Skiplagging is a travel hack that has gained popularity among frequent flyers looking to save money on airfare. It involves purchasing a ticket with a layover at the traveler’s desired destination, but instead of continuing on to the final destination, the traveler simply disembarks at the layover. While skiplagging may seem like a harmless way to save money and time, it has raised concerns among airlines and sparked legal battles. This article will discuss the implications of skiplagging, the legal issues surrounding it, and whether or not it can result in a ban for travelers. 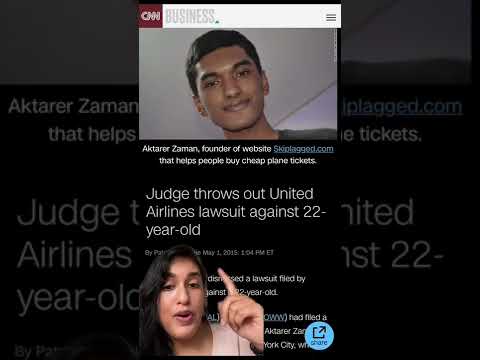
The Legal Implications of Using Skiplagged: Can You Be Banned?
If you are a frequent traveler, you may have heard of Skiplagged, a popular website and app that helps users save money on flights by finding hidden-city ticketing options. However, the question remains: is using Skiplagged legal? And can airlines ban passengers for doing so?
The short answer is: using Skiplagged is not illegal, but it can violate airline policies and result in consequences such as being banned from future flights.
📋 Content in this article
So, what exactly is hidden-city ticketing? It’s the practice of booking a flight with a layover at your desired destination, but instead of continuing to the final destination, you simply exit the airport at the layover point. This can often be cheaper than booking a direct flight to the same destination.
However, airlines prohibit this practice in their contract of carriage, which passengers agree to when booking a flight. By booking a hidden-city ticket, passengers are breaching the contract and can face consequences such as being denied boarding, having their frequent flyer miles revoked, or being charged the difference in fare.
While Skiplagged is not illegal, it is essentially a tool for finding and booking hidden-city tickets. By using the app or website, passengers are knowingly engaging in a practice that violates airline policies. As a result, airlines have the right to ban passengers from future flights for using Skiplagged.
What can you do if you are banned?
If you are banned from an airline for using Skiplagged, there is not much you can do. Airlines have the right to refuse service to anyone, and using Skiplagged is a breach of their contract of carriage. However, some passengers have had success with appealing their ban by explaining their situation and offering to pay the difference in fare.
Conclusion
Using Skiplagged may save you money, but it comes with risks. While it is not illegal, it can result in consequences such as being banned from future flights. It’s important to weigh the potential cost savings against the potential risks before using the app or website.
- Key takeaways:
- Hidden-city ticketing is the practice of booking a flight with a layover at your desired destination, but exiting the airport at the layover point instead of continuing to the final destination.
- Airlines prohibit hidden-city ticketing in their contract of carriage, and passengers who engage in this practice can face consequences such as being denied boarding or charged the difference in fare.
- Skiplagged is a tool for finding hidden-city tickets, and using it is a breach of airline policies.
- Airlines have the right to ban passengers from future flights for using Skiplagged.
- If you are banned from using an airline for using Skiplagged, there is not much you can do, but some passengers have had success with appealing their ban.
So, while using Skiplagged may seem like a smart way to save money, it’s important to understand the potential consequences before using it.
The Legal Implications of Missing a Flight: Can You Face Consequences for Skipping Air Travel?
Missing a flight can be a frustrating and stressful experience. It can also have legal implications that many travelers are not aware of. If you miss a flight, can you face consequences for skipping air travel?
Contract of Carriage
When you purchase a ticket for a flight, you enter into a contract of carriage with the airline. This contract outlines the terms and conditions of your travel, including the airline’s responsibilities and your responsibilities as a passenger.
If you miss your flight, you may be in breach of the contract of carriage. This could result in penalties, such as losing the value of your ticket or having to pay a fee to rebook your flight.
Security Concerns
Missing a flight can also raise security concerns. If you fail to show up for a flight, the airline may consider you a security risk. This could lead to additional screening or even law enforcement involvement.
Civil Penalties
In some cases, missing a flight can result in civil penalties. For example, if you miss a flight due to intoxication, you could be held liable for any expenses the airline incurs as a result of your behavior.
Criminal Penalties
While it is rare, missing a flight could potentially result in criminal penalties. For example, if you miss a flight because you were intentionally avoiding law enforcement, you could be charged with a crime.
Conclusion
While missing a flight may seem like a minor inconvenience, it can have serious legal implications. From breach of contract to criminal charges, travelers should be aware of the potential consequences of skipping air travel.
It is important to always read and understand the terms and conditions of your ticket, and to contact the airline if you are unable to make your scheduled flight.
