Understanding the Types of Delegated Legislation: A Comprehensive Guide to Orders in Council
Greetings, dear readers! Today, we embark on a journey to explore the intricate world of delegated legislation, with a specific focus on a fascinating type called “Orders in Council.” Whether you’re a law student, legal professional, or an individual simply curious about the inner workings of the legal system, this comprehensive guide aims to provide you with a clear understanding of this important legal concept.
📋 Content in this article
Delegated legislation refers to laws or regulations that are made by individuals or bodies other than the primary legislative body, such as Parliament. It is an essential component of modern governance, allowing for the efficient and effective implementation of laws and policies.
Orders in Council are a specific form of delegated legislation used primarily in countries with a parliamentary system of government, such as the United Kingdom, Canada, Australia, and New Zealand. They are made by the executive branch of government and authorized under statutory powers granted to them by Acts of Parliament.
So, what exactly are Orders in Council?
Orders in Council are legal instruments that allow the government to make laws or regulations without the need for parliamentary approval. They are typically used to enact legislation in urgent situations where waiting for Parliament to pass a law would be impractical or impossible. Additionally, Orders in Council are commonly used when implementing international agreements or treaties into domestic law.
How are Orders in Council made?
The process of making an Order in Council varies depending on the country and its legal framework. Typically, an Order in Council is drafted by government officials within the relevant department or ministry. The draft is then reviewed by legal advisors to ensure its compliance with existing laws and policies.
Once the draft Order in Council is finalized, it is presented to the executive authority for approval. In some cases, this authority may be the President or Prime Minister, while in others it may be a specific council or committee designated for this purpose.
After approval, the Order in Council is signed by the relevant authority and becomes legally binding. It is usually published in official government gazettes or similar publications to inform the public of its existence.
What are the key features of Orders in Council?
Orders in Council typically possess certain characteristics that distinguish them from other forms of delegated legislation:
1. Speed and Flexibility: By allowing the executive branch to enact laws quickly, Orders in Council enable a swift response to urgent situations or changing circumstances.
2. Temporary Nature: In most cases, Orders in Council have a limited duration and are automatically revoked after a specified period unless they are explicitly renewed or confirmed by Parliament.
3. Wide-Ranging Powers: Orders in Council can grant the government broad powers to make regulations on a wide range of matters, such as taxation, national security, public health, and many other areas necessary for governing a nation effectively.
4. Parliamentary Scrutiny: Although Orders in Council can bypass the usual parliamentary approval process, they are subject to parliamentary scrutiny. This ensures transparency and accountability in their use.
In conclusion, Orders in Council play a crucial role in the delegated legislation process. They enable governments to respond swiftly to emergencies, implement international obligations, and efficiently address complex policy issues. While their use may vary between jurisdictions, understanding the concept of Orders in Council provides valuable insight into the functioning of modern legal systems.
We hope this comprehensive guide has shed light on this intriguing aspect of delegated legislation. If you have any further questions or would like to explore related topics, don’t hesitate to consult legal professionals or engage in further research through reputable sources. Happy exploring!
Understanding the Aylesbury Mushroom Case: A Detailed Analysis
Understanding the Types of Delegated Legislation: A Comprehensive Guide to Orders in Council
Delegated legislation refers to laws made by bodies other than the legislative branch of government. These bodies typically include ministers, government departments, and local authorities. The purpose of delegated legislation is to allow for more efficient and flexible law-making, as it can address specific details and technical aspects that may be impractical for the legislative branch to handle.
One important form of delegated legislation is an Order in Council. An Order in Council is a legal instrument issued by the executive branch of government, usually at a national level. It is used to implement laws, regulations, or policies without the need for parliamentary approval. Orders in Council are often used in emergency situations when quick action is required, or when the issue at hand falls within the expertise of the executive branch.
Here are some key points to understand about Orders in Council:
1. Legal Authority: Orders in Council derive their legal authority from enabling legislation passed by the legislative branch. This legislation grants ministers or government departments the power to make regulations or rules through Orders in Council.
2. Scope and Content: Orders in Council can cover a wide range of matters, such as public health, transportation, and national security. They can set out specific requirements, procedures, or restrictions on individuals or organizations. The content of an Order in Council can vary depending on the issue it addresses.
3. Emergency Powers: Orders in Council are often used during times of emergency or crisis when there is insufficient time for the regular legislative process. For example, during a pandemic, an Order in Council may be issued to implement measures such as travel restrictions or mandatory quarantine.
4. Parliamentary Scrutiny: Although Orders in Council bypass the usual parliamentary approval process, they are subject to parliamentary scrutiny. This means that they can be examined and debated by members of parliament. However, this scrutiny usually takes place after the Order in Council has come into effect.
