Dear reader,
Welcome to this informative article on the legal framework of Britain, specifically focusing on the Constitution. In this piece, we will explore the key aspects of the British Constitution, its sources, and its impact on the legal system. Let’s dive in!
📋 Content in this article
1. Introduction to the British Constitution:
Unlike many countries, Britain does not have a single, written constitution. Instead, its constitution is a collection of laws, statutes, and customs that have developed over centuries. The British Constitution is often referred to as an unwritten or uncodified constitution.
2. Sources of the British Constitution:
The British Constitution draws its authority from various sources, including:
– Statutes: Acts of Parliament play a crucial role in shaping the constitutional framework. Key statutes, such as the Magna Carta of 1215 and the Human Rights Act of 1998, have had a significant impact on the development of constitutional principles.
– Common Law: Judicial decisions made by courts over time have contributed to the formation of constitutional principles. Precedents set by landmark cases play an important role in interpreting and defining constitutional rights and obligations.
– Conventions: Conventions are unwritten rules and practices that are followed out of tradition and respect for custom. They are not legally binding but have a substantial influence on how the government functions. Examples include the Prime Minister’s resignation after losing an election and the monarch’s role in appointing the Prime Minister.
3. Flexibility and Evolution:
One notable feature of the British Constitution is its flexibility. Unlike written constitutions that require formal amendment processes, the British Constitution can evolve and adapt to changing circumstances more easily. This flexibility allows for gradual changes to be made through legislation or judicial interpretation.
4. Parliamentary Sovereignty:
A fundamental concept in the British Constitution is parliamentary sovereignty. This means that Parliament is the supreme law-making body, and its laws are binding on all individuals and institutions within the country. Parliamentary sovereignty limits the power of the judiciary to invalidate legislation passed by Parliament.
5. Devolution:
Devolution is a key aspect of the British Constitution, granting varying degrees of legislative power to the devolved nations of Scotland, Wales, and Northern Ireland. These regions have their own elected assemblies or parliaments, which have the authority to make laws on certain issues.
In conclusion, the British Constitution is a unique legal framework that has evolved over centuries. Its sources include statutes, common law, and conventions. Flexibility, parliamentary sovereignty, and devolution are key concepts that shape the operation of the British Constitution. Understanding these fundamental aspects is crucial for comprehending the legal system in Britain.
Thank you for taking the time to delve into this topic with us. We hope this article has provided you with a clear introduction to the legal framework of Britain and its Constitution.
Understanding the Structure of the Legal System in the UK
Understanding the Legal Framework: The Constitution of Britain
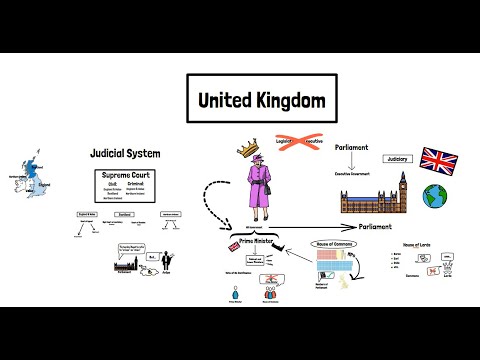
The legal system in the United Kingdom (UK) is governed by a complex framework that encompasses various statutes, common law principles, and constitutional conventions. At the core of this legal framework is the Constitution of Britain, which serves as the foundation for the country’s governance and legal structure.
1. Unwritten Constitution
Unlike many other countries, the UK does not have a single, written constitution. Instead, its constitution is largely based on a combination of statutes, judicial decisions, and constitutional conventions. This unique characteristic makes the UK’s constitution flexible and adaptable to changing circumstances.
2. Sources of Constitutional Law
The Constitution of Britain draws its authority from several key sources:
3. Separation of Powers
The UK follows a system of parliamentary democracy, where power is divided among three branches of government:
4. Devolved Powers
In addition to the central government, certain powers have been devolved to regional governments in Scotland, Wales, and Northern Ireland. These devolved governments have the authority to make decisions on specific policy areas, such as healthcare, education, and transportation, within their respective regions.
