Greetings!
As an experienced attorney in the United States, I have been given the opportunity to delve into the fascinating topic of biogas regulations in the United Kingdom. In this comprehensive guide, we will explore the various aspects of biogas regulations, providing a detailed understanding of the legal framework governing this renewable energy source.
📋 Content in this article
Let’s get started!
Understanding Biogas Regulations in the UK: A Comprehensive Guide
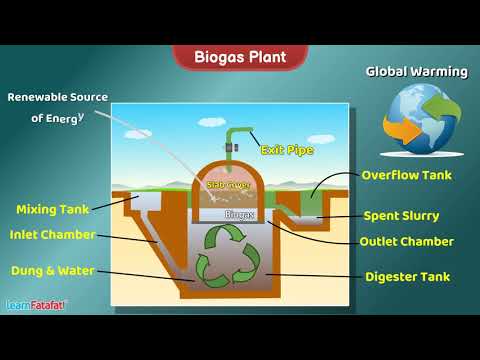
1. What is Biogas?
Biogas is a renewable energy source produced through the anaerobic digestion of organic materials such as agricultural waste, food waste, sewage sludge, and energy crops. It consists primarily of methane and carbon dioxide and can be used for electricity generation, heating, and as a vehicle fuel.
2. Importance of Biogas Regulations
Biogas has significant potential as a clean and sustainable energy source. However, due to its production process and the composition of gases involved, it is crucial to have well-defined regulations to ensure safety, environmental protection, and efficient utilization.
3. Regulatory Bodies
In the United Kingdom, biogas regulations are overseen by various regulatory bodies. The key players include the Department for Business, Energy & Industrial Strategy (BEIS), the Environment Agency (EA), and the Health and Safety Executive (HSE). These organizations collaborate to establish and enforce regulations that govern the production, distribution, and usage of biogas.
4. Permitting and Planning
To operate a biogas facility in the UK, obtaining the necessary permits and planning permissions is essential. The Environment Agency issues Environmental Permits under the Environmental Permitting Regulations 2016, which specify conditions for waste management, emissions control, and environmental protection.
5. Feed-in Tariffs (FiTs)
Under the Feed-in Tariffs scheme, biogas plant operators can receive payments for the renewable electricity they generate and export to the grid. FiTs provide financial incentives to encourage investment in biogas projects and promote the growth of renewable energy in the UK.
6. Renewable Heat Incentive (RHI)
The Renewable Heat Incentive is a government scheme that offers financial support to biogas heat producers. By providing payments for every unit of renewable heat generated, the RHI encourages the use of biogas for heating applications, such as district heating and industrial processes.
7. Grid Connection
Connecting a biogas plant to the electricity grid requires compliance with grid connection standards and regulations. The National Grid Electricity System Operator sets out requirements for connection and operation, including technical specifications and safety considerations.
8. Health and Safety
Biogas production involves potential health and safety hazards, such as gas leaks, fire risks, and exposure to harmful substances. The Health and Safety Executive provides guidance and regulations to ensure the safe operation of biogas facilities, protecting both workers and the surrounding environment.
9. Environmental Considerations
Biogas production can have environmental benefits, including reducing greenhouse gas emissions and diverting organic waste from landfills. However, it is crucial to manage environmental impacts properly. Regulations address issues such as odor control, waste management, and monitoring of emissions to safeguard environmental quality.
Understanding Biogas Regulations in the UK: A Comprehensive Overview
Understanding Biogas Regulations in the UK: A Comprehensive Guide
Biogas, a renewable source of energy derived from organic materials such as plant matter and animal waste, has gained significant attention in recent years due to its potential to reduce greenhouse gas emissions and contribute to a more sustainable energy future. In the United Kingdom (UK), biogas production is subject to various regulations and guidelines aimed at ensuring its safe and efficient production, transportation, and use. This comprehensive guide aims to provide an overview of the key regulations governing the biogas industry in the UK.
