As the cost of living continues to rise across the United States, many individuals find themselves struggling to make ends meet on their current salaries. While $75,000 per year may seem like a comfortable income, the reality is that it may not be sufficient to cover all of life’s expenses, especially in high-cost areas. In this article, we will explore the legal perspective of assessing the adequacy of a $75,000 annual income and provide insights into how individuals can determine if their income is truly sufficient to meet their needs. 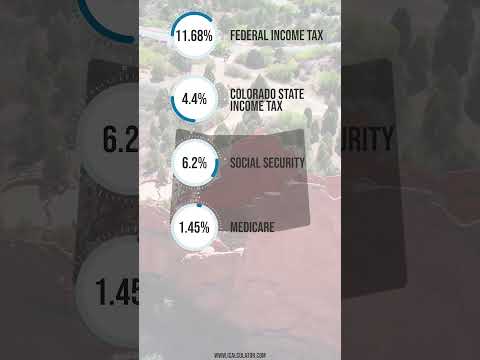
Understanding the Concept of Financial Sufficiency: Determining the Adequate Amount of Money
As a lawyer, I often encounter clients who are struggling with financial issues. One of the most common questions I get is, “How much money do I need to be financially sufficient?” This is a valid concern, and it is important to understand the concept of financial sufficiency.
Financial sufficiency is the state of having enough money to meet your basic needs and live comfortably. It is different for everyone and depends on various factors such as your lifestyle, location, and personal goals. Determining the adequate amount of money needed for financial sufficiency requires careful consideration of your current financial situation and future plans.
📋 Content in this article
Basic needs include housing, food, health care, transportation, and clothing. These are the necessities that you cannot do without. Once you have covered your basic needs, you can start thinking about other expenses such as entertainment, travel, and savings.
One way to determine your financial sufficiency is to create a budget. A budget is a plan that outlines your income and expenses. It is important to be realistic when creating a budget and include all sources of income and expenses. This will help you identify areas where you can cut back and save money.
Savings are an important part of financial sufficiency. It is recommended to have at least three to six months’ worth of living expenses saved in an emergency fund. This will provide a safety net in case of unexpected expenses or a job loss.
Another factor to consider is retirement planning. It is never too early to start planning for retirement. The amount of money you will need for retirement depends on your lifestyle and goals. A financial advisor can help you create a retirement plan and determine how much money you need to save.
Defining the Threshold: Evaluating the Relationship Between Income and Well-Being
As a society, we often equate higher income with greater well-being. However, research shows that beyond a certain point, this relationship may break down. Defining this threshold can help us better understand the complex relationship between income and well-being.
The Research
According to a study by Nobel Prize-winning economist Angus Deaton and psychologist Daniel Kahneman, there is a positive correlation between income and well-being up to a certain point. Specifically, they found that individuals with an annual income of around $75,000 reported the highest levels of well-being. Beyond this threshold, the relationship between income and well-being becomes weaker.
Why Does the Relationship Break Down?
There are a number of explanations for why the relationship between income and well-being may break down beyond a certain point. One possibility is that individuals with higher incomes are more likely to experience stress and anxiety related to their jobs and financial obligations. Additionally, higher income may lead to a greater focus on material possessions and a decrease in social connections, which can negatively impact well-being.
Implications for Policy
Defining the income threshold for optimal well-being has important policy implications. For example, policies that focus solely on increasing income may not necessarily result in greater well-being for individuals beyond a certain point. Instead, policies that address other factors such as job stress, social isolation, and access to healthcare may be more effective in promoting overall well-being.
Conclusion
While the relationship between income and well-being is complex, research suggests that there is a threshold beyond which higher income does not necessarily equate to greater well-being. By understanding this threshold and the various factors that impact well-being, we can develop more effective policies and interventions to promote overall well-being.
- Threshold: The point at which the relationship between income and well-being becomes weaker.
- Stress: Mental or emotional strain resulting from demanding circumstances.
- Anxiety: A feeling of worry, nervousness, or unease about something with an uncertain outcome.
