Understanding the Hierarchy of Laws: The Relationship Between Local Ordinances and State Laws
Greetings! Today, we will be delving into the fascinating world of legal hierarchy and exploring the intricate relationship between local ordinances and state laws. Whether you are a curious citizen, a law student, or simply someone interested in how laws are made and enforced, this article will provide you with a comprehensive overview of this important topic.
📋 Content in this article
What are Local Ordinances?
Local ordinances are laws enacted by local governments such as cities, counties, or townships. These laws are specifically tailored to address issues and concerns that are relevant to a particular local community. Local government bodies have the authority to create and enforce these ordinances based on their jurisdiction and the powers granted to them by the state.
What are State Laws?
On the other hand, state laws are statutes enacted by the legislative bodies of each individual state within the United States. These laws have a wider application as they govern the entire state rather than a specific locality. State legislatures have the power to pass laws on a wide range of issues that affect their respective states, including criminal law, family law, property law, and many others.
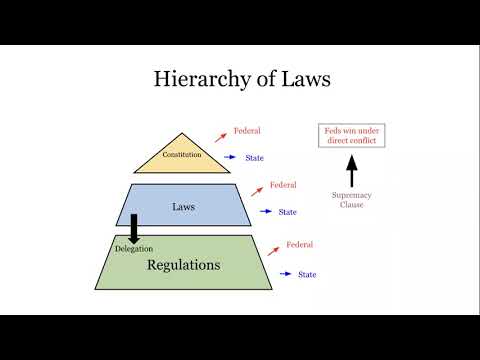
The Relationship between Local Ordinances and State Laws
Understanding the relationship between local ordinances and state laws is key to comprehending how the legal system functions at different levels. Generally, state laws take precedence over local ordinances in matters where there is a conflict or inconsistency between the two.
When a local ordinance conflicts with a state law, the state law will prevail. This principle ensures uniformity and consistency across the state, preventing a patchwork of conflicting ordinances from impeding or confusing the application of state laws. In essence, state laws serve as a framework within which local governments operate and exercise their powers.
However, it is important to note that local governments are not completely powerless in the face of state laws. They still have the authority to create and enforce ordinances on matters that are not covered by state laws or where the state has specifically delegated regulatory power to them.
The Process of Enacting Local Ordinances and State Laws
The process for enacting local ordinances and state laws differs. Local ordinances are typically passed by the local government’s legislative body, such as a city council or county commission. These bodies hold public hearings and allow for community input before making decisions.
On the other hand, state laws are enacted by the state legislature. The legislative process at the state level involves the introduction of bills, committee hearings, floor debates, and ultimately a vote by the legislators. This process ensures that state laws reflect the interests and needs of the entire state’s population.
Understanding the Hierarchy of Laws: A Comprehensive Overview
Understanding the Hierarchy of Laws: The Relationship Between Local Ordinances and State Laws
Introduction:
As a potential client, it is crucial to have a good understanding of how laws are structured and the hierarchy they follow. This article aims to provide a comprehensive overview of the relationship between local ordinances and state laws in the United States.
1. What are Local Ordinances?
2. What are State Laws?
3. The Relationship Between Local Ordinances and State Laws:
4. Preemption:
Understanding the Distinction: Local Laws vs. Ordinances Explained
Understanding the Hierarchy of Laws: The Relationship Between Local Ordinances and State Laws
In the United States, laws are created at various levels of government, and it is crucial to understand the hierarchy of these laws in order to navigate and comply with the legal system. One important aspect of this hierarchy is the relationship between local ordinances and state laws.
State Laws: State laws are legislative acts that apply to the entire state. They are enacted by state legislatures and cover a wide range of issues, such as criminal law, family law, and contract law. State laws are generally considered superior to local ordinances and take precedence over them.
Local Ordinances: Local ordinances, on the other hand, are laws enacted by local government bodies, such as city councils or county commissions. They are more specific in nature and apply only within the jurisdiction of the local government that enacted them. Local ordinances can address a wide range of issues, including zoning regulations, noise restrictions, and building codes.
The Relationship: The relationship between local ordinances and state laws is often described as a hierarchy, with state laws being at the top. This means that if there is a conflict between a local ordinance and a state law, the state law will generally prevail. This principle is based on the idea that state laws reflect the will of the entire state and should be uniform across all local jurisdictions.
However, it is important to note that local governments have the power to enact ordinances that are more stringent or restrictive than state laws as long as they do not directly conflict with them. For example, if a state law sets a minimum requirement for a certain activity, a local government can choose to set a higher requirement within its jurisdiction.
Preemption: In some cases, state laws explicitly preempt or override local ordinances on a particular subject. This means that the local government is prohibited from enacting any ordinances that conflict with the state law. Preemption can occur when the state government believes that uniformity is necessary or when there is a need to streamline regulations across the state.
It is important for individuals and businesses to be aware of both state laws and local ordinances that apply to their specific location. Violating either can lead to legal consequences, such as fines or penalties. It is always recommended to consult with an attorney who specializes in the relevant area of law to ensure compliance with all applicable laws and regulations.