1. Environmental Permitting Regulations
The Environmental Permitting Regulations 2016 establish the regulatory framework for biogas production facilities in the UK. This legislation requires operators of biogas plants to obtain an environmental permit from the appropriate regulatory authority, typically the Environment Agency or the Scottish Environment Protection Agency. The permit outlines the conditions and requirements necessary for the operation of a biogas plant, including emissions limits, waste management protocols, and monitoring obligations.
2. Feed-in Tariff Scheme
The Feed-in Tariff (FiT) Scheme is a government initiative designed to promote the generation of renewable energy, including biogas, by providing financial incentives to eligible producers. Under this scheme, biogas producers are paid a guaranteed rate for every unit of electricity generated from their plant. However, the FiT Scheme closed to new applicants in 2019, and new projects may need to explore alternative financing options.
3. Renewable Heat Incentive
The Renewable Heat Incentive (RHI) is another government scheme that provides financial support to biogas producers who generate heat instead of electricity. The RHI offers tariff payments over a set period of time based on the amount of renewable heat generated. To qualify for RHI payments, biogas systems must comply with certain eligibility requirements and undergo regular heat metering and reporting.
4. Health and Safety Regulations
The Health and Safety at Work Act 1974 and associated regulations play a crucial role in ensuring the safety of workers and the public in the biogas industry. These regulations cover a wide range of health and safety aspects, including risk assessments, training requirements, emergency procedures, and the handling of hazardous substances. Compliance with these regulations is essential to minimize the risk of accidents, injuries, and environmental harm.
5. Grid Connection and Gas Quality Standards
To inject biogas into the national gas grid, biogas producers must comply with Grid Connection Standards set by the Office of Gas and Electricity Markets (Ofgem). These standards outline the technical requirements for connecting biogas plants to the gas grid, including pressure levels, metering, and safety measures. Additionally, biogas must meet specific Gas Quality Standards defined by the Gas Safety Management Regulations 1996 to ensure its compatibility with existing gas infrastructure.
6. Waste Regulations
Biogas production involves the use of organic waste materials, and operators of biogas plants must comply with relevant waste management regulations. The Waste (England and Wales) Regulations 2011 and The Waste (Scotland) Regulations 2012 govern the handling, storage, transportation, and disposal of waste materials generated during biogas production. Compliance with these regulations is crucial to prevent environmental pollution and ensure proper waste management practices.
The Role of Biogas in the UK Gas Supply: Examining the Percentage
The Role of Biogas in the UK Gas Supply: Examining the Percentage
Biogas is a renewable energy source that has gained significant attention in recent years as the UK aims to transition to a more sustainable and low-carbon energy system. Biogas is produced through the anaerobic digestion of organic materials such as agricultural waste, food waste, and sewage sludge. This process breaks down the organic matter and produces a mixture of methane and carbon dioxide, which can then be used as a fuel.
The UK has set ambitious targets for increasing the use of renewable energy sources, including biogas, in its gas supply. One important aspect to understand is the percentage of biogas in the overall gas supply, as this determines the level of renewable energy being injected into the gas grid.
Understanding Biogas Regulations in the UK: A Comprehensive Guide
In order to promote the use of biogas and ensure its sustainability, the UK has implemented a comprehensive regulatory framework. These regulations govern various aspects of biogas production, storage, transportation, and injection into the gas grid.
Key points to consider when understanding biogas regulations in the UK include:
Understanding these regulations is crucial for anyone involved in the biogas industry in the UK. It ensures compliance with applicable laws and regulations, facilitates access to financial incentives, and promotes the sustainable growth of biogas as a renewable energy source.
As the UK continues its transition towards a low-carbon future, biogas will play an increasingly important role in the gas supply. By familiarizing yourself with the regulations surrounding biogas production and injection into the gas grid, you can take advantage of the opportunities provided by this growing industry while contributing to a more sustainable energy system.
Understanding the Essential Requirements for Biogas Production
Understanding Biogas Regulations in the UK: A Comprehensive Guide
Biogas production is an increasingly important industry that plays a critical role in addressing environmental concerns and promoting sustainable energy sources. The production of biogas involves the breakdown of organic materials, such as agricultural waste, sewage sludge, and food waste, through a process called anaerobic digestion. This process generates a mixture of methane and carbon dioxide, which can be harnessed as a renewable energy source.