5. European Union and Brexit
It is important to note that until January 31, 2020, the UK was a member of the European Union (EU). EU law had direct effect in the UK, and decisions of the European Court of Justice were binding. However, following a referendum in 2016, the UK voted to leave the EU. This process, known as Brexit, has resulted in significant changes to the UK’s legal framework.
In conclusion, understanding the legal framework in the UK revolves around comprehending the unique nature of its unwritten constitution, the sources of constitutional law, the separation of powers, devolved powers, and the impact of Brexit. By familiarizing yourself with these key concepts, you can navigate the UK’s legal system more effectively.
Understanding the Principle of the British Constitution: A Comprehensive Analysis
Understanding the Legal Framework: The Constitution of Britain
The Constitution of Britain: An Overview
The Constitution of Britain refers to the set of fundamental principles and rules that govern the political system of the United Kingdom. Unlike many other countries, Britain does not have a single written constitution codified in a single document. Instead, its constitution is a combination of statutes, common law, constitutional conventions, and European Union law (prior to Brexit).
The Principle of Parliamentary Supremacy
One of the key principles of the British Constitution is parliamentary supremacy. This means that Parliament is the supreme law-making body and has the power to make, amend, or repeal laws. No other institution, including the courts, can override or invalidate an Act of Parliament.
The Role of Constitutional Conventions
Constitutional conventions are unwritten rules that guide the behavior and actions of constitutional actors, such as the Prime Minister, Cabinet, and the Monarch. Although not legally binding, these conventions have significant political and constitutional importance. They help maintain the balance of power between different branches of government and ensure the smooth functioning of the constitutional framework.
The Role of Common Law
Common law plays a vital role in the British Constitution. It refers to legal principles developed by judges through their decisions in court cases over centuries. These principles form precedents that guide future judicial decisions. Common law helps fill gaps in statutory law and provides flexibility to adapt to changing societal needs.
Human Rights and the Constitution
In recent years, human rights have become an integral part of the British Constitution. The Human Rights Act 1998 incorporates the European Convention on Human Rights into domestic law. This ensures that individuals in the UK have certain fundamental rights and freedoms protected by law.
Devolution and the Constitution
Devolution refers to the transfer of powers from central government to regional bodies or governments. In the UK, devolution has led to the establishment of legislative bodies in Scotland, Wales, and Northern Ireland. These bodies have the authority to make laws on certain matters within their respective jurisdictions, while the UK Parliament retains authority over reserved matters.
Understanding the legal framework of the Constitution of Britain is crucial for individuals and businesses alike. It provides a foundation for understanding their rights and duties within the UK’s political and legal system. By grasping these concepts, individuals can make informed decisions and effectively navigate legal issues that may arise.
Understanding the Role of the Constitution as the Foundation of Our Nation
Understanding the Legal Framework: The Constitution of Britain
The Constitution of Britain serves as the legal framework that governs the nation and its people. It establishes the fundamental principles, structures, and functions of the government, ensuring stability, order, and protection of individual rights. This article aims to provide a detailed explanation of the role of the Constitution in Britain and highlight its significance in shaping the nation’s legal system.
1. Definition and Purpose:
The Constitution of Britain refers to a set of principles and laws that dictate the governance and functioning of the country. Unlike some countries, Britain does not have a single written constitution; instead, it relies on a combination of statutes, common law principles, and constitutional conventions. The purpose of the Constitution is to provide a legal framework that defines the powers and limitations of different branches of government, protects individual rights, and ensures the rule of law.
2. Sources of the Constitution:
The British Constitution draws from several sources, including:
a. Statutes: Statutes are laws enacted by Parliament and are considered to be one of the primary sources of the Constitution. These laws provide specific rules and regulations that govern various aspects of public life, such as human rights, constitutional reforms, and devolution.
b. Common Law: Common law refers to legal principles derived from court decisions and customs rather than legislative statutes. It plays a significant role in interpreting and developing constitutional principles and filling in gaps where there is no specific legislation.
c. Constitutional Conventions: Constitutional conventions are unwritten rules and practices that have evolved over time and are considered binding. They govern areas not covered by statutes or common law. Conventions help maintain political stability by ensuring the smooth functioning of government institutions.
