Hello and welcome! In this article, we will explore the role of statutes as primary sources of law in the United States. Statutes, also known as legislation or laws, play a central role in the American legal system. They are created by legislative bodies at various levels of government, including the U.S. Congress and state legislatures. Statutes are an essential part of the legal framework that governs our society.
What are statutes?
Statutes are written laws enacted by legislative bodies. They can be created at the federal, state, or local level. The process of creating statutes involves proposing, debating, amending, and ultimately passing a bill through the legislative process. Once a bill is signed into law by the appropriate authority, it becomes a statute.
📋 Content in this article
Why are statutes important?
Statutes serve as one of the primary sources of law in the United States. They establish rules and regulations that govern various aspects of our society. Statutes cover a wide range of areas, including criminal law, civil law, tax law, environmental law, and many others. They provide clarity and consistency in the legal system by establishing clear guidelines for conduct, rights, and obligations.
How do statutes interact with other sources of law?
While statutes are crucial in shaping the legal landscape, they are not the only source of law. The U.S. legal system relies on a combination of sources, including constitutional law, administrative regulations, and common law (court decisions). Statutes can interact with these other sources in different ways.
Statutes can reinforce or clarify constitutional provisions. For example, the First Amendment to the U.S. Constitution guarantees freedom of speech. Statutes can be enacted to define the limits and exceptions to this right.
Administrative regulations are rules created by government agencies to implement and enforce statutes. Statutes often grant government agencies the authority to create regulations that further define and specify the requirements set by the statutes.
Common law, on the other hand, refers to legal principles and rules that have developed through court decisions over time. Statutes can modify or override common law principles, but they can also be interpreted and applied by courts in conjunction with common law principles.
How are statutes interpreted and applied?
Interpreting statutes is a crucial task for the courts. When faced with a legal dispute, courts must analyze the language and intent of the statute to determine its meaning and application to the case at hand. Courts may consider legislative history, statutory language, and other relevant factors to ascertain the legislative intent behind a statute.
When applying a statute, courts must consider its constitutionality. If a statute conflicts with constitutional provisions, it may be deemed unconstitutional and unenforceable.
In conclusion, statutes play a significant role as primary sources of law in the United States. They establish rules and regulations that govern various aspects of our society. Understanding statutes and their interaction with other sources of law is essential for navigating the complex legal landscape in the United States.
The Role of Statues in Establishing Legal Precedence: A Comprehensive Analysis.
Understanding the Role of Statues as Primary Sources of Law in the United States
Introduction:
In the United States legal system, statutes play a crucial role as primary sources of law. Statutes are laws enacted by legislative bodies at the federal, state, or local level. These laws serve as the foundation of the legal framework within which individuals, businesses, and government entities operate. This article aims to provide a comprehensive analysis of the role of statutes in establishing legal precedence.
1. Definition and Types of Statutes:
Statutes can be defined as written laws enacted by legislative bodies. They set forth rules and regulations that govern various aspects of society. In the United States, statutes can be classified into three main types:
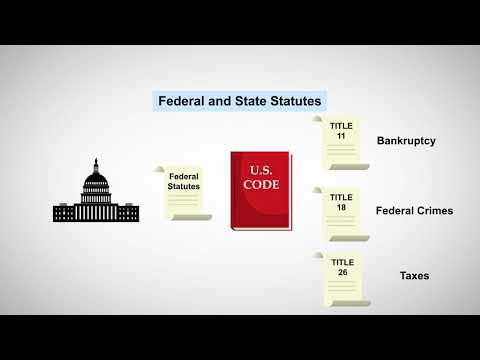
a. Federal Statutes: These are laws enacted by the United States Congress and apply to the entire nation. Federal statutes cover a wide range of areas, including criminal law, civil rights, taxation, and commerce.
b. State Statutes: Each state has its own legislative body that enacts laws specific to that state. State statutes govern matters such as family law, property law, contract law, and criminal law within their respective jurisdictions.
c. Local Ordinances: Local governments, such as cities and counties, have the authority to enact ordinances. These ordinances address issues that are relevant to the local community, such as zoning regulations, parking restrictions, and noise regulations.
2. Legal Precedence:
Legal precedence refers to the principle that courts should follow prior court decisions when deciding similar cases. It ensures consistency and predictability in the application of laws. Precedence is established through the interpretation and application of statutes by courts.
3. Role of Statutes in Establishing Legal Precedence:
Statutes play a pivotal role in establishing legal precedence. When a court interprets a statute to resolve a dispute or provide guidance in a case, its decision becomes a precedent that subsequent courts may rely upon. The court’s interpretation of the statute becomes binding on lower courts within the same jurisdiction.
4. Importance of Statutory Interpretation:
To establish legal precedence, courts must interpret statutes accurately and consistently. Statutory interpretation involves analyzing the language, legislative intent, and purpose of the statute to determine its meaning and application. Courts may rely on various methods of interpretation, such as textualism, purposivism, or a combination of both.
5. Relationship between Statutory Precedence and Common Law:
Common law refers to legal principles derived from court decisions rather than statutes. While statutes take precedence over common law, courts often interpret statutes in light of existing common law principles. This interplay between statutes and common law allows for the evolution and adaptation of legal principles based on changing societal values and needs.
