Greetings!
As a seasoned attorney in the United States, I have been given the opportunity to shed some light on the topic of Understanding the Grading Scale for Law in GCSE Examinations. While my expertise lies in U.S. law, I will do my best to provide you with an informative and comprehensive guide to help you navigate this subject.
📋 Content in this article
Please note that the information provided here is intended to be a general guide and may not reflect the specific grading scale used in your jurisdiction. It is always best to consult with your educational institution or examination board for the most accurate and up-to-date information.
Understanding the grading scale is essential for students undertaking GCSE Law examinations. These examinations are designed to assess your knowledge and understanding of key legal principles and concepts. The grading scale provides a standardized framework for evaluating your performance and determining your level of achievement.
In GCSE Law examinations, the grading scale typically ranges from 1 to 9, with 9 being the highest grade. Each grade corresponds to a specific level of achievement and demonstrates your proficiency in the subject matter.
To provide a clearer understanding, here is a breakdown of the grading scale:
- Grade 9: This grade represents an exceptional level of knowledge and understanding. Achieving a Grade 9 indicates that you have demonstrated an outstanding grasp of the subject matter and have excelled in your examination.
- Grade 8: A Grade 8 signifies a high level of proficiency in GCSE Law. It demonstrates that you have a strong understanding of the key legal principles and can apply them effectively in your examination.
- Grade 7: Attaining a Grade 7 indicates a solid understanding of the subject matter. It shows that you have grasped the fundamental legal concepts and can provide reasoned responses in your examination.
- Grade 6: This grade suggests a good level of knowledge and understanding. Achieving a Grade 6 demonstrates that you have a reasonable grasp of the key legal principles and can apply them adequately in your examination.
- Grade 5: A Grade 5 indicates a satisfactory level of achievement. It shows that you have a basic understanding of the subject matter and can provide coherent responses in your examination.
- Grade 4: Achieving a Grade 4 signifies a pass in GCSE Law. It demonstrates that you have a basic understanding of the subject matter, although there may be areas where further improvement is needed.
- Grade 3: This grade suggests a limited level of understanding. Attaining a Grade 3 indicates that you have a partial grasp of the subject matter, but there are significant areas where improvement is required.
- Grade 2: A Grade 2 represents a marginal level of attainment. It suggests that you have a very limited understanding of the subject matter and may need further study and revision.
- Grade 1: This grade indicates the lowest level of achievement. Achieving a Grade 1 suggests that you have not met the minimum requirements to demonstrate a basic understanding of the subject matter.
It is important to note that the specific requirements for each grade may vary depending on the examination board and jurisdiction. Therefore, it is advisable to consult the official guidelines and mark schemes provided by your examination board for detailed information on how each grade is assessed and awarded.
In conclusion, understanding the grading scale for law in GCSE examinations is crucial for students pursuing this subject. It provides a standardized framework for evaluating your performance and determining your level of achievement. Remember to consult your educational institution or examination board for specific information regarding the grading scale and requirements in your jurisdiction.
Best of luck with your studies and future examinations!
Understanding the GCSE Grading Scale: A Comprehensive Guide
Understanding the Grading Scale for Law in GCSE Examinations: A Comprehensive Guide
The GCSE (General Certificate of Secondary Education) examinations are a vital milestone in a student’s academic journey. These exams assess a student’s knowledge and understanding of various subjects, including law. Understanding the grading scale for law in GCSE examinations is crucial for students aiming to pursue a legal career.
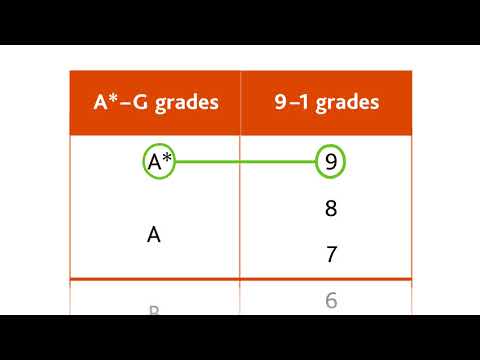
The grading scale for law in GCSE examinations is typically denoted by numbers ranging from 1 to 9. Each number corresponds to a specific level of achievement, with 9 being the highest. This scale replaces the previous letter-based grading system, where grades A*-G were assigned.
