Greetings! Today, we are going to delve into the fascinating world of zoning in storage. Zoning is an essential concept in urban planning and is crucial in determining how land and buildings can be used in a particular area. In this comprehensive guide, we will explore the various types of zoning that can be applied to storage facilities. So, let’s get started!
Understanding the Different Types of Zoning in Storage: A Comprehensive Guide
Understanding the Types of Zoning in Storage: A Comprehensive Guide
📋 Content in this article
Introduction:
When it comes to storage facilities, understanding the different types of zoning is crucial. Zoning regulations determine how land and buildings can be used, and they play a vital role in ensuring the safety, functionality, and compatibility of storage facilities with their surrounding communities. This comprehensive guide aims to provide an overview of the various types of zoning that may apply to storage facilities in the United States.
1. Residential Zoning:
Residential zoning is the most common type of zoning and is typically intended for housing purposes. In areas zoned for residential use, storing goods or running a commercial storage facility might not be permitted. However, there may be exceptions or special permits available for limited storage in some residential zones.
2. Industrial Zoning:
Industrial zoning is designed for manufacturing, warehousing, and other industrial activities. Storage facilities often fall under this zoning category since they involve the storage and distribution of goods. Industrial zones generally have fewer restrictions on storage operations compared to residential areas.
3. Commercial Zoning:
Commercial zoning is primarily for businesses engaged in retail, office, or service-related activities. While storage facilities may not be the primary use within a commercial zone, they are often allowed as accessory uses or with specific regulations in place. It is essential to review local ordinances to determine if storage facilities are permitted within a specific commercial zone.
4. Mixed-Use Zoning:
Mixed-use zoning allows for a combination of different land uses within a single area. These zones typically include a mix of residential, commercial, and sometimes industrial uses. Depending on local regulations, storage facilities may be allowed as long as they do not disrupt the overall character and functionality of the area.
5. Rural or Agricultural Zoning:
Rural or agricultural zoning is common in areas with large swaths of open land and agricultural activities. In such zones, storage facilities may face restrictions due to the preservation of agricultural land or the desire to maintain a rural character. However, some rural areas may have specific provisions for storage facilities related to agriculture, such as farm equipment storage.
6. Special Use Permits:
In certain cases, it may be possible to obtain a special use permit or variance that allows storage facilities in zones where they are not typically permitted. These permits often require a thorough review process, during which factors like traffic, environmental impact, and compatibility with the surrounding area are evaluated.
Understanding Storage Zones: A Comprehensive Guide
Understanding Storage Zones: A Comprehensive Guide
Storage zones play a crucial role in the world of storage facilities. Whether you are a business owner looking for a place to store your inventory or an individual in need of extra space, understanding storage zones is essential. This comprehensive guide aims to clarify the concept of storage zones and provide valuable insights into the different types of zoning in storage.
Storage zones are designated areas within a storage facility that are categorized based on various factors such as purpose, security, and accessibility. These zones are designed to meet specific storage needs and provide an organized structure within the facility.
Storage zones serve a vital purpose in ensuring efficient operations within a storage facility. They help optimize space utilization, streamline inventory management, and enhance security measures. By categorizing different types of storage areas, both businesses and individuals can easily locate their belongings and maintain an organized system.
1. Access Zones: These zones are typically located near the entrance of the storage facility and are easily accessible to customers. Access zones often house items that require frequent retrieval or quick access, such as seasonal inventory or personal belongings.
2. Climate-Controlled Zones: These zones are specially designed to maintain a consistent temperature and humidity level. Climate-controlled storage zones are ideal for storing delicate and sensitive items such as artwork, electronics, and important documents.
3. Drive-Up Zones: These zones are easily accessible by vehicles, allowing customers to conveniently load and unload their belongings. Drive-up zones are commonly used for storing large items such as furniture or vehicles that require easy access.
4. Bulk Storage Zones: These zones are dedicated to storing large quantities of items that may not require frequent access. Bulk storage zones are often used by businesses to store excess inventory, equipment, or materials.
5. Specialized Zones: These zones cater to specific storage needs and may include areas such as wine storage, vehicle storage, or commercial storage for businesses with unique requirements.
When selecting a storage facility, it is important to consider the types of storage zones offered and evaluate which ones align with your specific needs. Factors such as the nature of your belongings, frequency of access required, and level of security desired should be considered when determining the most suitable storage zones for your requirements.
