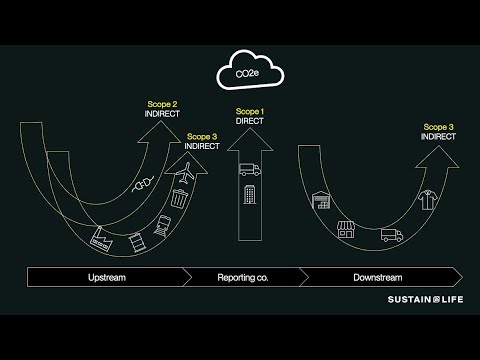
Understanding the Reduction in CO2 Emissions in Building Regulations: A Comprehensive Guide
Introduction:
📋 Content in this article
Greetings, dear readers! In this comprehensive guide, we will delve into the important topic of reduction in CO2 emissions in building regulations. We will explore the key concepts and regulations that govern this area, providing you with a clear understanding of the measures aimed at mitigating the impact of buildings on climate change. Let’s begin our journey towards a greener future!
I. What are CO2 emissions in the context of buildings?
CO2, or carbon dioxide, is a greenhouse gas that contributes to global warming and climate change. In the context of buildings, CO2 emissions refer to the amount of carbon dioxide released into the atmosphere as a result of various activities associated with the construction, operation, and maintenance of buildings.
II. Why is it essential to reduce CO2 emissions in buildings?
The built environment is a significant contributor to greenhouse gas emissions, with buildings accounting for a substantial portion of global energy consumption and CO2 emissions. Reducing CO2 emissions in buildings is crucial for several reasons:
1. Climate Change Mitigation: By reducing CO2 emissions, we can help mitigate the effects of climate change and work towards achieving global emission reduction targets set by international agreements such as the Paris Agreement.
2. Energy Efficiency: Building regulations aimed at reducing CO2 emissions often focus on improving energy efficiency. Energy-efficient buildings consume less energy, resulting in reduced reliance on fossil fuels and lower CO2 emissions.
3. Cost Savings: Energy-efficient buildings can lead to significant cost savings for both building owners and occupants. By implementing measures to reduce CO2 emissions, such as using energy-saving appliances or improving insulation, building owners can decrease their energy bills.
III. How are CO2 emissions reduced in building regulations?
Building regulations play a vital role in driving the reduction of CO2 emissions in buildings. These regulations typically focus on the following areas:
1. Energy Performance Standards: Building codes may establish minimum energy performance standards that new buildings must meet. These standards often include requirements for insulation, lighting, heating, cooling systems, and the use of renewable energy sources.
2. Building Retrofits: Regulations may also target existing buildings, requiring owners to undertake energy-efficient retrofits. This can include upgrading insulation, replacing outdated heating and cooling systems, or installing energy-efficient windows.
3. Renewable Energy Requirements: Some building regulations may mandate the use of renewable energy sources, such as solar panels or wind turbines, to generate a portion of a building’s energy needs.
IV. Compliance and Enforcement:
To ensure the effectiveness of building regulations, compliance and enforcement mechanisms are put in place. These may include inspections, certifications, and penalties for non-compliance. Building owners, developers, architects, and contractors must familiarize themselves with the specific regulations applicable in their jurisdiction to avoid legal consequences.
Ways to Reduce CO2 Emissions in Buildings: A Comprehensive Guide
Understanding the Reduction in CO2 Emissions in Building Regulations: A Comprehensive Guide
Reducing carbon dioxide (CO2) emissions is a critical component of addressing climate change and promoting environmental sustainability. In recent years, there has been an increasing focus on reducing CO2 emissions in buildings, as they are significant contributors to overall greenhouse gas emissions. This guide aims to provide a comprehensive understanding of the regulations and strategies involved in reducing CO2 emissions in buildings.
1. Importance of Reducing CO2 Emissions in Buildings
– Buildings account for a significant portion of global energy consumption and greenhouse gas emissions.
– Reducing CO2 emissions in buildings can help mitigate the impact of climate change and promote energy efficiency.
– Governments and regulatory bodies have recognized the need for stricter regulations to address this issue.
2. Building Regulations and Standards
– Building regulations and standards play a crucial role in driving the reduction of CO2 emissions in buildings.
– These regulations set out specific requirements and guidelines for energy efficiency and emission reduction in new and existing buildings.
– They may include provisions for building design, insulation, heating and cooling systems, lighting, and renewable energy integration.
3. Energy Efficiency Measures
– Energy efficiency measures are essential for reducing CO2 emissions in buildings.
– These measures focus on optimizing energy use by improving insulation, sealing air leaks, using energy-efficient appliances, and adopting advanced technologies.
– Examples of energy efficiency measures include installing double-glazed windows, using LED lighting, and incorporating smart building controls.
