Hello and welcome to this informative article on understanding the various types of zoning in networking! Whether you’re new to the world of networking or looking to expand your knowledge, this article will provide you with a comprehensive overview of zoning and its different types. So, let’s dive right in and explore this fascinating topic!
Understanding the Various Types of Zoning in Networking: A Comprehensive Guide
Understanding the Various Types of Zoning in Networking
📋 Content in this article
In the world of computer networking, zoning plays a crucial role in ensuring the efficient and secure flow of data. By segmenting a network into different zones, organizations can establish boundaries and control access to resources. However, zoning can take on various forms and serve different purposes depending on the specific needs of a network. In this guide, we will explore the different types of zoning commonly used in networking.
1. Physical Zoning: Physical zoning involves physically separating devices or resources on a network. This can be done by grouping devices together in specific areas or by using physical barriers such as walls or doors. Physical zoning is particularly useful in environments where there is a need for strict access control or compliance with regulatory requirements. For example, in a data center, physical zoning can help separate different customer environments to ensure data privacy and security.
2. Logical Zoning: Logical zoning, also known as virtual zoning, is a method of creating virtual boundaries within a network. Instead of relying on physical separation, logical zoning uses software-defined parameters to define zones and control access. This type of zoning is commonly used in virtualized environments where resources need to be shared among different applications or user groups. Logical zoning allows for more flexibility and scalability compared to physical zoning.
3. Access Control Lists (ACL) Zoning: ACL zoning involves using access control lists to define and enforce access permissions within a network. Access control lists are sets of rules that dictate which devices or users are allowed to access specific resources or services. ACL zoning can be implemented at various levels, such as at the switch port, VLAN, or router interface. This type of zoning provides granular control over network access but requires careful configuration and management.
4. Fabric Zoning: Fabric zoning is specific to Fibre Channel networks and is used to control access to storage area networks (SANs). In a SAN environment, fabric zoning can be implemented at the switch level to restrict access to storage devices and prevent unauthorized access or interference. Fabric zoning is often used in high-performance computing environments or in industries that deal with sensitive data, such as healthcare or finance.
5. Software-Defined Networking (SDN) Zoning: SDN zoning is an emerging concept that leverages software-defined networking principles to enable more dynamic and flexible zoning capabilities. With SDN zoning, network administrators can define and modify zones programmatically, allowing for faster provisioning, easier management, and improved security. This type of zoning is well-suited for modern network architectures that rely heavily on virtualization and cloud technologies.
In conclusion, understanding the various types of zoning in networking is essential for designing secure and efficient networks. By implementing the appropriate zoning techniques, organizations can enhance network performance, control access to resources, and ensure data confidentiality and integrity. Whether it’s physical zoning, logical zoning, ACL zoning, fabric zoning, or SDN zoning, each type has its own advantages and use cases. When designing a network, it’s crucial to carefully consider the specific requirements and objectives in order to choose the most suitable zoning approach.
Understanding Network Zones: A Comprehensive Guide for Better Connectivity
Understanding the Various Types of Zoning in Networking
In the world of computer networking, the concept of zoning plays a crucial role in ensuring efficient and secure communication between devices. Zoning is essentially the process of dividing a network into distinct segments or areas, with each zone having its own unique characteristics, permissions, and level of access. This article aims to provide a comprehensive guide to help you understand the various types of zoning in networking.
1. **Physical Zoning**:
Physical zoning involves physically dividing a network into different areas or zones. This can be achieved by using physical barriers such as walls, doors, or even separate buildings. The main purpose of physical zoning is to isolate different departments or secure sensitive areas from unauthorized access. Physical zoning can be particularly useful in large organizations where different departments might have unique security requirements.
2. **Logical Zoning**:
Logical zoning, on the other hand, does not involve physical barriers but rather utilizes logical configurations and settings to create isolated zones within a network. This type of zoning is typically implemented through the use of firewalls, virtual LANs (VLANs), or software-defined networks (SDN). Logical zoning allows for more flexibility and scalability as it doesn’t require physical changes to the network infrastructure.
3. **Administrative Zoning**:
Administrative zoning is concerned with the management and control of access rights within a network. It involves defining roles, responsibilities, and levels of access for different users or groups. Administrative zoning helps ensure that only authorized personnel have access to specific network resources and can help prevent unauthorized access or data breaches.
4. **Security Zoning**:
Security zoning focuses on implementing security measures within different zones to protect sensitive information and assets. This can include using encryption, intrusion detection systems (IDS), or access control mechanisms to safeguard critical data. Security zoning is especially important in networks where different zones have different security requirements, such as separating guest networks from internal networks or isolating financial systems from general employee access.
5. **Application Zoning**:
Application zoning involves grouping or segregating applications or services into different zones based on their requirements or use cases. This can help optimize network performance, improve resource allocation, and enhance security. For example, high-bandwidth applications might be placed in a separate zone to ensure they don’t impact the performance of other applications.
Understanding the different types of zoning in networking is essential for designing and implementing an effective and secure network infrastructure. By properly segmenting your network into distinct zones, you can enhance performance, improve security, and ensure that your network meets the unique requirements of your organization. Whether you opt for physical, logical, administrative, security, or application zoning, it is crucial to align your network zoning strategy with your organization’s goals and objectives.
