As the world becomes increasingly interconnected, the legal profession is no exception. With the rise of globalized business and the ease of communication, it is becoming more common for foreign nationals to practice law in the United States. However, the question of whether or not this practice is legal remains a complex and contentious issue. In this article, we will explore the legality of foreigners practicing law in the United States, examining the relevant laws, regulations, and ethical considerations. 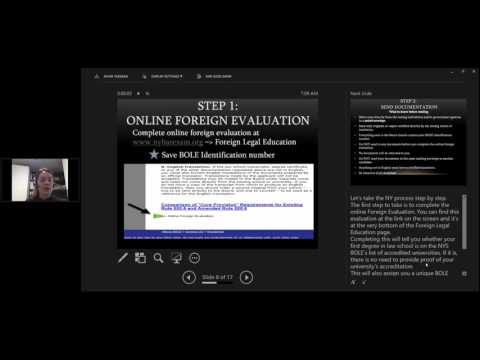
Foreigner’s Guide to Practicing Law in the US: Requirements and Limitations
Practicing law in the United States as a foreigner can be a challenging, yet rewarding experience. However, there are specific requirements and limitations that every foreign lawyer must meet before they can practice law in the US.
Requirements
- Educational Requirements: Foreign lawyers must have a law degree from an accredited law school in their home country.
- English Language Proficiency: Foreign lawyers must demonstrate proficiency in the English language by passing an English language test, such as the TOEFL or IELTS.
- Bar Exam: Foreign lawyers must pass the bar exam in the state where they want to practice law. Some states have additional requirements, such as completing a specific amount of coursework or obtaining a certain number of legal work experience hours.
Limitations
It’s important to note that foreign lawyers may face certain limitations when practicing law in the US:
📋 Content in this article
- Visa Requirements: Foreign lawyers must obtain the appropriate visa to work in the US. There are several visa categories available for foreign lawyers, including the H-1B visa for specialty occupations.
- State-by-State Regulations: Each state in the US has its own regulations regarding the practice of law. Foreign lawyers must comply with the rules and regulations of the state where they want to practice law.
- Restrictions on Practice Areas: Some states may restrict the practice areas in which foreign lawyers can practice. For example, some states may require foreign lawyers to have a certain level of expertise or experience in a particular area of law before they can practice in that area.
It’s important for foreign lawyers to consult with an experienced immigration lawyer to ensure that they understand all of the requirements and limitations of practicing law in the US before they begin their legal career in the United States.
Example: John, a lawyer from Canada, wants to practice law in New York. He has a law degree from a Canadian law school, is proficient in English, and has passed the New York bar exam. However, he must also obtain the appropriate visa to work in the US and comply with New York’s rules and regulations regarding the practice of law.
Navigating the Path to Practicing Law in the USA as a Foreign-Trained Lawyer
Practicing law in the United States as a foreign-trained lawyer can be a challenging process, but it is not impossible. There are several steps that you need to take in order to navigate the path to becoming a licensed lawyer in the USA.
Educational and Professional Requirements
The first step is to determine if your educational and professional background meets the requirements to practice law in the USA. Each state has its own set of requirements for foreign-trained lawyers, so it is important to research the specific requirements for the state where you plan to practice.
Some common requirements include a Juris Doctor (JD) degree from an American Bar Association (ABA)-accredited law school, passing the state bar exam, and completing a certain number of credit hours in specific legal courses.
Evaluation of Credentials
The next step is to have your educational and professional credentials evaluated by a credential evaluation agency. This agency will review your credentials and provide an assessment of how your education and professional experience compare to the requirements in the state where you plan to practice. This evaluation is necessary to determine if you need to complete additional coursework or exams.
Bar Exam
Once your credentials have been evaluated and you have determined the requirements for the state where you plan to practice, the next step is to prepare for and take the state bar exam. The bar exam is a comprehensive exam that tests your knowledge of the law and your ability to apply it to real-world scenarios.
It is important to note that passing the bar exam does not guarantee that you will be licensed to practice law in the USA. Some states require additional steps, such as completing a character and fitness assessment, before a license is granted.