5. Sunset Clauses and Review: Some Orders in Council have built-in sunset clauses, which means they automatically expire after a certain period unless renewed or replaced. Others may require periodic review to ensure their continued relevance and effectiveness.
6. Legal Challenges: Orders in Council can be challenged in court if they are believed to be ultra vires, meaning they exceed the legal authority granted to the issuing body. However, such challenges can be complex, and the court’s decision will depend on the specific circumstances and legal arguments presented.
Understanding the different types of delegated legislation, such as Orders in Council, is crucial for anyone engaging with the legal system. It is important to recognize their legal authority, scope, and implications. If you have any questions or concerns regarding Orders in Council or any other legal matters, it is advisable to consult with a qualified legal professional who can provide you with the necessary guidance.
Understanding the 4 Types of Delegated Legislation: A Comprehensive Guide
Understanding the 4 Types of Delegated Legislation: A Comprehensive Guide to Orders in Council
Delegated legislation refers to laws that are made by an authority other than the legislature. In the United States, this authority is typically granted to executive branch agencies and departments. One common form of delegated legislation is known as an Order in Council. In this comprehensive guide, we will explore the four types of delegated legislation and focus specifically on Orders in Council.
1. Orders in Council:
– An Order in Council is a type of delegated legislation that is made by the executive branch, specifically by the President or a Governor.
– It is often used to implement or supplement existing laws, or to address emergent issues that require immediate action.
– Orders in Council are typically used in situations where the legislature may not be able to act swiftly enough, such as during times of national emergency or when unexpected circumstances arise.
– These orders have the force of law and can have significant impact on individuals and organizations affected by them.
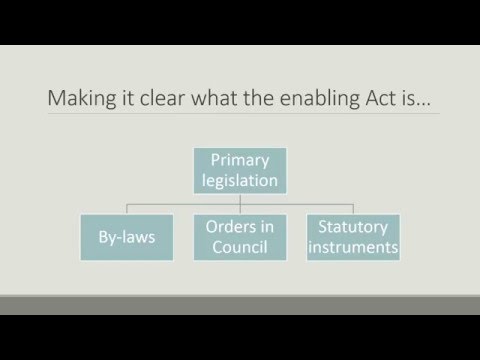
2. Statutory Instruments:
– Statutory Instruments are another type of delegated legislation, made by a Minister or other bodies with powers granted by statute.
– They are used to provide detailed regulations that support existing legislation.
– Statutory Instruments are often employed in areas where a high degree of technical expertise is required or where frequent updates to the law are necessary.
– They are subject to parliamentary scrutiny and can be challenged if they exceed the powers granted by the enabling statute.
3. Bylaws:
– Bylaws are delegated legislation made by local authorities, such as city councils or county boards.
– They are designed to address matters of local concern that may not be covered by general laws.
– Bylaws can regulate a wide range of issues, including zoning, noise control, public health, and licensing requirements.
– While they have the force of law within their jurisdiction, they cannot contradict or exceed the powers granted by higher-level legislation.
4. European Union Regulations:
– European Union (EU) Regulations are a type of delegated legislation that applies to member states of the EU.
– They are made by the European Commission and have a direct effect on member states, bypassing national legislatures.
– EU Regulations are binding and enforceable, and member states are required to incorporate them into their domestic laws.
– They cover a wide range of areas, including trade, agriculture, environmental protection, and consumer rights.
Understanding the different types of delegated legislation, such as Orders in Council, is essential for individuals and organizations that may be affected by these laws. The impact of delegated legislation can be significant and can have legal consequences. It is important to consult with legal professionals who specialize in administrative law to ensure compliance and to protect your rights.
Delegated legislation plays an important role in our legal system by allowing for more efficient and specialized lawmaking. However, it is also important to ensure that proper checks and balances are in place to prevent abuse of these powers. If you have questions about delegated legislation or need assistance navigating the legal implications of Orders in Council or other forms of delegated legislation, seek advice from an attorney with expertise in administrative law.
Understanding the Three Types of Delegated Legislation: A Comprehensive Guide
Understanding the Types of Delegated Legislation: A Comprehensive Guide to Orders in Council
Delegated legislation plays a vital role in the legal system of the United States. It refers to laws and regulations that are made by individuals or bodies other than the legislature, such as government ministers or agencies. One common form of delegated legislation is known as ‘Orders in Council’. In this comprehensive guide, we will explore the concept of Orders in Council, highlighting their importance and providing an understanding of the three types of delegated legislation.
