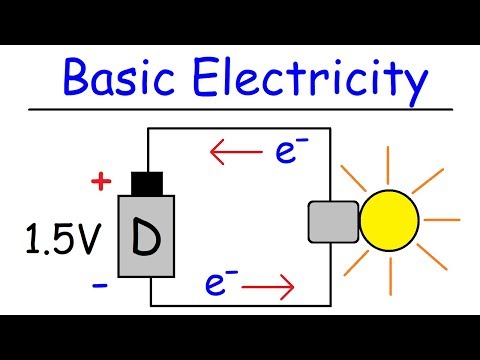
Welcome to this comprehensive overview of the three fundamental laws of electricity. In this article, we will delve into the essential principles that govern the behavior of electric charges and currents. By understanding these laws, you will gain valuable insights into how electricity functions and can be harnessed for various applications. So, let’s get started and explore the fascinating world of electricity!
Understanding the Three Key Principles of Electricity: A Comprehensive Guide
Understanding the Three Fundamental Laws of Electricity: A Comprehensive Overview
📋 Content in this article
Electricity is a fundamental aspect of our modern lives, powering our homes, businesses, and industries. However, the principles that govern electricity can often seem complex and intimidating. In this comprehensive overview, we will break down the three fundamental laws of electricity to help you gain a better understanding of this essential subject.
1. Ohm’s Law:
Ohm’s Law is a fundamental principle in electrical engineering and serves as the cornerstone for understanding the relationship between voltage, current, and resistance. It states that the current flowing through a conductor is directly proportional to the voltage applied across it and inversely proportional to the resistance offered by the conductor.
This law can be expressed using the formula: I = V / R
Where:
– I represents the current flow in Amperes (A)
– V represents the voltage in Volts (V)
– R represents the resistance in Ohms (Ω)
Understanding Ohm’s Law is crucial for determining the behavior of electrical circuits and calculating values such as current, voltage, and resistance.
2. Kirchhoff’s Laws:
Kirchhoff’s Laws are two basic principles that help analyze complex electrical circuits. These laws are named after Gustav Kirchhoff, a German physicist who formulated them in the mid-19th century.
a) Kirchhoff’s Current Law (KCL):
KCL states that the sum of currents entering a junction in an electrical circuit is equal to the sum of currents leaving that junction. In simpler terms, it emphasizes that current is conserved at any given point in a circuit.
b) Kirchhoff’s Voltage Law (KVL):
KVL states that the sum of voltages around any closed loop in an electrical circuit is equal to zero. In other words, the total voltage rise in a circuit is equal to the total voltage drop.
Kirchhoff’s Laws are essential tools for analyzing and solving complex electrical circuits. By applying these laws, engineers can determine the behavior of currents and voltages within a circuit, facilitating troubleshooting and design optimization.
3. Faraday’s Law of Electromagnetic Induction:
Faraday’s Law of Electromagnetic Induction explains the relationship between a changing magnetic field and the production of an electric current. This law was discovered by Michael Faraday, an English scientist, in the early 19th century.
The law states that the magnitude of the electromotive force (EMF) induced in a circuit is directly proportional to the rate of change of the magnetic field through that circuit. This principle forms the basis for the functioning of electric generators and transformers.
Faraday’s Law of Electromagnetic Induction has numerous practical applications, such as generating electricity in power plants and transmitting it over long distances.
In conclusion, understanding the three fundamental laws of electricity – Ohm’s Law, Kirchhoff’s Laws, and Faraday’s Law of Electromagnetic Induction – is essential for comprehending the behavior and functioning of electrical circuits. These laws provide a foundation for electrical engineering and play a vital role in various industries that rely on electricity.
Understanding the Three Fundamental Laws of Electricity: A Comprehensive Explanation
Understanding the Three Fundamental Laws of Electricity: A Comprehensive Overview
Electricity is an essential component of our modern lives, powering everything from our homes to our workplaces. Despite its ubiquitous presence, many people lack a comprehensive understanding of the principles that govern this powerful force. In this article, we will provide a detailed overview of the three fundamental laws of electricity, shedding light on the basic principles that underpin the functioning of electrical systems.