It is essential to understand what each grade represents in terms of a student’s performance in law. Here is a breakdown of the grading scale and its significance:
Grade 9: A grade 9 indicates an exceptional level of performance. It signifies that the student has demonstrated an excellent grasp of legal concepts and principles, and has provided well-reasoned arguments and analysis.
Grade 8: A grade 8 reflects a high level of achievement. It signifies that the student has shown a strong understanding of legal principles and has provided coherent and logical arguments.
Grade 7: A grade 7 denotes a good level of performance. It indicates that the student has displayed a sound understanding of legal concepts and has presented reasoned arguments.
Grade 6: A grade 6 represents a satisfactory level of achievement. It suggests that the student has shown a basic understanding of legal principles and has presented some relevant arguments, although they may lack depth or clarity.
Grade 5: A grade 5 indicates a moderate level of performance. It suggests that the student has demonstrated a limited understanding of legal concepts and has provided some relevant but undeveloped arguments.
Grade 4: A grade 4 reflects a below-average level of achievement. It signifies that the student has displayed a limited understanding of legal principles and has provided only basic arguments.
Grades 1-3: These grades represent a below-standard performance. They indicate that the student has shown a very limited understanding of legal concepts and has provided weak arguments or none at all.
Understanding the grading scale for law in GCSE examinations is essential for students considering a career in the legal field. Higher grades, such as 9, 8, and 7, demonstrate a strong aptitude for legal analysis and argumentation. These grades can enhance a student’s chances of gaining admission to prestigious law schools or securing internships at reputable law firms.
On the other hand, lower grades may not necessarily hinder a student’s legal aspirations. While they may indicate a need for further improvement, students with lower grades can still succeed by demonstrating their commitment to learning and improving their understanding of law through other means, such as pursuing relevant extracurricular activities or seeking mentorship.
Understanding GPA Conversion: What is a 4.0 GPA Equivalent to in the UK?
Understanding the Grading Scale for Law in GCSE Examinations: A Comprehensive Guide
In the United Kingdom, GCSE examinations are an important milestone for students pursuing a career in law. These exams assess a student’s knowledge and understanding of various subjects, including law. To accurately interpret and evaluate GCSE results, it’s crucial to have a clear understanding of the grading scale used in these examinations.
The Grading Scale
The grading scale for GCSE examinations in the UK is based on a numerical system ranging from 1 to 9, with 9 being the highest grade achievable. Each numerical grade corresponds to a particular level of achievement. This system replaced the traditional letter grades (A*-G) in 2017, aiming to provide more differentiation among students’ abilities.
Numerical Grades and Their Meanings
To better understand the grading scale, it is essential to familiarize oneself with the meanings associated with each numerical grade. Here is a breakdown of the numerical grades and their corresponding interpretations:
GPA Conversion: What is a 4.0 GPA Equivalent to in the UK?
As an attorney in the U.S., you may be familiar with the Grade Point Average (GPA) system used in American educational institutions. The GPA system provides a standardized way of evaluating a student’s overall academic performance. However, it is important to note that the GPA scale is not directly comparable to the GCSE grading scale.
In the UK, there is no direct equivalent of a 4.0 GPA. The GCSE grading scale is based on numerical grades, while the GPA system uses a scale from 0.0 to 4.0. It is not possible to convert a numerical grade from the GCSE system into a GPA equivalent.
It is worth mentioning that universities and colleges in the UK have their own admissions criteria, and they consider a range of factors beyond grades alone. These may include personal statements, letters of recommendation, extracurricular activities, and admissions tests. Therefore, it is important for students applying to UK universities to familiarize themselves with the specific requirements of each institution they are interested in.