3. Key Features:
a. Parliamentary Sovereignty: One of the fundamental principles of the British Constitution is parliamentary sovereignty. This means that Parliament has the ultimate authority to make and change laws, and no other body can override or challenge its decisions. However, this principle has been somewhat modified due to the UK’s membership in the European Union and the enactment of the Human Rights Act 1998.
b. Separation of Powers: The British Constitution does not have a strict separation of powers like some other countries. Instead, it follows a system of checks and balances, where powers are shared between the executive, legislative, and judicial branches. This allows each branch to exercise some control over the others and prevents any one branch from becoming too powerful.
c. Protection of Individual Rights: While Britain does not have a comprehensive Bill of Rights like the United States, the Constitution provides certain protections for individual rights. These rights are derived from common law principles and international human rights treaties. The Human Rights Act 1998 incorporates the European Convention on Human Rights into domestic law, allowing individuals to seek redress for violations of their rights in domestic courts.
4. Flexibility of the Constitution:
One notable characteristic of the British Constitution is its flexibility. Unlike a rigid constitution, which requires formal amendment procedures, the British Constitution can be changed through ordinary legislation. Parliament has the power to amend or repeal any existing laws or enact new ones without any special procedures. This flexibility allows the Constitution to adapt to changing circumstances and evolving societal needs.
In conclusion, understanding the Constitution of Britain is crucial for comprehending the legal framework that governs the nation. It serves as a guiding document that establishes principles, structures, and functions of the government while safeguarding individual rights. Despite its unwritten nature, the British Constitution is a vital aspect of the nation’s legal system, providing flexibility while ensuring stability and the rule of law.
Understanding the Legal Framework: The Constitution of Britain
As a seasoned attorney in the U.S., I recognize the importance of staying up-to-date on legal frameworks not only within my own jurisdiction but also on an international level. One such legal framework that holds significant value is the Constitution of Britain.
The Constitution of Britain serves as a foundational document that outlines the principles, powers, and structure of the British government. It establishes and defines the rights and responsibilities of both the government and its citizens. While Britain does not possess a single written constitution like the United States, its constitutional framework is derived from a combination of statutes, common law, conventions, and international treaties.
Understanding the Constitution of Britain is crucial for several reasons. First and foremost, it provides a framework for government actions and ensures that power is not concentrated in the hands of a few individuals or entities. This separation of powers and system of checks and balances helps protect individual rights and liberties, preventing abuse of authority.
Additionally, a sound understanding of the British Constitution is necessary for legal professionals who engage in transnational legal matters. Many countries, including the United States, have legal systems influenced by or modeled after the British legal tradition. Familiarity with the British Constitution helps attorneys navigate complex legal issues involving comparative law, international treaties, and human rights.
To stay well-informed about the Constitution of Britain, it is essential to refer to reliable and authoritative sources. Primary sources such as the statutes enacted by Parliament, judicial decisions, and official government publications provide a solid foundation for understanding the legal framework. Legal textbooks, articles written by legal scholars, and reputable online resources can also offer valuable insights into the intricacies of this complex system.
However, it is crucial to note that while this article strives for accuracy and reliability, readers should independently verify and contrast its content with other sources. The law is constantly evolving, and interpretations may vary among legal professionals. Consulting multiple sources and engaging in critical analysis is essential to ensure a comprehensive understanding of the subject matter.
In conclusion, understanding the Constitution of Britain is of utmost importance for legal professionals who deal with international matters and comparative law. It serves as a fundamental legal framework that shapes the British government and protects individual rights. Staying up-to-date on this topic ensures competence in legal practice and promotes a broader understanding of legal systems worldwide.