1. Ohm’s Law:
Ohm’s Law, named after the German physicist Georg Simon Ohm, is a fundamental law that relates the three major electrical quantities: voltage (V), current (I), and resistance (R). It states that the current flowing through a conductor is directly proportional to the voltage applied across it and inversely proportional to the resistance of the conductor. Mathematically, Ohm’s Law is expressed as:
V = I * R
This equation implies that if the voltage remains constant, an increase in resistance will decrease the current flowing through the conductor. Similarly, if the resistance remains constant, an increase in voltage will result in an increase in current.
Understanding Ohm’s Law is crucial for various electrical applications. It helps electricians and engineers determine the appropriate wire size, calculate power consumption, and understand how different electrical components interact within a circuit.
2. Kirchhoff’s Laws:
Kirchhoff’s Laws, named after Gustav Kirchhoff, a German physicist, are two fundamental principles that are used to analyze complex electrical circuits. These laws are primarily concerned with the conservation of charge and energy within a circuit.
Kirchhoff’s Current Law (KCL):
KCL states that the total current entering a junction in a circuit is equal to the total current leaving that junction. In other words, the sum of currents flowing into a point in a circuit must equal the sum of currents flowing out of that point. This law is based on the principle of charge conservation.
Kirchhoff’s Voltage Law (KVL):
KVL states that the algebraic sum of the voltages in any closed loop or mesh within a circuit is zero. In simpler terms, it means that the sum of the voltage drops across any elements (such as resistors, capacitors, or inductors) in a closed loop is equal to the sum of voltage rises across other elements in that loop. KVL is based on the principle of energy conservation.
Kirchhoff’s Laws enable us to analyze complex electrical circuits by applying principles of charge and energy conservation. These laws are crucial in planning, designing, and troubleshooting electrical systems.
3. Faraday’s Law of Electromagnetic Induction:
Faraday’s Law, formulated by the British scientist Michael Faraday, describes the relationship between a changing magnetic field and an induced electromotive force (emf) or voltage in a conductor. It states that the magnitude of the induced emf is directly proportional to the rate at which the magnetic field changes with time and is given by:
emf = -dΦ/dt
where emf represents the electromotive force, dΦ is the change in magnetic flux, and dt is the change in time.
Faraday’s Law has significant practical applications, particularly in generating electricity. It forms the basis for the operation of electric generators and transformers. It also explains how electromagnetic devices, such as induction cooktops and wireless charging pads, work.
In conclusion, understanding the three fundamental laws of electricity – Ohm’s Law, Kirchhoff’s Laws, and Faraday’s Law – is essential for anyone working with or interested in electricity. These laws provide a solid foundation for analyzing and designing electrical circuits and systems, ensuring their safe and efficient operation. By grasping these fundamental principles, individuals can gain a deeper appreciation for the wonders and complexities of electricity.
Understanding the 3 Fundamental Principles of Electricity: A Comprehensive Guide
Understanding the Three Fundamental Laws of Electricity: A Comprehensive Overview
Electricity is a fundamental aspect of our modern world, powering everything from our homes to our workplaces. But have you ever wondered how electricity actually works? In this comprehensive overview, we will delve into the three fundamental laws of electricity that form the basis of our understanding of this powerful force.
1. Ohm’s Law
One of the most basic and widely known principles in electricity is Ohm’s Law. Named after the German physicist Georg Simon Ohm, this law states that the current flowing through a conductor between two points is directly proportional to the voltage across the two points, while inversely proportional to the resistance.
In mathematical terms, Ohm’s Law can be expressed as:
V = I x R
Where:
– V represents voltage,
– I represents current, and
– R represents resistance.
This equation allows us to calculate any one of these variables when the other two are known. For example, if we know the voltage and resistance in a circuit, we can determine the current flowing through it.
2. Kirchhoff’s Laws
Next, we turn our attention to Kirchhoff’s Laws, which are two fundamental principles that govern the behavior of electric circuits. These laws are named after Gustav Kirchhoff, a German physicist who made significant contributions to the study of electricity in the mid-19th century.