Understanding the Grading System in GCSE: Is a Grade 7 Considered Good?
Understanding the Grading Scale for Law in GCSE Examinations: A Comprehensive Guide
When it comes to GCSE examinations, understanding the grading system is essential for students to gauge their performance and determine their level of achievement. In this comprehensive guide, we will focus specifically on the grading scale for law subjects in GCSE examinations. This guide aims to provide a detailed explanation of the grading scale and answer the question: Is a Grade 7 considered good?
The GCSE Grading Scale
GCSE examinations are graded on a scale of 9 to 1, with 9 being the highest grade and 1 being the lowest. The grading system was introduced in 2017 to replace the previous A* to G scale. The new grading system is designed to provide more differentiation between students’ performance and to align with international standards.
Understanding Grade 7
Grade 7 is often considered a high achievement and is equivalent to the old A grade under the previous grading system. It is important to note that Grade 7 represents a strong understanding of the subject matter and an ability to apply knowledge effectively. Achieving a Grade 7 demonstrates a high level of competence and places students in a favorable position for further study or future career paths related to law.
Factors to Consider
While Grade 7 is generally seen as a good grade, it is crucial to consider other factors when evaluating academic performance. Grades alone do not provide a complete picture of a student’s abilities or potential. Universities and employers often consider additional criteria, such as personal statements, extracurricular activities, and references, when assessing applicants.
Progression and Future Opportunities
GCSE grades, including Grade 7, play a significant role in determining future opportunities for further study or employment. Higher grades, such as Grade 7 or above, can open doors to advanced level courses, including A-levels and vocational qualifications, in the field of law. These qualifications can pave the way for admission to prestigious universities and enhance career prospects in legal professions.
As an attorney practicing law in the United States, I am often asked to provide guidance on various legal matters. While my expertise lies primarily in U.S. law, I understand the importance of staying informed about legal systems and processes around the world. One area of particular interest is the grading scale for law in GCSE examinations.
GCSE examinations are a series of tests taken by students in the United Kingdom at the age of 16. These exams cover a wide range of subjects, including law. Understanding the grading scale for law in GCSE examinations is crucial for students who wish to pursue further studies or careers in the legal field.
The Grading Scale for Law in GCSE Examinations:
1. Grade 9: This is the highest possible grade in GCSE examinations and represents exceptional performance and understanding of the subject matter. Achieving a grade 9 in law demonstrates a deep understanding of legal concepts, strong analytical skills, and the ability to apply legal principles effectively.
2. Grades 7-8: These grades indicate a strong performance in the examination. Students who achieve grades 7-8 have demonstrated a good understanding of legal principles, effective application of legal knowledge, and the ability to analyze legal issues critically.
3. Grades 4-6: These grades represent a satisfactory level of performance. Students who achieve grades 4-6 have demonstrated a basic understanding of legal concepts and principles, but may need further development in their analytical and critical thinking skills.
4. Grades 1-3: These grades indicate a below-average performance. Students who achieve grades 1-3 have shown limited understanding of legal concepts and may need significant improvement in their analytical and critical thinking abilities.
It is important to note that these grades are determined by the examination board and can vary from year to year. It is essential for students and educators to stay up-to-date with any changes or updates to the grading scale.
Staying Up-to-Date:
Staying informed about the grading scale for law in GCSE examinations is crucial for students, educators, and anyone involved in the legal field. However, it is important to remember that the information provided in this article is based on general knowledge and may not reflect the most current grading scale.
To ensure accurate and reliable information, it is recommended to verify and contrast the content of this article with official sources such as the examination board’s website or official publications. These sources will provide the most up-to-date information on the grading scale for law in GCSE examinations.
In conclusion, understanding the grading scale for law in GCSE examinations is important for students interested in pursuing further studies or careers in the legal field. However, it is crucial to verify and contrast the information provided in this article with official sources to ensure accuracy and reliability.
