As a lawyer, it is important to understand the complexities of familial relationships. This includes understanding the degree of cousinship, which can have legal implications in cases involving inheritance, property rights, and even marriage. In this article, we will explore the distance of 4th cousins and what it means in terms of genealogy and the law. 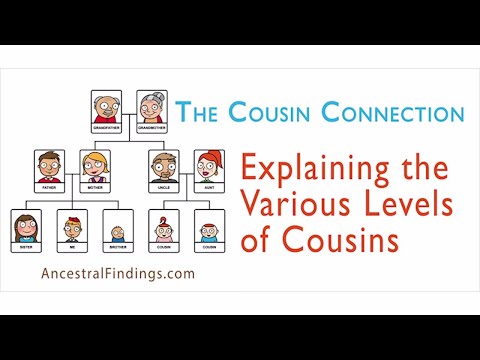
First, let’s define what we mean by “degree of cousinship.” Cousins are individuals who share a common ancestor, but the degree of cousinship is determined by the number of generations between the two cousins and their shared ancestor. The closer the relationship, the lower the degree of cousinship.
For example, first cousins share a grandparent, second cousins share a great-grandparent, and third cousins share a great-great-grandparent. Fourth cousins, on the other hand, share a common ancestor who is a great-great-great-grandparent.
While fourth cousins may seem distant, it is important to note that they still share a significant amount of DNA. In fact, according to geneticists, fourth cousins share approximately 0.2% of their DNA. This may not seem like a lot, but it is enough to potentially impact certain legal situations.
📋 Content in this article
In the following sections, we will explore the legal implications of fourth cousin relationships and how understanding the degree of cousinship can be important in legal cases.
But first, let’s dive deeper into the genealogy of fourth cousins and what it means to share a common ancestor who is a great-great-great-grandparent.
Genealogy of Fourth Cousins
Fourth cousins share a common ancestor who is a great-great-great-grandparent. This means that the ancestor is five generations removed from both cousins.
To put this into perspective, consider the following family tree:
- Generation 1: Great-great-great-grandparent
- Generation 2: Great-great-grandparent
- Generation 3: Great-grandparent
- Generation 4: Grandparent
- Generation 5: Parent
- Generation 6: Cousin
- Generation 7: Fourth Cousin
As you can see, the common ancestor is five generations removed from both the cousin and the fourth cousin. This means that they share a relatively small amount of genetic material, but it is still enough to potentially impact certain legal situations.
Exploring the Genetic Relationship between Fourth Cousins: A Legal Perspective
As genetic testing becomes more accessible and affordable, many people are curious about their family history and genetic makeup. This curiosity can lead to the discovery of distant relatives, including fourth cousins. But what does it mean to be genetically related as fourth cousins, and are there any legal implications of this relationship?
Understanding Fourth Cousin Relationships
Fourth cousins share a set of great-great-great-grandparents. This means that they share about 0.2% of their DNA, which may not sound like a lot, but it’s enough to establish a genetic connection. While fourth cousins are not considered close relatives, they are still part of your family tree.
The Legal Perspective
From a legal standpoint, being a fourth cousin has no significant implications. In the United States, marriage between fourth cousins is legal in all states. However, some states have laws prohibiting marriage between first cousins, and some even prohibit marriage between second cousins. It’s essential to research the laws in your state before pursuing a romantic relationship with a distant cousin.
Additionally, genetic testing and family history research may uncover previously unknown relatives, including fourth cousins. In some cases, this information can be relevant to legal matters such as inheritance and estate planning. For example, if a person dies without a will, their fourth cousins may be entitled to a portion of their estate.
The Importance of Genetic Testing
Genetic testing can provide valuable information about your family history and genetic makeup. It can also help establish connections with distant relatives, including fourth cousins. However, it’s essential to use reputable testing services and understand the limitations of the results. Genetic testing cannot provide a complete picture of your family history, and it’s important to combine genetic information with traditional genealogical research to build a comprehensive family tree.