Example: A person with an annual income of $100,000 may not necessarily be happier than someone with an annual income of $75,000, especially if they experience high levels of stress and social isolation.
This highlights the importance of addressing multiple factors in promoting overall well-being.
Understanding the Cost of Living: A Comprehensive Guide to Achieving Your Ideal Lifestyle
Living a comfortable life is a goal that everyone aspires to achieve. However, the road to achieving this goal can be challenging, especially when it comes to managing finances. Understanding the cost of living is crucial in achieving your ideal lifestyle, as it helps you budget effectively and make informed financial decisions.
What is Cost of Living?
Cost of living refers to the amount of money needed to sustain a certain standard of living in a particular location. This includes expenses such as housing, food, transportation, healthcare, and taxes.
- Housing: The cost of housing varies depending on the location, size of the house, and the type of neighborhood you live in. Renting is usually cheaper than owning a house, but it depends on the location.
- Food: The cost of food varies depending on the location, the type of food, and the quality. Eating out is usually more expensive than cooking at home.
- Transportation: The cost of transportation varies depending on the location, the type of transportation, and the distance. Owning a car is usually more expensive than using public transportation.
- Healthcare: The cost of healthcare varies depending on the location, the type of healthcare, and the quality. Health insurance is usually expensive, but it is necessary to cover unexpected medical expenses.
- Taxes: The cost of taxes varies depending on the location, the type of taxes, and the income. Income taxes are usually higher in cities than in rural areas.
How to Calculate Your Cost of Living
Calculating your cost of living involves adding up all your monthly expenses and comparing them to your income. This will help you determine your monthly budget and how much money you need to sustain your ideal lifestyle.
Here’s an example:
If your monthly expenses are:
- Rent: $1000
- Food: $500
- Transportation: $200
- Healthcare: $300
- Taxes: $400
Your total monthly expenses would be $2400. If your monthly income is $3000, then you have $600 left for savings or other expenses.
Tips for Managing Your Cost of Living
Managing your cost of living is essential in achieving your ideal lifestyle. Here are some tips to help you manage your expenses:
- Create a budget: Creating a budget helps you keep track of your expenses and ensure that you don’t overspend.
- Reduce unnecessary expenses: Cut down on expenses that are not necessary to reduce your monthly expenses.
- Shop around: Compare prices of goods and services to find the best deals.
- Save for emergencies: Set aside some money for unexpected expenses, such as medical emergencies.
By understanding the cost of living and managing your expenses effectively, you can achieve your ideal lifestyle and live a comfortable life.
Money and Happiness: The Correlation between Financial Stability and Emotional Well-being
It is a common belief that money can’t buy happiness, but is it really true? Studies have shown that there is a correlation between financial stability and emotional well-being.
Financial stability can provide individuals with a sense of security and peace of mind. When individuals have enough money to cover their basic needs, they are less likely to experience stress and anxiety related to finances. This can lead to better mental health and overall happiness.
On the other hand, financial stress can have a negative impact on mental health. Constantly worrying about money and struggling to make ends meet can lead to depression, anxiety, and other mental health issues.
It is important to note that while financial stability can contribute to happiness, it is not the only factor. Other factors such as relationships, career satisfaction, and physical health also play a role in overall well-being.
Some may argue that money can actually bring unhappiness, as it can lead to materialism and a focus on accumulating possessions rather than experiences. However, it is important to distinguish between the pursuit of wealth for the sake of material possessions and the pursuit of financial stability for the sake of security and peace of mind.
- Financial stability can positively contribute to:
- Reduced stress and anxiety
- Better mental health
- Increased sense of security
It is important to strive for a healthy balance between financial stability and other important factors that contribute to overall well-being. By prioritizing financial stability while also valuing relationships, career satisfaction, and experiences, individuals can lead fulfilling and happy lives.
For example, a person who has financial stability may be able to afford to take time off work to travel and create meaningful experiences, which can lead to greater happiness. On the other hand, a person who is constantly stressed about finances may not have the opportunity to enjoy these experiences.