Kirchhoff’s First Law, also known as the «law of conservation of charge,» states that the sum of currents entering a node (or junction) in a circuit is equal to the sum of currents leaving that node. In simpler terms, it means that charge cannot be created or destroyed within a circuit.
Kirchhoff’s Second Law, also known as the «voltage law,» states that in any closed loop or mesh in a circuit, the sum of the electromotive forces (emfs) and the sum of the potential drops must be equal to zero. In other words, it means that energy is conserved within a circuit.
These laws enable us to analyze complex circuits and determine the electrical quantities at different points within them. By applying Kirchhoff’s Laws, we can solve for unknown currents or voltages in a circuit.
3. Faraday’s Law of Electromagnetic Induction
Lastly, we come to Faraday’s Law of Electromagnetic Induction, which describes the relationship between magnetic fields and electric currents. This law was formulated by the British scientist Michael Faraday in the early 19th century.
Faraday’s Law states that a change in the magnetic field within a closed loop of wire induces an electromotive force (emf) or voltage across that loop. The magnitude of this induced emf is directly proportional to the rate of change of the magnetic field.
This law forms the basis for many electrical devices, such as generators and transformers. It explains how electricity can be generated by moving a magnet through a coil of wire or vice versa.
In summary, understanding these three fundamental laws of electricity – Ohm’s Law, Kirchhoff’s Laws, and Faraday’s Law of Electromagnetic Induction – provides a solid foundation for comprehending how electricity functions in circuits and systems. Whether you are an aspiring electrician or simply interested in learning more about the science behind electricity, familiarizing yourself with these principles will enhance your understanding of this fascinating field.
Understanding the Three Fundamental Laws of Electricity: A Comprehensive Overview
As a seasoned attorney in the United States, it is crucial to stay informed about various topics, including the laws governing electricity. Electricity is an integral part of our daily lives and understanding its fundamental laws is essential for both legal professionals and the general public.
The Three Fundamental Laws of Electricity:
1. Ohm’s Law: Ohm’s Law states that the current flowing through a conductor between two points is directly proportional to the voltage across the two points, while keeping the resistance constant. In simpler terms, it means that when voltage increases, the current also increases, and when resistance increases, the current decreases.
2. Kirchhoff’s Laws: Kirchhoff’s Laws are two principles that help in understanding the behavior of current and voltage in electrical circuits.
– Kirchhoff’s Current Law (KCL): KCL states that the sum of currents entering a node (a point where multiple currents meet) is equal to the sum of currents leaving that node. In other words, the total current entering a point must equal the total current leaving that point.
– Kirchhoff’s Voltage Law (KVL): KVL states that the algebraic sum of the voltage drops (or rises) around any closed loop in a circuit is zero. This simply means that the sum of voltage rises must equal the sum of voltage drops in a closed loop.
3. Faraday’s Law of Electromagnetic Induction: Faraday’s Law states that a change in the magnetic field through a conductor induces an electromotive force (EMF) or voltage across the conductor. This principle forms the basis for the operation of generators, transformers, and many other electrical devices.
The Importance of Staying Up-to-Date:
Staying up-to-date with the laws governing electricity is crucial for several reasons. First and foremost, as an attorney, it is essential to have a comprehensive understanding of the laws that govern electrical systems and devices. This knowledge allows attorneys to effectively represent clients in cases involving electrical accidents, product liability claims, or contract disputes related to electrical services.
Furthermore, staying informed about the fundamental laws of electricity enables attorneys to provide accurate advice to clients who may be involved in the generation, transmission, or distribution of electric power. Understanding these laws allows attorneys to navigate complex regulations and compliance issues effectively.
It is important to note that while this article provides a comprehensive overview of the three fundamental laws of electricity, it is always advisable to verify and contrast the information with authoritative sources. The field of electricity is constantly evolving, and new research and advancements may impact our understanding of these laws. It is the responsibility of legal professionals to ensure they stay up-to-date with any changes or updates in the laws governing electricity.
In conclusion, understanding the three fundamental laws of electricity is essential for attorneys to effectively navigate legal matters related to electrical systems and devices. Staying up-to-date with this topic ensures that attorneys can provide accurate advice to clients and stay ahead in an ever-changing legal landscape.