Understanding the Role of Statues as Primary Sources in Historical Research
Understanding the Role of Statues as Primary Sources of Law in the United States
Statutes play a crucial role in the legal system of the United States. They are laws enacted by legislative bodies, such as Congress at the federal level or state legislatures, and they serve as primary sources of law. In this article, we will explore the significance of statutes and their role in shaping the legal landscape in the United States.
1. What is a Statute?
A statute is a law enacted by a legislative body. It is a written rule that has been formally adopted through a legislative process. Statutes can cover a wide range of legal issues, including criminal offenses, civil rights, taxation, property rights, and many others. They are binding and enforceable, meaning that individuals and organizations must comply with the provisions set forth in statutes.
2. The Hierarchy of Laws
In the United States legal system, statutes hold a prominent position as primary sources of law. The hierarchy of laws establishes the order in which different sources of law are considered when resolving legal disputes. Under this hierarchy, statutes generally rank above other sources, such as administrative regulations and case law.
3. Enactment Process
Statutes are created through a formal legislative process. At the federal level, a bill must be introduced in either the House of Representatives or the Senate. The bill goes through various stages of review, debate, and amendment before being voted on by both chambers. If approved by both chambers, it is sent to the President for signature or veto. Similarly, at the state level, bills are introduced and go through a similar process within the respective state legislature.
4. Interpretation of Statutes
Once a statute has been enacted, its interpretation becomes crucial. Courts play a significant role in interpreting statutes when hearing cases that involve the application of these laws. When interpreting a statute, courts aim to ascertain the legislative intent behind the law and apply it to the specific case at hand. This process involves examining the language of the statute, considering its purpose, and analyzing relevant legislative history.
5. Amendments and Repeals
Statutes are not set in stone and can be amended or repealed. As society evolves and legal needs change, legislative bodies have the authority to modify or revoke existing statutes. Amendments can either add new provisions or modify existing ones, while repeals abolish the entire statute. The process for amending or repealing a statute is similar to the enactment process, involving the introduction of a bill, review, debate, and voting.
In conclusion, statutes are primary sources of law in the United States and play a critical role in shaping the legal framework of the country. They are laws enacted by legislative bodies and are binding and enforceable. Understanding statutes, their enactment process, interpretation, and potential for amendment or repeal is essential for navigating the legal system in the United States.
Understanding the Sources of Law in the United States
Understanding the Role of Statutes as Primary Sources of Law in the United States
In the United States, the legal system is complex and multifaceted. To navigate this system effectively, it is important to understand the sources of law that govern our society. One of the primary sources of law in the United States is statutes.
Statutes, also known as legislation or laws, are formal rules enacted by a legislative body, such as Congress or a state legislature. They are written documents that establish legal obligations and rights for individuals and organizations. Statutes can be created at the federal level, applying to the entire country, or at the state level, applying only within a specific state.
The role of statutes in our legal system is crucial. Here are some key points to help you understand their significance:
In conclusion, statutes serve as primary sources of law in the United States. They carry significant weight and authority, often taking precedence over other sources of law. Understanding the role of statutes is crucial for navigating the legal system and ensuring compliance with the law.
Understanding the Role of Statutes as Primary Sources of Law in the United States
As an attorney practicing law in the United States, it is crucial to have a thorough understanding of the role that statutes play as primary sources of law. Statutes are laws enacted by legislative bodies at the federal, state, and local levels, and they form the backbone of our legal system. This article aims to provide a comprehensive overview of the importance of statutes and the need for attorneys to stay up-to-date on this topic.
The Authority of Statutes
Statutes have the highest level of authority in the legal system. They are enacted by elected representatives in legislative bodies, such as the U.S. Congress or state legislatures. Once a statute is passed, it becomes binding law and must be followed by individuals and entities within their jurisdiction. The authority of statutes supersedes other sources of law, including common law and regulations.
Interpreting Statutes
Interpreting statutes can be a complex task for attorneys. The language used in statutes may not always be clear or unambiguous, leading to various interpretations. When faced with interpreting a statute, attorneys must consider the text itself, legislative history, and the intent behind its enactment. Courts may also look to precedent and other legal doctrines to aid in interpreting statutes.
Importance of Staying Up-to-Date
Staying up-to-date on statutes is of paramount importance for attorneys. The legal landscape is constantly evolving, with new statutes being enacted and existing ones being amended or repealed. Failing to stay current on these changes can have serious consequences for legal practitioners and their clients.
By not being aware of changes in statutes, attorneys risk providing inaccurate advice or missing crucial legal arguments in court. This can result in adverse outcomes for their clients and potentially harm their professional reputation. Additionally, attorneys have an ethical duty to maintain competence in their practice areas, which includes staying informed about changes in statutory law.
Verifying and Contrasting
While this article provides a general understanding of the role of statutes as primary sources of law, it is crucial for readers to verify and contrast the content with other reliable sources. The legal system is complex, and statutes can vary depending on jurisdiction. It is always wise to consult official legal resources, such as statutes themselves, case law, legal treatises, and reputable legal publications.
Furthermore, legal interpretation is subjective, and different attorneys or courts may have varying interpretations of the same statute. Engaging in legal research and consulting with colleagues or legal experts can help attorneys gain a more comprehensive perspective on the interpretation and application of statutes.
In conclusion, understanding the role of statutes as primary sources of law is essential for attorneys practicing in the United States. Staying up-to-date on changes in statutory law is crucial for providing accurate advice and effective representation. However, it is important for readers to independently verify and contrast the content of this article with other reliable sources to ensure accuracy and applicability to their specific jurisdiction.