Example:
John missed his flight to New York because he overslept. He did not inform the airline, and did not show up at all. The airline considered him a security risk, and John had to go through additional screening before being allowed to board the next flight. He also had to pay a fee to rebook his flight.
- Missing a flight can result in penalties and additional fees.
- It is important to read and understand the terms and conditions of your ticket.
- Intentionally avoiding a flight could result in criminal charges.
Legal Implications of Skiplagging: An Analysis of Airline Contracts and Passengers’ Rights
Skiplagging, also known as hidden city ticketing, is a travel practice that involves a passenger booking a flight with a layover in their desired destination, but instead of traveling to the final destination, they disembark at the layover airport.
While this may seem like a harmless way to save money or time, it can have serious legal implications for both passengers and airlines. To understand these implications, it is important to analyze airline contracts and passengers’ rights.
Airline Contracts
Most airlines have clauses in their contracts of carriage that prohibit skiplagging. These clauses typically state that passengers must travel to their final destination as booked, and that any deviation from the itinerary may result in the cancellation of the remaining flight segments.
For example, United Airlines’ contract of carriage states:
- “Passengers are prohibited from using hidden city ticketing or purchasing a ticket with the intent to use only a portion of the ticketed itinerary.”
- “If you are found to have engaged in prohibited conduct, we may take one or more of the following actions: refuse to carry you on any of our flights in the future, cancel any remaining portion of your itinerary, confiscate any United Airlines flight coupons or tickets in your possession, and/or assess you for the actual value of the ticket.”
Other airlines, such as Delta and American Airlines, have similar clauses in their contracts of carriage.
Passengers’ Rights
Passengers who engage in skiplagging may face consequences such as the cancellation of their remaining flight segments, loss of frequent flyer miles, and even legal action from the airline. However, there are also some risks associated with the airline’s actions.
Passengers may have the right to compensation if their flight is canceled or delayed due to skiplagging. According to the US Department of Transportation, if a passenger is involuntarily bumped from a flight or experiences a significant delay, they may be entitled to compensation depending on the circumstances.
Additionally, passengers who miss a flight due to skiplagging may have the right to a refund or alternative transportation to their final destination, depending on the airline’s policies.
Conclusion
While skiplagging may seem like a convenient and cost-effective way to travel, it is important to understand the legal implications for both passengers and airlines. Passengers who engage in skiplagging may face consequences such as the cancellation of their remaining flight segments, loss of frequent flyer miles, and legal action from the airline. However, they may also have the right to compensation if their flight is canceled or delayed due to skiplagging. It is essential to carefully review airline contracts of carriage and passengers’ rights before engaging in this travel practice.
Understanding the Legal Implications of Being Blacklisted from Air Travel in the United States
Air travel is an essential mode of transportation for many individuals in the United States. Whether for business or personal reasons, the ability to travel by air is a crucial part of modern life. However, for those who have been blacklisted from air travel, this privilege is no longer available.
Blacklisting is a term used to describe the process of being denied access to air travel. This can occur for a variety of reasons, ranging from national security concerns to unpaid debts. Regardless of the reason, being blacklisted from air travel can have serious legal implications.
One of the most significant legal implications of being blacklisted from air travel is the potential violation of an individual’s right to travel. The right to travel is a constitutional right that is protected by the United States Constitution. This right has been interpreted by courts to include the right to travel by air.
However, this right is not absolute, and there are circumstances under which it can be restricted. For example, the government may restrict an individual’s right to travel if they pose a threat to national security. Additionally, private companies, such as airlines, have the right to deny travel to individuals for various reasons, including failure to comply with airline rules and regulations.
- One of the legal implications of being blacklisted from air travel is the potential violation of an individual’s right to travel.
- The right to travel is a constitutional right that is protected by the United States Constitution.
- This right has been interpreted by courts to include the right to travel by air.
- The government may restrict an individual’s right to travel if they pose a threat to national security.
- Private companies, such as airlines, have the right to deny travel to individuals for various reasons, including failure to comply with airline rules and regulations.
Another legal implication of being blacklisted from air travel is the potential violation of an individual’s due process rights. Due process is a constitutional right that ensures that individuals are given fair treatment under the law. This includes the right to a fair and impartial hearing before being denied a fundamental right, such as the right to travel by air.
If an individual believes that they have been wrongfully blacklisted from air travel, they may have legal recourse. This may include filing a lawsuit against the government or private company responsible for the blacklisting. However, these cases can be complex and require the assistance of an experienced attorney.
Overall, being blacklisted from air travel can have serious legal implications. If you believe that you have been wrongfully blacklisted, it is important to seek legal advice to understand your rights and options.
Example: John Smith was denied boarding on a flight and learned that he had been blacklisted from air travel due to unpaid debts. He contacted an attorney who helped him file a lawsuit against the company responsible for the blacklisting. The attorney argued that John’s due process rights had been violated, and the court ultimately ruled in John’s favor.
