Greetings!
As a seasoned attorney in the United States, I have been tasked with shedding light on the topic of Understanding Directives: Are They Considered Laws? Directives, often referred to as executive orders or executive actions, are an important aspect of governance. However, it is essential to distinguish them from actual laws.
📋 Content in this article
In the United States, laws are statutes enacted by the legislative branch of government. They undergo a rigorous process that involves proposal, debate, and approval by elected officials. Laws affect the entire country and carry significant legal weight.
On the other hand, directives are orders issued by the executive branch of government, typically by the President or a high-ranking official. These directives are usually aimed at guiding the actions of federal agencies or officials. While directives can shape and influence policy, they do not hold the same legal authority as laws.
Directives are not created through the same legislative process as laws. They do not require approval from Congress or undergo extensive debate. Instead, they are issued unilaterally by the executive branch to manage and direct the implementation of existing laws or policies.
Although directives may not have the same legal standing as laws, they can still have a significant impact. They can provide guidance to agencies, establish priorities, and outline objectives for executive branch officials. Additionally, directives can be challenged in court if they exceed the authority granted to the executive branch or violate constitutional principles.
It is also worth noting that directives can be subject to change or revocation by subsequent administrations. When a new President takes office, they often issue their own directives, which can replace or modify those issued by previous administrations.
So, while directives play a crucial role in shaping and directing government actions, they are distinct from laws. Laws are enacted through a formal legislative process and carry legal weight throughout the country, while directives are executive orders that guide agency actions but do not have the same legal status.
In conclusion, directives are not considered laws, but they serve as important tools for the executive branch to guide the implementation of existing laws and policies.
I hope this explanation has provided clarity on this topic. If you have any further questions, I’m here to assist you.
Understanding Directives in EU Law: A Comprehensive Guide
Understanding Directives: Are They Considered Laws?
In the realm of European Union (EU) law, directives play a crucial role in harmonizing regulations and ensuring consistency among member states. However, it is important to understand that while directives are binding legal instruments, they are not considered laws in the traditional sense. This article aims to provide a comprehensive guide to understanding directives in EU law and their relationship to national legislation.
1. What is a Directive?
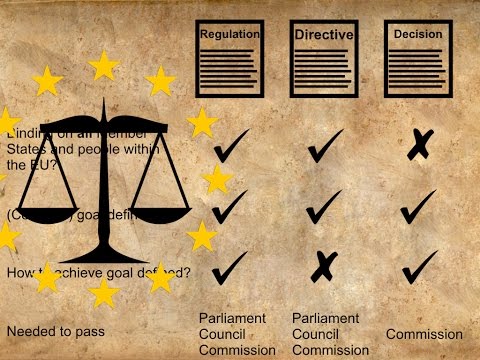
A directive is a legal instrument adopted by the EU institutions that sets out specific objectives to be achieved by member states within a given timeframe. Unlike regulations, which are directly applicable and binding on member states without requiring further action, directives require transposition into national law. This means that member states must incorporate the provisions of the directive into their domestic legislation to give it legal effect.
2. Purpose and Function of Directives
Directives serve as a means for the EU to harmonize laws across member states on specific matters of common interest. They are used to facilitate the creation of a single European market by eliminating barriers to trade and ensuring fair competition. Directives cover a wide range of areas, including consumer protection, environmental regulations, employment rights, and product standards.
3. Direct Effect and Direct Applicability
While directives themselves are not considered laws, they can have direct effect under certain conditions. Direct effect means that individuals can rely on the provisions of a directive before national courts, even if it has not been fully transposed into national law. However, for a directive to have direct effect, it must be clear, precise, and unconditional.
Some directives also have direct applicability, which means they are automatically binding on member states without the need for further action or transposition into national law. Directly applicable directives are often referred to as “self-executing” and do not require additional implementation measures.
