Understanding the Concept of Code Repetition: How Programs Run the Same Code Repeatedly
Greetings, readers! Today, we are going to delve into the fascinating world of code repetition and how it affects the way computer programs run. Code repetition, also known as looping or iteration, is a fundamental concept in programming that allows a set of instructions to be executed multiple times.
📋 Content in this article
So, how does this concept work? Imagine you have a task that needs to be performed repeatedly, such as counting from 1 to 10. Instead of manually writing out each number and executing the task ten separate times, we can use code repetition to automate the process.
In programming, we use loops to achieve code repetition. Loops are structures that enable a block of code to be executed repeatedly until a certain condition is met. There are two main types of loops: for loops and while loops.
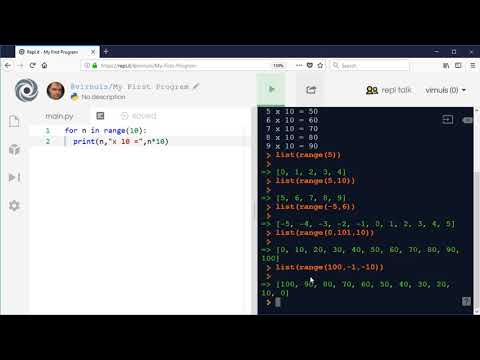
A for loop is commonly used when we know how many times we want the code to repeat. It consists of three parts: initialization, condition, and incrementation. The loop repeatedly executes the block of code as long as the condition remains true. <= 10; i++) {
// Code to be executed repeatedly
}
“`
In this case, the loop will execute the code ten times, with the variable `i` starting at 1 and incrementing by 1 after each execution until it reaches 10.
On the other hand, a while loop is used when we don’t know in advance how many times the code needs to be repeated. The loop continues executing until the specified condition evaluates to false.
Here’s an example:
“`
int i = 1;
while (i <= 10) {
// Code to be executed repeatedly
i++;
}
“`
In this scenario, the loop will execute the code as long as the value of `i` is less than or equal to 10. The variable `i` is incremented within the loop to avoid an infinite loop.
Loops are powerful tools in programming as they allow us to efficiently perform tasks that involve repetitive actions. They save time, effort, and make our code more concise and manageable.
It’s important to note that while code repetition can be beneficial, it’s crucial to avoid excessive or unnecessary repetition. This can lead to inefficiency and make the code harder to maintain and understand. Therefore, it’s important to strike a balance and use loops judiciously.
In conclusion, code repetition through loops is a fundamental concept in programming. It allows us to automate repetitive tasks, making our programs more efficient and concise. By understanding and utilizing loops effectively, we can write cleaner and more powerful code.
Thank you for joining me on this exploration of code repetition. Happy coding!
Understanding the Concept of Iteration in Programming: Repeating Code for Efficient Execution
Understanding the Concept of Code Repetition: How Programs Run the Same Code Repeatedly
In the world of programming, one fundamental concept that plays a crucial role in enhancing the efficiency and effectiveness of software is code repetition. Code repetition refers to the practice of running the same code multiple times within a program. This concept is often implemented through a technique called iteration. Iteration allows programs to perform a set of instructions repeatedly until a certain condition is met or a specific number of iterations have been completed.
By understanding and utilizing the concept of code repetition, programmers can write more efficient and concise programs that achieve their desired outcomes with less effort. Let’s dive deeper into the concept of code repetition and explore how it is achieved through iteration.
1. The Need for Code Repetition:
– Many programming tasks require performing the same actions multiple times.
– Without code repetition, programmers would need to manually write and execute the same set of instructions over and over again.
– Code repetition not only saves time and effort but also improves code readability and maintainability.
2. Introducing Iteration:
– Iteration is a control structure that allows a program to repeatedly execute a block of code until a certain condition is met.
– It provides a way to automate code repetition by specifying the number of iterations or defining a condition that determines when the repetition should stop.
3. Types of Iteration:
– For Loop: A common type of iteration that repeats a block of code for a specified number of times. The loop initializes a variable, checks a condition, executes the code block, and updates the variable after each iteration.
– While Loop: Another popular type of iteration that continues executing a block of code as long as a specified condition remains true. The loop evaluates the condition before each iteration and stops when the condition becomes false.
– Do-While Loop: Similar to the while loop, but it executes the code block at least once before checking the condition. If the condition is true, it continues with additional iterations.
– For Each Loop: Specialized for iterating over collections, such as arrays or lists, and executing the code block for each element in the collection.
4. Benefits of Code Repetition:
– Reduces redundancy: By using iteration, programmers can avoid duplicating code and instead write a single block of code that is executed repeatedly.
– Improves readability: Code repetition allows programmers to express repetitive tasks in a concise and structured manner, making the code easier to understand and maintain.
– Enhances efficiency: By automating repetitive tasks, iteration helps optimize program execution and improves overall performance.
5. Considerations and Best Practices:
– Be cautious of infinite loops: Make sure to define a condition or a limit that will eventually terminate the iteration to prevent the program from running indefinitely.
– Choose the appropriate type of iteration: Different scenarios may require different types of loops. Understanding the requirements of the task at hand will help in selecting the most suitable iteration structure.
In conclusion, understanding the concept of code repetition and how it is achieved through iteration is crucial for writing efficient and effective programs. By utilizing iteration techniques such as for loops, while loops, do-while loops, and for-each loops, programmers can automate repetitive tasks, improve code readability, and optimize program performance.
Understanding the Programming Concept of Repetition: A Comprehensive Guide
Understanding the Concept of Code Repetition: How Programs Run the Same Code Repeatedly
In the world of programming, one of the key concepts to grasp is the idea of code repetition. Code repetition refers to the practice of running the same block of code multiple times within a program. This concept is crucial in developing efficient and scalable software solutions. In this guide, we will explore the concept of code repetition and delve into its importance in programming.