Networking and Job Search
After passing the bar exam and meeting all other requirements, the final step is to network and search for a job. Networking is important in any field, but it is particularly important in the legal profession. Attend legal conferences and events, join professional organizations, and connect with other lawyers in your area.
It is also important to research potential employers and job opportunities. Look for firms or organizations that have experience working with foreign-trained lawyers and are open to hiring individuals with diverse backgrounds.
Conclusion
While the path to practicing law in the USA as a foreign-trained lawyer may seem daunting, it is possible with the right preparation and determination. Research the requirements for the state where you plan to practice, have your credentials evaluated, prepare for and pass the bar exam, and network and search for job opportunities. With hard work and perseverance, you can achieve your goal of practicing law in the United States.
Legal Practice in the US: Citizenship Requirements for Lawyers
Legal practice in the US is regulated by the individual states rather than the federal government, and each state has its own set of requirements for becoming a lawyer. One of the most important requirements is citizenship.
Citizenship Requirements
Citizenship requirements for lawyers vary from state to state but, in general, you must be a citizen or a legal permanent resident of the United States to practice law. Some states allow non-citizens to practice law if they meet certain requirements, such as having a work visa or a green card.
In addition to meeting citizenship requirements, aspiring lawyers must also obtain a law degree and pass the bar exam in the state where they wish to practice. The bar exam is a comprehensive test of a lawyer’s knowledge of the law and is required by all states.
Immigration Status and Legal Practice
If you are a non-citizen interested in practicing law in the US, it is important to understand the immigration requirements for obtaining a work visa or a green card. You may need to work in the US for several years before you can apply for citizenship or legal permanent residency.
Immigration status can also affect your ability to practice law in certain areas. For example, if you plan to practice immigration law, you may need to be a citizen or legal permanent resident yourself in order to represent clients in court.
Conclusion
Becoming a lawyer in the US is a complex process that requires a significant investment of time, effort, and money. Citizenship requirements are just one of the many factors to consider when pursuing a legal career in the US.
Important Takeaways:
- Citizenship requirements for lawyers vary from state to state.
- Non-citizens may be allowed to practice law in certain states if they meet certain requirements.
- Immigration status can affect your ability to practice law in certain areas.
Example: John is a legal permanent resident of the US and has obtained his law degree. He wants to practice law in California, but he is not sure if he meets the citizenship requirements. After researching the state’s requirements, he finds out that legal permanent residents are allowed to practice law in California as long as they have passed the bar exam.
Foreign Attorney Representation in the US: Legal Implications and Considerations
Foreign attorneys who wish to practice law in the United States face a number of legal implications and considerations. The American Bar Association (ABA) has established guidelines for foreign attorney representation in the US. Understanding these guidelines is essential for foreign attorneys who wish to practice law in the US.
Legal Implications
One of the most important legal implications of foreign attorney representation in the US is that foreign attorneys must be licensed to practice law in the US. This means that they must pass the bar exam in the state where they wish to practice law. In addition, they must meet any other requirements established by the state bar association.
Another legal implication is that foreign attorneys may be subject to disciplinary action if they violate the rules of professional conduct in the state where they are licensed to practice law. This can include conduct such as misrepresenting their qualifications or engaging in unethical behavior.
Considerations
Foreign attorneys who wish to practice law in the US must also consider a number of other factors. For example, they must determine whether their foreign law degree will be recognized in the state where they wish to practice law. They must also consider whether they will be required to complete additional coursework or training in order to meet the requirements for licensure in the state.
Foreign attorneys must also consider the potential impact of cultural differences on their ability to practice law in the US. This can include differences in legal terminology, as well as differences in legal and ethical norms.
Conclusion
Foreign attorney representation in the US can be a complex and challenging process. However, by understanding the legal implications and considerations involved, foreign attorneys can take the necessary steps to successfully practice law in the US.
- Example: A foreign attorney who earned a law degree in their home country and wishes to practice law in New York must pass the New York bar exam and meet any other requirements established by the New York State Bar Association.
