Welcome to this informative article on Understanding the Four Types of Law in the United States!
Before we embark on this journey of exploring the intricacies of the US legal system, it is important to note that the following information is intended to provide a general understanding and should not substitute for professional legal advice. As with any legal matter, it is always wise to consult with a qualified attorney or trusted legal source for specific guidance.
Now, let’s dive right into the fascinating world of US law! The United States legal system is a complex web of rules and regulations, but at its core, it is built upon four main types of law: constitutional law, statutory law, administrative law, and common law. Each plays a crucial role in shaping and governing our society.
📋 Content in this article
1. Constitutional Law:
Think of constitutional law as the foundation upon which the entire US legal system stands. The United States Constitution is the supreme law of the land and establishes the framework for our government and individual rights. It outlines the powers and limitations of each branch of government, as well as guarantees certain fundamental rights to all citizens. Cases involving constitutional law often involve issues such as free speech, equal protection under the law, and due process.
2. Statutory Law:
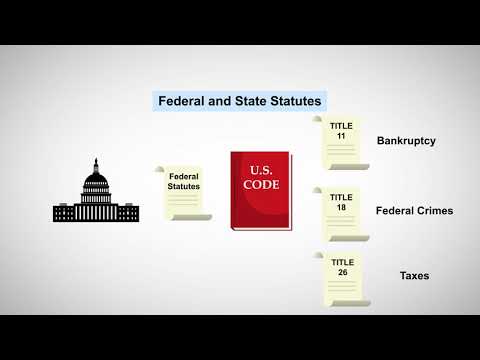
Statutory law refers to laws created by legislative bodies, such as Congress or state legislatures. These laws can take the form of statutes, codes, or ordinances and cover a wide range of topics, from criminal offenses to tax regulations to civil rights. Statutory law is created through a democratic process and is intended to reflect the will of the people. When conflicts arise, courts interpret and apply these statutes to specific cases.
3. Administrative Law:
Administrative law governs the activities of administrative agencies, which are entities created by legislatures to oversee specific areas of government regulation. These agencies are responsible for implementing and enforcing laws within their respective jurisdictions.
Understanding the Four Types of Laws in the U.S. and Their Significance
Understanding the Four Types of Laws in the U.S. and Their Significance
In the United States, the legal system is complex and diverse, consisting of various types of laws that govern different aspects of society. It is essential to understand these different types of laws and their significance in order to navigate the legal landscape effectively. Here, we will explore the four main types of laws in the U.S. and discuss why they are important.
1. Constitutional Law:
Constitutional law is the foundation of the U.S. legal system. It refers to the body of law derived from the U.S. Constitution, which sets forth the framework and principles upon which our government operates. Constitutional law establishes the basic rights and freedoms of individuals, ensuring that the government respects and protects them. It also outlines the structure and powers of the three branches of government – the legislative, executive, and judicial branches. Constitutional law is of utmost importance as it serves as a safeguard against governmental abuse of power and protects individual liberties.
2. Statutory Law:
Statutory law is created by legislative bodies such as Congress at the federal level or state legislatures at the state level. It refers to written laws that have been enacted by these legislative bodies and are contained in statutes or codes. Statutory law covers a broad range of issues, including criminal offenses, property rights, contracts, and more. These laws are binding and must be followed by individuals and organizations within their jurisdiction. Understanding statutory law is crucial as it provides clear guidelines for behavior and helps maintain order within society.
3. Administrative Law:
Administrative law encompasses regulations and rules that are established by administrative agencies to implement and enforce statutes passed by the legislative bodies. These agencies have been granted specific authority by Congress or state legislatures to create regulations that address specific areas such as environmental protection, workplace safety, healthcare regulations, and more.
Understanding the Four Main Sources of Law in the United States
Understanding the Four Main Sources of Law in the United States
In the United States, the legal system is based on a framework that draws from various sources of law. These sources provide the foundation for the development and application of legal principles that govern our society. Understanding these sources is essential for anyone seeking to navigate the complexities of the U.S. legal system.
The four main sources of law in the United States are:
- Constitutional Law: The United States Constitution is the supreme law of the land. It outlines the structure of the federal government, establishes the rights and responsibilities of citizens, and sets limits on governmental power. Constitutional law serves as a framework for all other laws in the country. interpreted and applied by the courts to ensure compliance with its provisions.
- Statutory Law: Statutory law refers to laws enacted by legislative bodies at the federal, state, and local levels. These laws are created by elected representatives and cover a wide range of topics, including criminal offenses, civil rights, taxation, and business regulations. Statutory law is codified in official statutes, which are collected and organized in legal codes.
- Administrative Law: Administrative law encompasses rules, regulations, and decisions made by administrative agencies within the executive branch of government. These agencies are granted authority by the legislature to implement and enforce specific laws. Examples of administrative agencies include the Environmental Protection Agency (EPA), the Federal Trade Commission (FTC), and the Federal Aviation Administration (FAA). Administrative law plays a crucial role in shaping public policy and ensuring compliance with statutory requirements.
- Common Law: Common law, also known as case law or judge-made law, refers to legal principles developed through court decisions. Unlike statutory law, which is created by legislatures, common law evolves through the interpretation and application of legal principles in actual cases.
Title: Understanding the Four Types of Law in the United States: A Comprehensive Overview
Introduction:
In the United States, the legal system is a complex framework that governs our society. is imperative for individuals to have a basic understanding of the four types of law that exist within this system. This article aims to provide readers with a comprehensive overview of these four types of law and emphasize the importance of staying current on this topic. However, it is crucial to verify and cross-reference the content of this article with reliable and up-to-date legal resources.1. Constitutional Law:
Definition: Constitutional law is the supreme law of the land, derived from the United States Constitution. establishes the structure and powers of the federal government, guarantees fundamental rights to individuals, and defines the relationship between the government and its citizens.Importance: Understanding constitutional law is crucial as it forms the foundation for all other areas of law in the United States. protects individual rights and liberties, ensures separation of powers, and outlines the limitations on government authority.
2. Statutory Law:
Definition: Statutory law refers to laws enacted by legislative bodies at the federal, state, and local levels. These laws are written and codified, covering a wide range of topics such as criminal offenses, civil rights, taxation, and more.Importance: Familiarity with statutory law is essential as it directly affects our daily lives. Statutes define what actions are legal or illegal, establish the rights and obligations of citizens, and provide guidelines for resolving disputes.
3. Administrative Law:
Definition: Administrative law encompasses rules, regulations, and decisions made by administrative agencies at the federal, state, and local levels. These agencies are authorized by legislation to enforce specific laws within their jurisdiction.Importance: Understanding administrative law is vital as it governs various aspects of public policy and ensures the proper functioning of government agencies.