Understanding the 5 Zones of Security Access: A Comprehensive Guide
Understanding the Various Types of Zoning in Networking: A Comprehensive Guide
In the world of networking, zoning refers to the division of a network into smaller, more manageable segments. These segments, or zones, help enforce security measures and control access within the network. By understanding the different types of zoning, businesses can implement effective security protocols and protect their sensitive information.
1. Logical Zoning: Logical zoning involves dividing a network into virtual segments based on logical criteria such as departments, user roles, or applications. This type of zoning allows for granular control over who can access specific resources within the network. By assigning users to specific zones, organizations can limit access to sensitive data and prevent unauthorized users from compromising the network.
2. Physical Zoning: Physical zoning, on the other hand, involves dividing a network based on physical location or infrastructure. This is commonly done by creating separate physical networks for different departments or floors within an organization. Physical zoning helps reduce network congestion and improves performance by isolating traffic to specific areas. Additionally, it enhances security by preventing unauthorized access between physically separated zones.
3. Administrative Zoning: Administrative zoning focuses on segregating network resources based on administrative boundaries. This can be done by granting different levels of access to various teams or individuals within an organization. By implementing administrative zoning, businesses can ensure that employees only have access to the resources necessary for their roles, minimizing the risk of a security breach caused by human error or malicious intent.
4. Firewall Zoning: Firewall zoning involves creating separate zones within a network that are protected by firewalls. Firewalls act as a barrier between different zones, monitoring and controlling incoming and outgoing traffic. By implementing firewall zoning, organizations can filter network traffic, detect and block unauthorized access attempts, and prevent the spread of malware or other malicious activities.
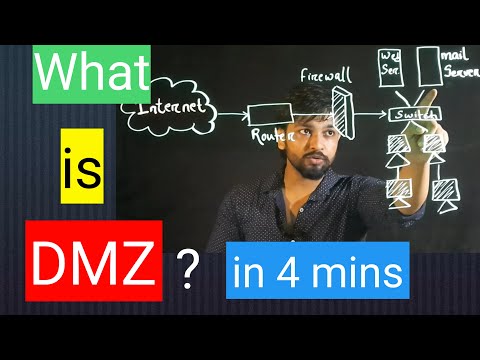
5. Demilitarized Zone (DMZ): A DMZ is a separate zone within a network that acts as a buffer between the internal network and the external internet. It is designed to host public-facing servers, such as web servers or email servers, that need to be accessed by external users. The DMZ is isolated from the internal network through firewalls and other security measures, reducing the risk of unauthorized access to critical resources.
Understanding and implementing these different types of zoning is crucial for maintaining a secure network environment. By carefully dividing and controlling access to network resources, businesses can mitigate the risk of data breaches, protect their sensitive information, and ensure the smooth operation of their network infrastructure.
If you require further assistance or guidance in implementing zoning measures for your network, it is advisable to consult with a professional in the field of network security. They can assess your specific needs and provide tailored solutions to enhance the security of your network.
Understanding the Various Types of Zoning in Networking
In today’s digital age, networking has become an integral part of our personal and professional lives. From connecting devices to sharing data, networking plays a crucial role in ensuring seamless communication. However, to maintain an organized and secure network, it is essential to have a good understanding of zoning.
Zoning in networking refers to the process of dividing a network into separate zones or compartments. Each zone contains a specific set of devices or resources that are logically grouped together based on certain criteria. By implementing zoning, network administrators can control access, security, and traffic flow within their network.
There are various types of zoning in networking, each serving a different purpose. It is important to familiarize ourselves with these types to effectively manage and maintain our networks. Here are some common types of zoning:
1. Port Zoning: Port zoning involves creating zones based on physical switch ports. Devices connected to the same switch port are grouped together within a zone. This type of zoning is straightforward and easy to implement, making it suitable for small-scale networks. However, it can become challenging to manage as the network grows.
2. WWN Zoning: World Wide Name (WWN) zoning is based on the unique identifier assigned to each Fibre Channel device. Devices with the same WWN are grouped together within a zone, regardless of their physical connection. This type of zoning provides more flexibility and scalability compared to port zoning.
3. Soft Zoning: Soft zoning allows for more granular control by grouping devices based on their World Wide Port Name (WWPN). In this type of zoning, specific ports on a device are assigned to a zone rather than the entire device itself. Soft zoning provides enhanced security as it limits access to specific ports only.
4. Hard Zoning: Hard zoning is the most restrictive form of zoning. It involves physically isolating devices by creating separate physical fabrics or switches. Each fabric or switch operates independently, and devices in one fabric cannot communicate with devices in another fabric. Hard zoning provides the highest level of security but can be complex and costly to implement.
In addition to these types, there may be other zoning methods specific to certain networking technologies or vendors. It is crucial to stay up-to-date with the latest developments in networking and verify and contrast the content of this article with reputable sources.
By understanding the various types of zoning, network administrators can effectively manage resources, control access, and enhance security within their networks. Regularly evaluating and adjusting zoning configurations is essential to ensure that the network remains efficient, secure, and adaptable to changing needs.
In conclusion, zoning in networking plays a vital role in maintaining an organized and secure network. By implementing the appropriate zoning techniques, network administrators can effectively manage and control access to resources. However, it is important to stay informed about the latest developments in networking and verify the information provided in this article with reputable sources.