4. Transposition of Directives
Transposition is the process of incorporating the provisions of a directive into national law. Each member state has the freedom to choose the appropriate legal and administrative measures to transpose a directive, provided they achieve the desired outcome. However, member states must notify the European Commission of the measures taken to ensure compliance with EU law.
Failure to transpose a directive within the specified timeframe or inadequate transposition can lead to infringement proceedings against the member state by the European Commission, which has the power to take legal action before the Court of Justice of the European Union (CJEU).
5. Relationship with National Legislation
Once a directive has been transposed into national law, it becomes part of the domestic legal framework. This means that individuals and businesses must comply with the provisions of the directive, as well as any corresponding national legislation. The national courts are responsible for interpreting and applying both the directive and national laws.
In cases where there is a conflict between a directive and national legislation, the principles established by the CJEU dictate that national courts must interpret domestic laws in a manner consistent with EU law. This principle, known as the principle of consistent interpretation, ensures that EU law takes precedence over conflicting national laws.
Understanding the Significance of Rules and Directives in Everyday Life
Understanding Directives: Are They Considered Laws?
In our everyday lives, we encounter a myriad of rules and directives that govern various aspects of our behavior and actions. From traffic regulations to workplace policies, these rules play a crucial role in ensuring order and promoting the well-being of individuals and society as a whole. It is important to understand the significance of rules and directives, especially when it comes to distinguishing between them and laws.
Rules and Directives:
1. Rules and directives are guidelines or instructions that are put in place to regulate certain behaviors or actions. They are typically established by organizations, institutions, or authorities with the aim of maintaining order, promoting safety, or achieving specific objectives.
2. Rules can be informal, such as social norms or customs, or they can be formal, like the rules of a game or the policies of a company. Directives, on the other hand, are more specific instructions or commands given by an authority figure or governing body.
Characteristics of Laws:
1. Laws, on the other hand, are official rules that are enacted and enforced by a recognized authority, such as a legislative body. They are generally more formal in nature and carry legal consequences for non-compliance.
2. Laws are created through a legislative process, which involves the proposal, debate, and approval of bills by elected representatives. Once enacted, laws are generally applicable to everyone within the jurisdiction in which they are established.
Distinguishing Between Directives and Laws:
1. One key distinction between directives and laws is their enforceability. Directives typically carry less severe consequences for non-compliance compared to laws. While non-compliance with directives may result in disciplinary actions or sanctions within specific organizations or contexts, violations of laws can lead to criminal charges or civil lawsuits.
2. Another distinguishing factor is the authority from which they originate. Directives are usually issued by specific organizations or authorities within their respective domains, such as employers, schools, or government agencies. Laws, on the other hand, are created and enforced by the government as a whole and apply to the entire jurisdiction.
Importance of Understanding Directives:
1. Understanding directives is crucial because they often play a significant role in shaping our rights and obligations within specific contexts. For example, in the workplace, employees are expected to adhere to company policies and directives to maintain a productive and harmonious work environment.
2. Directives can also have a direct impact on individuals’ rights and responsibilities within certain institutions or organizations. Familiarizing oneself with these directives can help individuals navigate their rights and obligations effectively.
3. It is important to note that directives can sometimes conflict with laws, and in such cases, laws generally take precedence. However, it is advisable to seek legal counsel or clarification in situations where there is ambiguity or potential conflict between directives and laws.
In conclusion, understanding the significance of rules and directives in everyday life is essential for navigating various social contexts and institutions. While rules and directives provide guidance and maintain order, it is important to recognize the distinction between them and laws. Laws carry more significant legal consequences for non-compliance and are enacted by a recognized governing body. By understanding directives and their relationship to laws, individuals can better navigate their rights and obligations in different contexts.
Understanding the Legally Binding Nature of Directives: A Comprehensive Analysis
Understanding Directives: Are They Considered Laws?
Directives are an important aspect of the legal system, but it is crucial to understand their nature and how they differ from laws. In this article, we will explore the concept of directives and delve into their legally binding nature.
What are directives?