Understanding Port Zoning vs. WWN Zoning in Networking: A Comprehensive Comparison
Understanding the Types of Zoning in Storage: A Comprehensive Guide
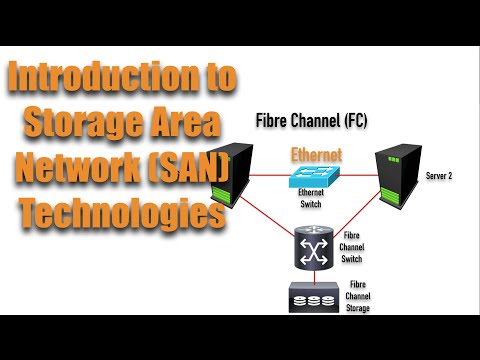
Zoning is a crucial concept in storage networking that allows for the efficient and secure management of data. It involves dividing a storage area network (SAN) into separate zones, each with its own set of devices and resources. By implementing zoning, organizations can control and manage access to their storage resources, ensuring that only authorized devices are allowed to communicate with specific storage devices or network ports.
When it comes to storage zoning, two common types are Port Zoning and WWN (World Wide Name) Zoning. Let’s explore the differences between these two types and understand their unique features and advantages.
Port Zoning:
Port Zoning, also known as fabric-based zoning, is a type of zoning where devices are grouped together based on the physical ports they are connected to in the SAN fabric. In Port Zoning, a switch port acts as a boundary for each zone, and devices connected to that port belong to that specific zone. This means that all devices connected to the same switch port can communicate with each other, while communication between devices in different zones is restricted.
Here are some key points about Port Zoning:
However, there are some considerations to keep in mind with Port Zoning:
WWN Zoning:
WWN Zoning, also known as name-based zoning, is a type of zoning where devices are grouped together based on their unique World Wide Names (WWNs). WWNs are unique identifiers assigned to devices in a SAN, similar to a MAC address in Ethernet networks. In WWN Zoning, devices with matching WWNs are placed in the same zone, ensuring that they can communicate with each other.
Here are some key points about WWN Zoning:
However, there are some considerations to keep in mind with WWN Zoning:
In conclusion, both Port Zoning and WWN Zoning offer different approaches to zoning in storage networking. Port Zoning provides simplicity and granular control based on physical connectivity, while WWN Zoning offers flexibility and scalability based on device characteristics. The choice between these types of zoning depends on the specific needs and requirements of an organization’s storage environment. Consulting with a qualified professional can help determine the most suitable approach for your storage networking needs.
Understanding the Types of Zoning in Storage: A Comprehensive Guide
As our society continues to evolve and expand, the need for storage facilities has become increasingly important. Whether it is for personal use or business purposes, having access to a secure and well-maintained storage unit can alleviate many common challenges associated with limited space. However, it is crucial to have a solid understanding of the types of zoning regulations that govern the establishment and operation of storage facilities.
Zoning regulations are laws enacted by local government bodies to regulate land use within a specific jurisdiction. These regulations are designed to ensure that different types of land use are appropriately separated and that the surrounding areas are protected from nuisances and adverse impacts. When it comes to storage facilities, there are typically three primary types of zoning classifications: residential, commercial, and industrial.
1. Residential Zoning:
Residential zoning is primarily intended for housing purposes. It is designed to create a peaceful and harmonious environment for residents. Storage facilities are generally not permitted in areas zoned for residential use due to concerns about noise, traffic, and the potential negative impact on property values. However, some municipalities may allow limited storage units within residential areas, subject to certain restrictions and conditions.
2. Commercial Zoning:
Commercial zoning is designated for areas where businesses and commercial activities can operate. Depending on local regulations, storage facilities may be allowed in commercially zoned areas with proper permits and compliance with set standards. However, the specific requirements can vary significantly from one jurisdiction to another. It is essential to consult local zoning ordinances and obtain any necessary permits before establishing a storage facility in a commercial zone.
3. Industrial Zoning:
Industrial zoning is typically reserved for heavy industrial activities, manufacturing plants, and warehouses. These areas are often located away from residential neighborhoods due to potential noise, pollution, and safety concerns. Unlike residential or commercial zoning, industrial zoning usually allows for the operation of larger-scale storage facilities without significant restrictions. However, it is essential to understand that industrial zoning regulations can vary significantly between jurisdictions. Compliance with all local regulations is crucial to avoid legal issues and potential penalties.
It is important to emphasize that zoning regulations can vary significantly from one jurisdiction to another. It is advisable to verify the specific zoning requirements and limitations imposed by the local government before establishing or operating a storage facility. Consulting with a qualified attorney or land use professional who specializes in zoning issues can provide valuable guidance and ensure compliance with all relevant regulations.
In conclusion, understanding the types of zoning regulations that apply to storage facilities is of utmost importance for anyone considering entering this industry. Residential, commercial, and industrial zoning each have their own set of regulations and restrictions that must be carefully adhered to. Staying up-to-date on these regulations and seeking professional advice when needed can help to ensure a successful and legally compliant operation.