4. Renewable Energy Integration
– Integrating renewable energy sources into buildings is a key strategy for reducing CO2 emissions.
– Renewable energy systems, such as solar panels or wind turbines, can generate clean energy onsite, reducing reliance on fossil fuels.
– Incentives and policies may exist to encourage the installation of renewable energy systems in buildings.
5. Sustainable Building Design
– Sustainable building design aims to minimize the environmental impact of buildings throughout their lifecycle.
– Strategies include using sustainable materials, optimizing building orientation for natural light and ventilation, and implementing green roofs or walls.
– Sustainable building design can significantly contribute to reducing CO2 emissions in buildings.
6. Monitoring and Reporting
– Monitoring and reporting systems help track and assess the performance of buildings in terms of CO2 emissions.
– These systems provide valuable data that can identify areas for improvement and inform future building regulations.
– Regular monitoring and reporting are essential to ensure continued progress in reducing CO2 emissions in buildings.
In conclusion, understanding the reduction in CO2 emissions in building regulations is crucial for promoting sustainability and combating climate change. By implementing energy efficiency measures, integrating renewable energy sources, adopting sustainable building design practices, and implementing robust monitoring and reporting systems, we can make significant strides in reducing CO2 emissions in buildings.
Understanding Legislation to Reduce CO2 Emissions: A Comprehensive Overview
Understanding the Reduction in CO2 Emissions in Building Regulations: A Comprehensive Guide
In recent years, there has been a growing concern about the impact of carbon dioxide (CO2) emissions on the environment and the urgency to reduce them. Governments around the world have recognized the need for action and have implemented various measures to reduce CO2 emissions. One significant area where such measures are being taken is in building regulations. This article aims to provide a comprehensive guide to understanding the reduction in CO2 emissions in building regulations.
1. What are building regulations?
Building regulations are a set of legal requirements that dictate how buildings must be designed and constructed to ensure the health, safety, welfare, and energy efficiency of occupants. These regulations are typically enforced by local authorities or building control bodies and cover various aspects of building construction and performance.
2. Why are CO2 emissions a concern in building regulations?
Buildings are significant contributors to CO2 emissions due to their energy consumption for heating, cooling, lighting, and operation of appliances. Reducing CO2 emissions in the built environment is crucial to mitigate climate change and achieve sustainability goals. Building regulations play a crucial role in setting standards and requirements that aim to promote energy efficiency and reduce CO2 emissions from buildings.
3. How do building regulations reduce CO2 emissions?
Building regulations set specific targets and requirements that buildings need to meet in terms of energy efficiency and CO2 emissions. These requirements can include measures such as:
– Minimum insulation levels to reduce heat loss/gain
– Efficient heating, cooling, and ventilation systems
– Use of renewable energy sources
– Energy-efficient lighting and appliances
– Monitoring and reporting of energy consumption
4. Compliance with building regulations
Compliance with building regulations is a legal requirement for builders, developers, and property owners. Failure to comply can result in penalties, fines, and even the inability to sell or rent the property. Compliance is typically achieved through design and construction practices that meet the specific requirements outlined in the regulations.
5. Benefits of complying with CO2 emission reduction regulations
Complying with CO2 emission reduction regulations offers several benefits, including:
– Reduced energy consumption and lower utility bills for occupants
– Improved indoor air quality and comfort
– Enhanced marketability and value of the property
– Contributing to global sustainability efforts and combating climate change
6. Evolving nature of building regulations
Building regulations are not static and are subject to change over time. Governments regularly review and update these regulations to align with evolving environmental goals, technological advancements, and industry best practices. Staying informed about the latest changes and complying with updated regulations is crucial for builders, developers, and property owners.
In conclusion, understanding the reduction in CO2 emissions in building regulations is essential for anyone involved in the construction or management of buildings. Building regulations provide a framework for achieving energy efficiency and reducing CO2 emissions, promoting sustainable practices in the built environment. Compliance with these regulations not only helps protect the environment but also provides numerous benefits for occupants and property owners alike.
Understanding CO2 Emission Reduction: Benefits, Methods, and Impact
Understanding the Reduction in CO2 Emissions in Building Regulations: A Comprehensive Guide
In recent years, there has been a growing global concern about the impact of carbon dioxide (CO2) emissions on climate change. As a response to this concern, governments around the world, including the United States, have started implementing regulations aimed at reducing CO2 emissions. This article aims to provide a comprehensive guide to understanding the reduction in CO2 emissions in building regulations.
1. The Importance of Reducing CO2 Emissions
Reducing CO2 emissions is crucial in mitigating climate change. CO2 is a greenhouse gas that traps heat in the Earth’s atmosphere, leading to global warming and other adverse effects on the environment and human health. By reducing CO2 emissions, we can help slow down the pace of global warming and protect our planet for future generations.