Directives are instruments of the legislative branch that are used to guide and instruct certain individuals or entities within a specific jurisdiction. They are typically issued by governmental bodies, such as federal agencies or executive branches of government, to provide guidance or establish policies. Directives serve as a way to supplement and clarify existing laws or regulations.
How do directives differ from laws?
While it is clear that directives play a significant role in shaping the legal landscape, it is important to note that they are not considered laws in the traditional sense. Laws are formal rules enacted by a legislative body and are binding on all individuals and entities within a jurisdiction. Directives, on the other hand, are often issued by administrative bodies and are binding on a specific group of individuals or entities.
Legally binding nature of directives
Directives can carry legal weight and have a legally binding nature on those to whom they are directed. However, this binding effect is typically limited to the specific group or individuals for whom the directive is intended. It is important to recognize that directives do not create new laws or have the same level of authority as statutes or regulations.
The legally binding nature of directives stems from the authority granted to the issuing body and the obligations imposed on the targeted group. Failure to comply with a directive can result in legal consequences, such as penalties, fines, or other enforcement measures. It is essential for individuals and entities subject to directives to carefully review and understand their obligations to ensure compliance with the directives.
Challenges with directives
While directives can provide much-needed guidance and clarity, they can also present challenges. One challenge is the potential for conflicting or overlapping directives from different governmental bodies. This can create confusion and uncertainty regarding which directive takes precedence.
Another challenge is the interpretation of directives. Directives may be vaguely worded or open to different interpretations, leading to disagreements and legal disputes. It is important for individuals and entities subject to directives to consult legal counsel or seek clarification from the issuing body to ensure a proper understanding of their obligations.
Understanding Directives: Are They Considered Laws?
As a seasoned attorney, it is essential to stay up-to-date on legal concepts and developments. One topic that requires continuous attention is understanding directives and their legal implications. Directives are instruments used by governments and governing bodies to provide guidance and instructions to individuals or organizations. However, it is crucial to remember that directives are not automatically considered laws in the United States.
In the U.S., laws are typically enacted by legislative bodies at the federal, state, or local level. These bodies have the authority to create, amend, or repeal laws, which then become binding rules that govern society. Laws are commonly found in legal codes and statutes and are enforceable by the government through the judicial system.
On the other hand, directives, also known as executive orders, memoranda, or policy statements, are commands issued by executives or administrators within government agencies. They are intended to guide the implementation of laws or provide interpretive guidance on existing statutes. Directives often outline specific procedures, policies, or actions that need to be followed within a particular agency or department.
It is essential to note that while directives can have practical implications and affect how government agencies operate, they do not automatically carry the same legal weight as laws. Directives cannot create new legal obligations or expand existing ones beyond what is already authorized by law. In other words, directives cannot grant rights or impose duties on individuals or organizations that are not already established by law.
However, directives can play a significant role in shaping the interpretation and application of existing laws. They can provide valuable insights into how a particular agency or department intends to implement and enforce certain laws. They can also serve as persuasive authority in legal proceedings, influencing court decisions and administrative adjudications.
To fully understand the legal implications of a directive, it is crucial to examine its relationship with existing laws. Directives must be consistent with and authorized by the underlying statutory framework. If a directive conflicts with an existing law, the law prevails.
It is important to emphasize that this article provides a general overview of directives and their relationship to laws in the United States. The legal landscape is complex and subject to change. Therefore, it is always prudent to verify and contrast the content of this article with current legal sources, such as statutes, court decisions, and legal commentary.
As an attorney, staying updated on legal developments, including directives and their implications, is crucial to providing accurate and reliable advice to clients. Remaining vigilant about changes in the law allows attorneys to effectively navigate legal issues and ensure the best possible outcomes for their clients.
In conclusion, while directives can provide valuable guidance and insights, they are not considered laws in the United States automatically. Understanding the relationship between directives and existing laws is essential for legal professionals to navigate the complexities of our legal system effectively. Always verify and contrast the content of this article with current legal sources to ensure accuracy and reliability.
