Welcome to this comprehensive guide on understanding your legal options for negligence in healthcare. In this informative article, we will explore the intricacies of this complex topic, providing you with a solid foundation to navigate the legal landscape. It is important to note that while this article aims to be a helpful resource, it is always advisable to cross-reference the information provided with other sources or consult with a legal professional to fully understand your specific situation.
Now, let’s dive into the world of negligence in healthcare. In any medical setting, whether it be a hospital, clinic, or doctor’s office, patients expect to receive a certain standard of care. However, there are instances where this standard is not met, resulting in harm or injury to the patient. This is where the concept of negligence comes into play.
Negligence in healthcare refers to the failure of a healthcare professional or institution to exercise the appropriate level of care and skill that a reasonably competent professional would have provided under similar circumstances. This failure, known as a breach of duty, can lead to serious consequences for the patient. It is essential to establish four key elements to prove negligence in a healthcare setting:
📋 Content in this article
- Duty: The healthcare professional or institution owed a duty of care to the patient. This duty arises from the established doctor-patient relationship or the hospital’s responsibility to provide a safe environment.
- Breach: The healthcare professional or institution breached that duty by failing to meet the required standard of care. This breach can occur through acts of commission (doing something they should not have done) or acts of omission (failing to do something they should have done).
- Causation: The breach of duty directly caused harm or injury to the patient. It must be established that the harm would not have occurred if the healthcare professional or institution had not been negligent.
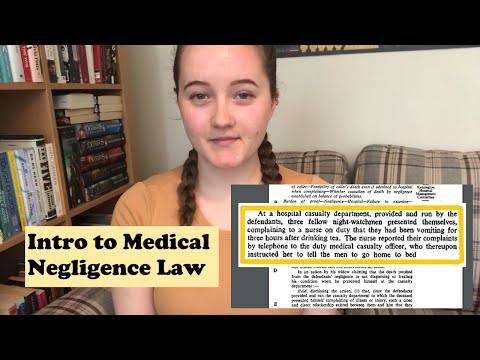
- D
Understanding the Four Elements of Negligence in Healthcare
Understanding the Four Elements of Negligence in Healthcare: A Comprehensive Guide to Your Legal Options
Introduction:
Navigating the legal landscape can be overwhelming, especially when it comes to matters of healthcare negligence. Understanding the four elements of negligence is essential in determining your legal options and seeking justice for any harm caused by medical professionals. This comprehensive guide will provide you with a clear understanding of these elements and empower you to make informed decisions.1. Duty of Care:
The first element of negligence is establishing a duty of care. In healthcare, this refers to the legal obligation of healthcare professionals to provide a certain standard of care to their patients. This duty is established when a doctor-patient relationship is formed, or when a healthcare professional assumes responsibility for a patient’s care. Examples include doctors, nurses, surgeons, and other medical practitioners.2. Breach of Duty:
A breach of duty occurs when a healthcare professional fails to meet the expected standard of care. This means that they did not act in a manner that a reasonable medical professional would under similar circumstances. To prove a breach of duty, it is important to gather evidence such as medical records, witness statements, and expert opinions to demonstrate that the healthcare professional deviated from the standard of care.3. Causation:
Causation refers to the link between the breach of duty and the harm suffered by the patient. There are two types of causation: actual cause and proximate cause. Actual cause means that the harm would not have occurred without the healthcare professional’s breach of duty. Proximate cause means that the harm was a reasonably foreseeable consequence of the breach of duty.4. Damages:
The final element of negligence is the existence of damages or harm suffered by the patient.Understanding the Three Types of Negligence in Healthcare: A Comprehensive Overview
Understanding the Three Types of Negligence in Healthcare: A Comprehensive Overview
When it comes to healthcare, negligence can have serious consequences for patients. Understanding the different types of negligence is essential for individuals who believe they have suffered harm due to the actions or inactions of healthcare providers. In this comprehensive guide, we will explore the three main types of negligence in healthcare and provide an overview of your legal options if you believe you have been a victim.
1. Medical Negligence:
Medical negligence, also known as medical malpractice, occurs when a healthcare professional fails to provide a standard level of care, resulting in harm to the patient. This can include misdiagnosis, surgical errors, medication mistakes, or failure to obtain informed consent. To establish a claim of medical negligence, four elements must be proven: duty, breach of duty, causation, and damages. - Duty: The healthcare provider had a duty to provide care to the patient.
- Breach of Duty: The provider breached their duty by failing to meet the standard level of care.
- Causation: The breach of duty directly caused harm to the patient.
- Damages: The patient suffered physical, emotional, or financial harm as a result of the negligence.
- Duty: The nurse had a duty to provide competent care to the patient.
- Breach of Duty: The nurse failed to meet the standard level of care expected in their role.
- Causation:
Title: Understanding your Legal Options for Negligence in Healthcare: A Comprehensive Guide
Introduction:
In the complex world of healthcare, understanding your legal options for negligence is of utmost importance. Medical errors can have devastating consequences, and it is crucial for patients and their families to be aware of their rights and available remedies. This comprehensive guide aims to provide you with valuable insights into the legal aspects of healthcare negligence in the United States. However, it is important to note that laws can vary across jurisdictions and are subject to change. Therefore, it is recommended that readers verify and cross-reference the information provided here with local statutes and consult with legal professionals for specific cases.1. Defining Negligence in Healthcare:
Negligence in healthcare refers to the failure of a healthcare professional or institution to meet the accepted standard of care, resulting in harm or injury to a patient. This breach of duty may occur through actions, omissions, or a failure to diagnose or treat a medical condition.2. Establishing a Negligence Claim:
To establish a successful negligence claim in healthcare, the following elements must generally be proven:– Duty: The healthcare professional owed a duty of care to the patient, meaning they had a legal obligation to provide competent treatment.
– Breach: The healthcare professional breached their duty by failing to meet the accepted standard of care.
– Causation: The breach of duty directly caused harm or injury to the patient.
– Damages: The patient suffered actual damages as a result of the breach of duty.3. Types of Negligence Claims in Healthcare:
Understanding the different types of negligence claims can help you comprehend the scope of your legal options. Some common categories include:– Medical Malpractice: This involves negligence by a healthcare professional, such as a doctor, nurse, or surgeon, in providing treatment or care.
2. Nursing Negligence:
Nursing negligence refers to the failure of a nurse to perform their duties in a competent and responsible manner, resulting in harm to the patient. This can include medication errors, failure to monitor vital signs, neglecting patient needs, or inadequate communication with other healthcare professionals. Like medical negligence, nursing negligence requires establishing duty, breach of duty, causation, and damages.