1. What is Delegated Legislation?
Delegated legislation refers to laws and regulations that are made by someone other than the legislature. In the United States, this form of legislation is created by individuals or bodies that have been given the authority to do so by an Act of Congress. Delegated legislation is necessary as it allows for the detailed and technical aspects of laws to be developed and modified without requiring the attention and time of the legislature.
2. The Importance of Orders in Council:
Orders in Council are a specific type of delegated legislation that hold significant importance. They are made by the President or a government minister under powers granted to them by an Act of Congress. Orders in Council are usually used in situations where there is an urgent need for legislation, or when it is not practical for the full legislative process to be followed.
Orders in Council can be used to make laws on a wide range of issues, including matters related to national security, public health, and emergency situations. They provide a flexible and efficient way for the government to respond quickly to changing circumstances and address pressing issues without delay.
3. The Three Types of Delegated Legislation:
a) Statutory Instruments:
Statutory instruments are one type of delegated legislation that are made by government ministers under powers granted to them by an Act of Congress. They are used to fill in the details of an Act, providing specific regulations and rules that are necessary for the Act to be effectively implemented. Statutory instruments are often used to update and modify existing legislation without requiring a full amendment to the Act itself.
b) Bylaws:
Bylaws are another type of delegated legislation that are made by local authorities or other bodies that have been granted the power to do so by an Act of Congress. Bylaws are used to regulate specific matters within a local area, such as parking regulations or building standards. They are an important way for local authorities to address issues that are unique to their jurisdiction and ensure that laws are tailored to the specific needs of their community.
c) Orders in Council:
As mentioned earlier, Orders in Council are made by the President or a government minister under powers granted to them by an Act of Congress. They are used in situations where there is an urgent need for legislation or when a full legislative process would be impractical. Orders in Council can be used to address a wide range of issues and provide the government with the flexibility to respond quickly to changing circumstances.
In conclusion, understanding the types of delegated legislation, such as Orders in Council, is essential for anyone seeking a comprehensive understanding of the legal system in the United States. Delegated legislation plays an important role in filling in the details of Acts of Congress and addressing urgent and specific issues. By familiarizing themselves with the three types of delegated legislation – statutory instruments, bylaws, and Orders in Council – individuals can gain a deeper understanding of how laws are created and implemented in our country.
Please note that while this article provides a comprehensive overview, it is always advisable to consult with a legal professional for specific legal advice related to your situation.
Understanding the Types of Delegated Legislation: A Comprehensive Guide to Orders in Council
The realm of law is vast and intricate, filled with an enormous amount of information that is constantly evolving. As legal professionals, it is crucial to stay up-to-date on various topics, including delegated legislation. This article aims to provide a comprehensive guide specifically focusing on Orders in Council, a type of delegated legislation commonly used in the United States.
Before delving into the intricacies of Orders in Council, it is important to understand the concept of delegated legislation itself. Delegated legislation refers to laws or regulations that are made by individuals or bodies other than the legislature. These laws are authorized by an Act of Parliament and are typically used to fill in the details of a broader legislative framework.
Orders in Council are a specific type of delegated legislation that are made by the executive branch of the government. They are typically used to address matters of public policy or national importance that require immediate action and cannot wait for parliamentary approval. The authority to make Orders in Council is derived from specific enabling powers granted by an Act of Parliament.
Orders in Council can take various forms and serve different purposes. Some common examples include making changes to existing legislation, implementing international agreements, establishing administrative bodies, or reacting to emergency situations. They can also be used to transfer powers between government departments or modify existing regulatory frameworks.
When making an Order in Council, the executive branch must follow certain procedural requirements to ensure transparency and accountability. This typically involves consultation with relevant stakeholders and providing an opportunity for public input. However, the level of scrutiny and consultation may vary depending on the urgency and nature of the matter being addressed.
While Orders in Council can be an efficient way to address pressing issues, it is important to note that they are subject to certain limitations and safeguards. The power to make Orders in Council is granted by Parliament and can be restricted or repealed if deemed necessary. Additionally, Orders in Council must be consistent with the broader legislative framework and cannot override primary legislation.
Staying up-to-date on delegated legislation, including Orders in Council, is of utmost importance for legal professionals. The legal landscape is constantly evolving, and new Orders in Council may be introduced, modified, or repealed. As such, it is crucial to verify and contrast the content of this article with current legislation and consult reliable legal sources for the most accurate and up-to-date information.
In conclusion, understanding the types of delegated legislation, such as Orders in Council, is essential for legal professionals. By staying well-informed on this topic, practitioners can effectively navigate the complex legal landscape and provide valuable advice to their clients. However, it is crucial to always verify and contrast information with current legislation to ensure accuracy and reliability.