2. Building Regulations and CO2 Emission Reduction
Building regulations play a vital role in promoting energy efficiency and reducing CO2 emissions. These regulations set standards and requirements for new construction or major renovations, ensuring that buildings are designed and constructed with energy-efficient features and systems. By enforcing these regulations, governments aim to reduce the carbon footprint of the built environment.
3. Benefits of CO2 Emission Reduction in Buildings
Reducing CO2 emissions in buildings offers numerous benefits, including:
– Environmental benefits: By reducing energy consumption, buildings with lower CO2 emissions contribute to the overall reduction of greenhouse gas emissions and help combat climate change.
– Economic benefits: Energy-efficient buildings often have lower operating costs, saving owners and occupants money on energy bills. Additionally, these buildings may have higher property values and attract more tenants or buyers.
– Health benefits: Energy-efficient buildings provide better indoor air quality, thermal comfort, and natural lighting, promoting occupants’ well-being and productivity.
4. Methods for Reducing CO2 Emissions in Buildings
There are several methods and strategies for reducing CO2 emissions in buildings. These include:
– Energy-efficient building design: Incorporating passive design strategies, such as orienting buildings to maximize natural light and ventilation, can lower energy demands.
– Efficient HVAC systems: Installing energy-efficient heating, ventilation, and air conditioning (HVAC) systems can significantly reduce energy consumption.
– Renewable energy sources: Integrating renewable energy sources like solar panels or wind turbines can help generate clean energy on-site, reducing reliance on fossil fuels.
– Building insulation: Proper insulation and sealing can minimize heat loss or gain, reducing the need for excessive heating or cooling.
5. Impact of CO2 Emission Reduction in Building Regulations
The impact of CO2 emission reduction in building regulations is significant. By implementing these regulations, governments can:
– Drive market transformation: Building regulations encourage the adoption of energy-efficient technologies and practices, creating a demand for sustainable building materials and services.
– Encourage innovation: Regulations push the construction industry to develop new technologies and strategies to meet energy efficiency standards.
– Contribute to global climate goals: CO2 emission reduction in buildings contributes to national and international efforts to reduce greenhouse gas emissions and combat climate change.
In conclusion, understanding the reduction in CO2 emissions in building regulations is essential for both building professionals and the general public. By embracing energy-efficient building practices and complying with these regulations, we can collectively make a significant impact on reducing CO2 emissions, contributing to a more sustainable future for all.
Understanding the Reduction in CO2 Emissions in Building Regulations: A Comprehensive Guide
As an attorney, it is essential to stay informed about various legal topics, including the reduction in CO2 emissions in building regulations. The importance of this subject cannot be overstated, as governments around the world are increasingly focusing on sustainable development and combating climate change. This guide aims to provide a comprehensive overview of the key concepts and principles related to the reduction in CO2 emissions in building regulations.
1. Background: The issue of CO2 emissions and their impact on climate change has gained significant attention in recent years. Buildings are one of the major contributors to CO2 emissions due to their energy consumption, construction materials, and waste generation. To address this issue, governments have implemented regulations to reduce CO2 emissions in the construction and operation of buildings.
2. Building Regulations: Building regulations are legal requirements that dictate the design, construction, and operation of buildings to ensure public safety, health, and welfare. In recent years, many jurisdictions have included provisions in their building regulations specifically aimed at reducing CO2 emissions.
3. CO2 Emissions Reduction Strategies: Various strategies can be employed to reduce CO2 emissions in buildings. Some common approaches include improving energy efficiency through the use of insulation, energy-efficient appliances, and renewable energy sources. Additionally, sustainable materials and construction practices can be utilized to minimize the carbon footprint of buildings.
4. Energy Performance Certificates (EPCs): Energy Performance Certificates are documents that provide information about the energy efficiency of a building. They are often required as part of building regulations and help assess a building’s environmental impact. EPCs can provide valuable insights into a building’s CO2 emissions and guide efforts to reduce them.
5. Local Building Codes: Building codes vary from jurisdiction to jurisdiction, and it is crucial to be aware of the specific regulations applicable to a particular area. Staying up-to-date with local building codes ensures compliance with CO2 emissions reduction measures and helps avoid potential legal issues.
6. Verification and Contrasting Information: While this guide provides a comprehensive overview, it is important to verify and contrast the information presented. Building regulations and CO2 emissions reduction strategies can vary based on location and are subject to change. Consulting legal professionals, government resources, and industry experts is recommended to ensure accurate and up-to-date information.
In conclusion, understanding the reduction in CO2 emissions in building regulations is crucial for attorneys and other professionals in the built environment. By staying informed about the background, strategies, and regulations related to CO2 emissions reduction, legal practitioners can assist clients effectively and ensure compliance with environmental standards. However, it is always advisable to verify and contrast the information provided in this guide with local regulations and expert opinions to ensure accuracy and relevance.