To summarize, understanding the hierarchy of laws is crucial in navigating the legal system. State laws take precedence over local ordinances, but local governments may enact more stringent regulations as long as they do not conflict with state laws. It is essential to stay informed about both state and local laws to ensure compliance and avoid legal issues.
Understanding the Distinctions between Local, State, and Federal Laws in the United States
Understanding the Hierarchy of Laws: The Relationship Between Local Ordinances and State Laws
When it comes to the legal system in the United States, it is important to understand the hierarchy of laws and how they interact with one another. At the most basic level, we have local ordinances, which are laws enacted by local governments such as cities or counties. These ordinances address matters that are specific to the local community, such as zoning regulations, noise restrictions, or parking rules.
State laws, on the other hand, are enacted by state legislatures and apply to the entire state. They cover a wide range of issues, from criminal offenses and family law matters to taxation and education. State laws can vary significantly from one state to another, as each state has its own legislative process and priorities.
While local ordinances and state laws are important in their own right, they both operate under the umbrella of federal law. Federal laws are enacted by Congress and apply to the entire country. They address matters that are of national concern, such as immigration, civil rights, and interstate commerce.
In terms of hierarchy, federal law takes precedence over state laws. This means that if there is a conflict between a federal law and a state law on the same issue, the federal law will prevail. For example, if a state law allows for the possession of marijuana for medical purposes, but federal law prohibits it, federal law will take precedence.
Similarly, state laws generally take precedence over local ordinances. However, this can vary depending on the specific state’s constitution and laws. Some states grant significant powers to local governments and allow them to enact ordinances that are stricter or more specific than state laws. In these cases, local ordinances can prevail over conflicting state laws on certain issues.
It is also important to note that local ordinances must not violate any federal or state constitutional provisions. If a local ordinance is found to be unconstitutional, it can be challenged in court and struck down.
In summary, understanding the hierarchy of laws in the United States is crucial to navigate the legal landscape. While local ordinances address matters specific to a local community, state laws apply to the entire state, and federal laws encompass the entire nation. Federal law takes precedence over state laws, and state laws generally take precedence over local ordinances, although there can be exceptions. It is always wise to consult with a legal professional to ensure compliance with the applicable laws in your jurisdiction.
Understanding the Hierarchy of Laws: The Relationship Between Local Ordinances and State Laws
As citizens of the United States, we are subject to a complex web of laws and regulations that govern our daily lives. At times, it can be confusing to determine which laws take precedence over others. One important aspect of this legal landscape is understanding the hierarchy of laws, particularly the relationship between local ordinances and state laws.
Local ordinances, also known as municipal ordinances, are laws enacted by local governments such as cities, counties, or towns. These ordinances address a wide range of issues that directly affect the local community, including zoning regulations, noise restrictions, building codes, and business licensing requirements. They are designed to promote public safety, regulate behavior, and maintain order within the specific jurisdiction.
State laws, on the other hand, are enacted by state legislatures and govern the entire state. These laws cover a broader scope of issues that affect the entire population, such as criminal offenses, traffic regulations, marriage and divorce laws, and taxation. State laws are intended to provide a consistent legal framework throughout the state and ensure uniformity in certain areas where local variances could create confusion or conflict.
When it comes to determining which laws take precedence, it is important to understand that state laws generally supersede local ordinances. This means that if there is a conflict between a local ordinance and a state law on the same subject matter, the state law will prevail. For example, if a city has an ordinance that allows individuals to consume alcohol in public parks, but the state has a law prohibiting public alcohol consumption, the state law will take precedence over the local ordinance.
However, it is crucial to note that there are exceptions to this general rule. Some states have granted certain powers to local governments to enact laws that are more restrictive than state laws. For instance, a state may allow cities to establish higher minimum wage rates or impose stricter environmental regulations. In such cases, the local ordinances would prevail over conflicting state laws within the specific jurisdiction.
To complicate matters further, there may also be federal laws that supersede both state laws and local ordinances. The U.S. Constitution grants certain powers to the federal government, and Congress has the authority to enact laws that apply nationwide. For example, federal civil rights laws prohibit discrimination in employment, housing, and public accommodations, and they override any conflicting state or local laws.
Given the complexity of this legal framework, it is essential for individuals, businesses, and legal professionals to stay up-to-date on the relationship between local ordinances and state laws in their respective jurisdictions. This can be done by consulting reliable sources such as official government websites, legal publications, or seeking advice from qualified attorneys familiar with the local laws.
It is important to remember that laws are constantly changing and evolving, and what may be accurate at the time of writing this article might have changed in the future. Therefore, it is crucial to verify and contrast the information presented here with the most current laws and regulations in your jurisdiction.
In conclusion, understanding the hierarchy of laws and the relationship between local ordinances and state laws is essential to navigate the legal landscape effectively. While state laws generally supersede local ordinances, there are exceptions based on state-specific powers granted to local governments. Staying informed and seeking professional legal advice when necessary will ensure compliance with the applicable laws and regulations in your jurisdiction.