Conclusion
Exploring the genetic relationship between fourth cousins can be a fascinating journey, but it’s important to understand the legal implications and limitations of genetic testing. While being a fourth cousin has no significant legal implications, it’s essential to research the laws in your state before pursuing a romantic relationship with a distant cousin. Additionally, genetic testing can provide valuable information about your family history, but it’s important to use reputable testing services and combine genetic information with traditional genealogical research.
References:
- https://www.familysearch.
org/blog/en/fourth-cousins/ - https://www.nbcnews.com/health/health-news/what-are-odds-finding-out-you-re-fourth-cousins-rcna1195
- https://www.livescience.com/33129-why-are-we-our-own-cousins-genetically-speaking-.
Exploring the Genetic Relationship: Understanding the Amount of Shared DNA with Fourth Cousins.
As genealogy becomes increasingly popular, people are becoming more interested in understanding their genetic relationships with distant relatives. Fourth cousins are relatives with whom you share a great-great-great-grandparent. Exploring the amount of shared DNA with fourth cousins can help you understand your family tree and genetic makeup.
Shared DNA is the amount of genetic material that two people have in common. The amount of shared DNA between fourth cousins is typically quite small, ranging from 0.1% to 2.0%. This is because each generation introduces new genetic material, making it less likely for shared DNA to remain significant over time.
It is important to note that while fourth cousins may share a small amount of DNA, it does not necessarily mean that they will have any noticeable physical or behavioral similarities. Shared DNA only provides an estimate of relatedness and cannot determine specific traits or characteristics.
DNA testing is a useful tool for exploring genetic relationships with distant relatives. DNA tests can reveal the amount of shared DNA between two people and provide insight into their potential relationship. However, it is important to keep in mind that DNA testing is not always 100% accurate and should be used in conjunction with traditional genealogical research to confirm relationships.
By exploring the amount of shared DNA with fourth cousins, you can gain a greater understanding of your family tree and genetic makeup. While the amount of shared DNA may be small, it can still provide valuable insights into your ancestry and help you connect with distant relatives.
Summary
- Fourth cousins are relatives with whom you share a great-great-great-grandparent
- Shared DNA between fourth cousins is typically quite small, ranging from 0.1% to 2.0%
- Shared DNA only provides an estimate of relatedness and cannot determine specific traits or characteristics
- DNA testing is a useful tool for exploring genetic relationships with distant relatives
- DNA testing should be used in conjunction with traditional genealogical research to confirm relationships
Example: John and Sarah are fourth cousins. After taking a DNA test, they discover that they share 0.5% of their DNA. This small amount of shared DNA confirms their genetic relationship as fourth cousins and provides insight into their family tree and ancestry.
Understanding the Overabundance of 4th Cousins on Ancestry: Exploring the Science behind Genetic Genealogy
Understanding the Degree of Cousinship: Exploring the Relationship Between 4th Cousins
When it comes to genealogy, the degree of cousinship can be confusing. One question that often comes up is: What is the relationship between 4th cousins?
First, let’s define what we mean by “4th cousins.” Two individuals are 4th cousins if they share a great-great-great-grandparent. This means that their common ancestor is the great-great-great-grandparent of one of them and the same for the other.
To better understand the relationship between 4th cousins, it’s helpful to look at the degree of kinship between them. The degree of kinship refers to the number of generations between two individuals and their most recent common ancestor.
For example, two individuals who share a set of great-grandparents are considered 2nd cousins. The degree of kinship between them is two, because there are two generations between them and their common ancestor.
So, what is the degree of kinship between 4th cousins? The answer is four. There are four generations between two individuals who share a great-great-great-grandparent.
While 4th cousins are relatively distant relatives, it’s still possible to establish a connection with them through genealogical research. For example, you might discover that a 4th cousin shares a common interest or hobby with you, or that you have other relatives in common.
Conclusion
