships, which were divided into smaller sections. Each section measured one square mile or 640 acres.
– The availability of affordable land through this ordinance attracted thousands of settlers, including farmers, miners, and entrepreneurs, seeking new opportunities and a chance to build a better future for themselves and their families.
– The orderly surveying and numbering system introduced by the Land Ordinance ensured that land parcels were accurately recorded and documented. This helped establish a clear legal framework for property rights, enabling individuals to secure ownership and transfer land with confidence.
Key Features of the Land Ordinance of 1785:
– The ordinance divided the western territories into a grid-like pattern, establishing a uniform system for land surveying and numbering.
– Townships, measuring six miles square, were the primary units of land division, further divided into 36 smaller sections.
– The northeast section of each township, known as Section 16, was reserved for public education.
– The sale of land was conducted through public auctions, allowing individuals to bid on available plots within the designated townships.
– The minimum price for each acre of land was set at $1, ensuring affordability for potential buyers.
The Impact of the Land Ordinance 1785 on Public Education: A Comprehensive Analysis
Understanding the Land Ordinance of 1785: Its Purpose and Impact on United States Citizens
The Land Ordinance of 1785, also known as the Northwest Ordinance, was a significant piece of legislation passed by the Continental Congress during the early years of the United States. It laid the groundwork for the orderly settlement and development of the western territories.
Purpose of the Land Ordinance:
The primary purpose of the Land Ordinance of 1785 was to establish a system for surveying and selling public lands in the newly acquired territories west of the Appalachian Mountains. The Congress recognized the need to organize and distribute these lands in a fair and predictable manner, which would incentivize settlement and promote economic growth.
Surveying and Grid System:
One of the key provisions of the Land Ordinance was the establishment of a surveying system that divided the land into a grid-like pattern. This system allowed for the systematic and efficient mapping of the townships, which were then further divided into sections. Each section consisted of 640 acres, further divided into quarter-sections of 160 acres.
Sale and Distribution of Public Lands:
Under the Land Ordinance, public lands were to be sold through public auctions. The minimum price for these lands was set at one dollar per acre. This ensured that the land was affordable for potential settlers while also generating revenue for the federal government. The proceeds from these land sales were designated for public education.
Impact on Public Education:
Perhaps one of the most far-reaching consequences of the Land Ordinance was its impact on public education. The Ordinance set aside one section of each township (approximately 640 acres) for the establishment of public schools. This was a visionary provision that recognized the importance of education in fostering an informed citizenry and ensuring the success of the new nation.
Encouraging Settlers:
By setting aside sections of land for public education, the Land Ordinance also aimed to attract settlers to the western territories. The presence of public schools provided a strong incentive for families to move to these areas, as it ensured access to education for their children. This, in turn, helped promote the growth and development of these frontier communities.
Legacy of the Land Ordinance:
The Land Ordinance of 1785 laid the foundation for the expansion of the United States beyond the original thirteen colonies. Its provisions for surveying, selling, and distributing public lands not only facilitated westward expansion but also had a lasting impact on the development of public education in America.
In conclusion, the Land Ordinance of 1785 played a crucial role in shaping the future of the United States. By establishing a systematic approach to surveying and distributing public lands, it promoted westward expansion and provided a framework for the establishment of public education. Its legacy continues to be felt today, as the impact of this legislation is still evident in our nation’s land use practices and educational system.
Understanding the Land Ordinance of 1785: Its Purpose and Impact on United States Citizens
Introduction:
The Land Ordinance of 1785 was a significant piece of legislation passed by the Continental Congress during the early years of the United States. This historic ordinance laid the groundwork for the organized and systematic surveying and sale of public lands in the newly formed nation. In this article, we will explore the purpose of the Land Ordinance of 1785 and its impact on United States citizens. It is important to note that while every effort has been made to provide accurate and reliable information, readers are encouraged to verify and contrast the content of this article with other credible sources.
Understanding the Purpose:
The Land Ordinance of 1785 was designed to establish a uniform system for surveying and selling the vast tracts of public land that had come under federal control after the American Revolution. The primary goals of this ordinance were to promote westward expansion, encourage settlement, and generate revenue for the young nation.
Under this ordinance, the territory west of the original 13 colonies was divided into a grid-like system known as the Public Land Survey System (PLSS). This system created a series of townships, each measuring six miles by six miles, which were further divided into 36 sections, each comprising one square mile or 640 acres. The land was then made available for purchase through public auctions.
Impact on United States Citizens:
The Land Ordinance of 1785 had several significant impacts on United States citizens:
1. Encouraging Westward Expansion: By providing a clear framework for surveying and selling public lands, the ordinance played a crucial role in promoting westward expansion. It allowed settlers to acquire land easily, thereby incentivizing migration towards previously uncharted territories.
2. Economic Development: The sale of public lands generated significant revenue for the federal government, which was used to pay off war debts and fund various public infrastructure projects. This boost in economic development helped spur the growth of young towns and cities across the expanding nation.
3. Land Distribution and Ownership: The Public Land Survey System established by the ordinance ensured that land was divided and distributed in an organized and equitable manner. It allowed for the establishment of private property rights, which was crucial for encouraging settlement and the development of a stable agricultural economy.
4. Local Government and Education: The Land Ordinance of 1785 also set aside one section of each township for the benefit of local schools. This provision, known as the “school section,” helped promote education and the establishment of local governments in newly settled areas.
Staying Up-to-Date:
While the Land Ordinance of 1785 has had a lasting impact on the United States, it is essential to stay up-to-date on this topic. As our understanding of history evolves and new research emerges, it is crucial to verify and contrast the content of this article with other credible sources. Historians, scholars, and experts continue to uncover new insights into the Land Ordinance of 1785 and its significance, making it important to remain informed about any developments in this field.
Conclusion:
The Land Ordinance of 1785 played a pivotal role in shaping the early years of the United States. By establishing a uniform system for surveying and selling public lands, it encouraged westward expansion, fueled economic development, facilitated land distribution and ownership, and promoted education and local governance. As with any historical topic, it is important to stay informed and verify information to ensure an accurate understanding of the Land Ordinance of 1785 and its impact on United States citizens.
