Hello and welcome! Today, we will be diving into the fascinating topic of ‘The Acquisition of Western Territory: How the United States Government Gained Control over Lands.’ Let’s explore the historical events and legal mechanisms that allowed the United States to expand its territory and establish control over vast landmasses.
The Westward Expansion of the United States: How Land Acquisition Shaped the Nation
The Acquisition of Western Territory: How the United States Government Gained Control over Lands
📋 Content in this article
The history of the United States is marked by a remarkable period of growth and expansion, known as the Westward Expansion. This expansion was driven by the desire to acquire and control vast territories in the western part of the country. The acquisition of western territory played a crucial role in shaping the nation and its development. In this article, we will explore the concept of land acquisition and how it influenced the Westward Expansion of the United States.
Understanding the Acquisition of Western Lands by the United States
The Acquisition of Western Territory: How the United States Government Gained Control over Lands
Throughout its history, the United States government has expanded its territory through various means, including treaties, purchase agreements, and armed conflict. The acquisition of western lands played a crucial role in the growth and development of the nation. Understanding this process is essential in comprehending the historical and legal context of land ownership in the United States.
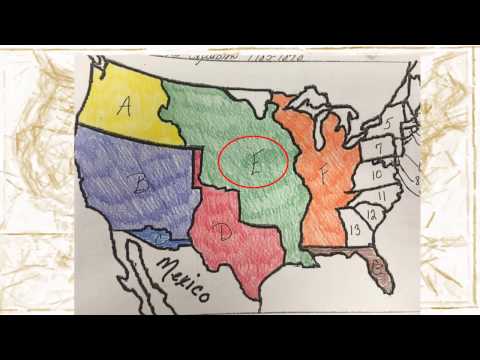
One of the most significant acquisitions of western territory was the Louisiana Purchase in 1803. This transaction involved the purchase of a vast territory from France, doubling the size of the United States. The acquisition included present-day states such as Arkansas, Missouri, Iowa, Oklahoma, Kansas, Nebraska, and parts of Minnesota, North Dakota, South Dakota, New Mexico, Texas, Montana, Colorado, and Wyoming. The Louisiana Purchase marked a turning point in the expansion of the United States westward.
The Treaty of 1818 with Britain established a joint occupation of Oregon Country, which encompassed present-day Oregon, Washington, Idaho, and parts of Montana and Wyoming. This agreement allowed both nations to settle in the area peacefully. However, as American settlers moved westward into Oregon Country, conflicts arose, leading to negotiations that ultimately resulted in the Oregon Treaty of 1846.
The acquisition of Texas was a complex process that had significant legal implications. Initially an independent republic following its separation from Mexico in 1836, Texas sought annexation into the United States. In 1845, the U.S. Congress approved Texas’s request for annexation, making it the 28th state. However, Mexico disputed Texas’s independence and subsequent annexation, leading to the Mexican-American War (1846-1848).
The Mexican-American War resulted in the Treaty of Guadalupe Hidalgo, which ended hostilities between Mexico and the United States. Under this treaty, Mexico ceded a vast amount of territory to the United States, including present-day California, Nevada, Utah, Arizona, New Mexico, and parts of Colorado and Wyoming. This acquisition further expanded the United States westward.
The Gadsden Purchase was a small but significant acquisition of land from Mexico. It involved the purchase of a strip of land in present-day southern Arizona and southwestern New Mexico. The purpose of this acquisition was to facilitate the construction of a southern transcontinental railroad route. The Gadsden Purchase solidified the United States’ control over the southern parts of the acquired Mexican Cession.
These acquisitions of western lands by the United States government shaped the nation’s boundaries and contributed to its westward expansion. Understanding these historical events is crucial in comprehending the complexities of land ownership and territorial disputes that continue to impact legal matters in the United States today.
The Acquisition of the Northwest Territory: A Historical Perspective
The Acquisition of Western Territory: How the United States Government Gained Control over Lands
Introduction
The acquisition of western territory played a crucial role in shaping the United States as we know it today. By expanding its territorial holdings, the U.S. government not only gained control over vast resources but also paved the way for westward expansion and the development of new states. This article will provide a historical perspective on the acquisition of western territory, focusing on the acquisition of the Northwest Territory.
The Importance of Acquiring Western Territory
1. Expanding Economic Opportunities: The acquisition of western territory provided the United States with access to valuable natural resources such as land, minerals, and timber. This allowed for increased economic growth and development.
2. Ensuring National Security: By gaining control over strategic locations and natural boundaries, the U.S. government could better protect its citizens and secure its borders from potential threats.
3. Facilitating Westward Expansion: Acquiring western territory opened up new lands for settlement and provided opportunities for individuals seeking a better life. This led to increased migration westward, contributing to the growth and development of the nation.
The Acquisition of the Northwest Territory
1. The Treaty of Paris (1783): The American Revolution resulted in Britain recognizing the independence of the United States through the Treaty of Paris in 1783. This granted the U.S. control over a significant portion of western territory east of the Mississippi River.
2. The Northwest Ordinance (1787): To govern this newly acquired land, the U.S. government enacted the Northwest Ordinance in 1787. This legislation established a framework for organizing territories and defining the process for their admission as states.
3. The Louisiana Purchase (1803): One of the most significant acquisitions of western territory was the Louisiana Purchase in 1803. The U.S. purchased approximately 828,000 square miles of land from France, doubling the size of the country. This acquisition opened up vast expanses of land for settlement and exploration.
4. The Treaty of Guadalupe Hidalgo (1848): Following the Mexican-American War, the United States acquired an additional 525,000 square miles of western territory through the Treaty of Guadalupe Hidalgo. This included present-day California, Nevada, Utah, Arizona, and parts of Colorado, Wyoming, New Mexico, and Texas.
The Acquisition of Western Territory: How the United States Government Gained Control over Lands
As an attorney, it is crucial to stay up-to-date on various legal topics to provide accurate and reliable information to clients. One such important topic is the acquisition of western territory by the United States government. Understanding the historical context and legal principles behind this acquisition is essential for any attorney practicing in the U.S.
The acquisition of western territory refers to the process by which the United States government obtained control over vast lands west of the original thirteen colonies. This expansion occurred through a combination of negotiations, treaties, purchases, wars, and other diplomatic efforts.
To fully comprehend this topic, it is important to have a solid understanding of the key events and legal concepts associated with the acquisition of western territory. Below are some significant milestones in this process:
These are just a few examples of how the United States government expanded its control over western territories. It is important to note that each acquisition involved complex legal negotiations and considerations, and the details and legal implications can vary from case to case.
To stay informed on this topic, it is essential for attorneys to verify and contrast the content of any article, including this one. Legislation, court decisions, and academic research can provide additional insight into the historical context and legal framework of the acquisition of western territory.
By keeping abreast of these developments, attorneys can better serve their clients when dealing with legal matters involving land rights, property disputes, indigenous rights, and other related issues. Additionally, understanding the historical underpinnings of this topic contributes to a comprehensive understanding of U.S. history and the development of its legal system.
In conclusion, staying up-to-date on the acquisition of western territory by the United States government is of utmost importance for attorneys practicing in the U.S. This topic has significant legal implications and understanding its historical context and legal principles is crucial for providing accurate legal advice. Remember to verify and contrast the content of any article, including this one, to ensure accuracy and reliability.