Why is Code Repetition Important?
Code repetition plays a fundamental role in programming for several reasons. First and foremost, it enables developers to write less code by reusing existing blocks of code. This promotes efficiency and maintainability as it reduces the chances of introducing errors and simplifies the debugging process. By avoiding duplication of code, programmers can focus on writing clean and concise code that is easier to understand and modify in the future.
Types of Code Repetition
There are different ways in which code repetition can be implemented in a program. Let’s explore some common techniques:
Benefits and Challenges of Code Repetition
While code repetition offers numerous advantages, it also poses certain challenges that programmers need to be aware of:
In conclusion, understanding the concept of code repetition is essential for any aspiring programmer. By leveraging techniques such as loops, functions, and recursion, developers can write efficient, maintainable, and scalable programs. However, it is crucial to strike a balance between code repetition and code abstraction to ensure optimal performance and readability.
Understanding Code Repetition: A Key Concept in Programming
Understanding the Concept of Code Repetition: How Programs Run the Same Code Repeatedly
In the world of programming, code repetition is a key concept that plays a crucial role in how programs are designed and executed. Code repetition refers to the practice of using the same piece of code multiple times within a program. This concept is fundamental to programming because it allows developers to write efficient and concise code.
When writing a program, developers often encounter situations where a certain task needs to be performed multiple times. Instead of writing the same set of instructions over and over again, code repetition allows developers to write the instructions once and execute them multiple times.
Code repetition can be achieved through the use of loops. A loop is a programming construct that allows a section of code (known as the loop body) to be executed repeatedly until a certain condition is met. There are several types of loops commonly used in programming, including for loops, while loops, and do-while loops.
For loops are commonly used when the number of iterations is known in advance. They consist of three parts: an initialization statement, a condition, and an increment/decrement statement. The loop body is executed as long as the condition is true, and the increment/decrement statement updates the loop control variable to eventually terminate the loop.
While loops, on the other hand, are used when the number of iterations is not known in advance and depends on a certain condition. The loop body is executed as long as the condition remains true. It is important to ensure that the condition eventually evaluates to false to avoid an infinite loop.
Do-while loops are similar to while loops, but with one key difference: the condition is checked after the loop body has been executed at least once. This guarantees that the loop body will execute at least once, regardless of the initial condition.
By utilizing code repetition and loops, programmers can greatly enhance the efficiency and readability of their code. Instead of duplicating code, they can encapsulate the repetitive logic within a loop and reduce the overall size of the program. This not only saves development time but also makes the code easier to maintain and debug.
However, it is important to exercise caution when using code repetition. Overusing or misusing loops can lead to inefficient code execution and may introduce bugs or logical errors. It is essential for programmers to carefully analyze the requirements of their program and determine the appropriate level of code repetition.
In conclusion, understanding the concept of code repetition is crucial for any programmer. It allows for efficient and concise code by eliminating unnecessary duplication. By using loops, programmers can harness the power of code repetition to streamline their programs and enhance their functionality.
Understanding the Concept of Code Repetition: How Programs Run the Same Code Repeatedly
As technology continues to advance at an astonishing rate, it is essential for professionals in various fields to stay up-to-date with the latest knowledge and concepts. This holds true for attorneys as well, especially in today’s digital age where technology plays an ever-increasing role in legal practice.
One such concept that is crucial for attorneys to understand is code repetition, or the process by which programs execute the same code multiple times. Code repetition is a fundamental aspect of programming that allows for the efficient execution of complex tasks. However, it is important to note that this article is written from a non-expert perspective, and readers should always verify and contrast the content with reliable sources.
When a program encounters a repetitive task, it can be inefficient and time-consuming to write the same lines of code over and over again. To overcome this challenge, programmers utilize loops, which are constructs that enable the execution of a block of code multiple times. There are different types of loops, such as for loops and while loops, each with its own use case.
For loops are commonly used when the number of iterations is known in advance. They consist of three main components: an initialization statement, a condition statement, and an increment/decrement statement. The initialization statement sets the initial value of a variable, the condition statement checks whether the loop should continue executing, and the increment/decrement statement updates the value of the variable after each iteration.
While loops, on the other hand, are used when the number of iterations is not known in advance or when a condition needs to be continuously monitored. While loops execute a block of code as long as a specific condition remains true. It is crucial to ensure that the condition eventually becomes false to prevent an infinite loop, which can lead to program crashes or excessive resource consumption.
Understanding and utilizing code repetition effectively can greatly enhance an attorney’s ability to analyze and process large volumes of information efficiently. In the legal field, attorneys often work with vast amounts of data, such as contracts, legal documents, and evidence. By incorporating loops into their practice, attorneys can automate repetitive tasks, such as searching for specific keywords or analyzing patterns in documents.
Furthermore, a basic understanding of code repetition can also provide attorneys with the ability to communicate effectively with technology experts, programmers, and software developers. Collaboration between attorneys and technologists is becoming increasingly important in areas such as e-discovery, data analysis, and cybersecurity. Being able to understand the concept of code repetition allows attorneys to engage in meaningful discussions and contribute to the development of innovative legal solutions.
In conclusion, as technology continues to shape the legal profession, it is crucial for attorneys to stay up-to-date with fundamental concepts such as code repetition. By understanding how programs run the same code repeatedly through loops, attorneys can enhance their efficiency, automate repetitive tasks, and effectively collaborate with technology experts. However, it is essential to verify and contrast the information provided in this article with reliable sources in order to ensure accuracy and completeness.