In the United Kingdom, the government has implemented regulations to promote and regulate the biogas industry. These regulations are designed to ensure that biogas production is safe, environmentally friendly, and economically viable. This comprehensive guide aims to provide an overview of the essential requirements for biogas production in the UK.
1. Planning Permission and Environmental Impact Assessments:
2. Feedstock Selection and Waste Management:
3. Health and Safety Regulations:
4. Digestion Process Optimization:
5. Grid Connection and Energy Distribution:
6. Compliance with Renewable Energy Standards and Incentives:
7. Monitoring, Reporting, and Compliance:
Understanding the essential requirements for biogas production in the UK is crucial for both potential investors and operators in this industry. Compliance with these regulations not only ensures the sustainability of biogas production but also contributes to the reduction of greenhouse gas emissions and the transition towards a cleaner, more sustainable energy future.
Please note that this guide provides a general overview and should not be considered as legal advice. It is always recommended to consult with professionals familiar with UK biogas regulations for specific guidance tailored to your circumstances.
Understanding Biogas Regulations in the UK: A Comprehensive Guide
As a seasoned attorney in the U.S., I understand the importance of staying up-to-date on various legal topics, including biogas regulations. Biogas, a renewable energy source derived from organic waste, has gained significant attention in recent years due to its potential to reduce greenhouse gas emissions and contribute to the transition to a sustainable energy future.
This comprehensive guide aims to provide readers with a detailed understanding of biogas regulations in the United Kingdom. However, it is crucial to note that laws and regulations evolve over time, and it is always prudent to verify and contrast the content of this article with current legislation and legal guidance.
1. Overview of Biogas Regulations in the UK
– The United Kingdom has implemented a comprehensive legal framework to support the production and utilization of biogas.
– The key legislation governing biogas includes the Renewable Heat Incentive (RHI) scheme, the Feed-In Tariffs (FIT) scheme, and the Renewable Transport Fuel Obligations (RTFO).
– These regulations aim to incentivize the development of biogas projects and ensure their compliance with environmental objectives.
2. Regulatory Bodies and Responsible Authorities
– The Department for Business, Energy & Industrial Strategy (BEIS) plays a central role in formulating and implementing biogas regulations in the UK.
– Other relevant bodies include the Office of Gas and Electricity Markets (Ofgem), the Environment Agency (EA), and the Scottish Environment Protection Agency (SEPA) for Scotland.
– These authorities oversee various aspects, such as accreditation, compliance, and environmental impact assessments.
3. Permitting and Licensing Requirements
– Biogas projects typically require permits and licenses to operate legally.
– The type of permits needed depends on factors such as project size, feedstock used, and end-use of biogas.
– The Environment Agency and SEPA issue permits for environmental protection, while Ofgem administers accreditation schemes for renewable energy subsidies.
4. Feed-In Tariffs (FIT) and Renewable Heat Incentive (RHI) Schemes
– The FIT scheme provides financial incentives to small-scale biogas projects that generate electricity, with tariffs varying based on project size and technology.
– The RHI scheme supports larger biogas projects that produce heat, offering long-term payments based on the amount of renewable heat generated.
– Eligibility criteria, application processes, and tariff rates are subject to change and should be consulted directly with the responsible authorities.
5. Renewable Transport Fuel Obligations (RTFO)
– The RTFO requires fuel suppliers to ensure a certain percentage of their fuel is derived from renewable sources, including biomethane produced from biogas.
– Compliance with the RTFO is monitored by the Department for Transport and can involve meeting sustainability criteria and registering as a renewable fuel producer.
In conclusion, understanding biogas regulations is vital for anyone involved in or considering entering the renewable energy sector in the UK. However, it is crucial to emphasize that laws and regulations can change, and it is essential to verify and contrast the information provided in this article with up-to-date legislation and guidance from relevant authorities.
